Saturn V facts for kids

The launch of Apollo 11 on Saturn V SA-506, July 16, 1969
|
|
| Function |
|
|---|---|
| Manufacturer |
|
| Country of origin | United States |
| Project cost | US$6.417 billion (equivalent to $48 billion in 2022) |
| Cost per launch | US$185 million (equivalent to $1.394 billion in 2022) |
| Size | |
| Height | 363 ft (111 m) |
| Diameter | 33 ft (10 m) |
| Mass | 6,221,000 to 6,537,000 lb (2,822,000 to 2,965,000 kg) |
| Stages | 3 |
| Capacity | |
| Payload to LEO | 141,136 kg (311,152 lb) |
| Payload to TLI | 52,759 kg (116,314 lb) |
| Associated rockets | |
| Family | Saturn |
| Derivatives | Saturn INT-21 |
| Comparable |
|
| Launch history | |
| Status | Retired |
| Launch sites | Kennedy Space Center, LC-39 |
| Total launches | 13 |
| Successes | 12 |
| Partial failures | 1 (Apollo 6) |
| First flight | November 9, 1967 (AS-501 Apollo 4) |
| Last flight | May 14, 1973 (AS-513 Skylab) |
| First stage – S-IC | |
| Length | 138 ft (42 m) |
| Diameter | 33 ft (10 m) |
| Empty mass | 303,000 lb (137,000 kg) |
| Gross mass | 4,881,000 lb (2,214,000 kg) |
| Engines | 5 × F-1 |
| Thrust | 7,750,000 lbf (34,500 kN) sea level |
| Specific impulse | 263 s (2.58 km/s) sea level |
| Burn time | 168 seconds |
| Fuel | LOX / RP-1 |
| Second stage – S-II | |
| Length | 81.5 ft (24.8 m) |
| Diameter | 33 ft (10 m) |
| Empty mass | 88,400 lb (40,100 kg) |
| Gross mass | 1,093,900 lb (496,200 kg) |
| Engines | 5 × J-2 |
| Thrust | 1,155,800 lbf (5,141 kN) vacuum |
| Specific impulse | 421 s (4.13 km/s) vacuum |
| Burn time | 360 seconds |
| Fuel | LOX / LH2 |
| Third stage – S-IVB | |
| Length | 58.3 ft (17.8 m) |
| Diameter | 21.7 ft (6.6 m) |
| Empty mass | 33,600 lb (15,200 kg) |
| Gross mass | 271,000 lb (123,000 kg) |
| Engines | 1 × J-2 |
| Thrust | 232,250 lbf (1,033.1 kN) vacuum |
| Specific impulse | 421 s (4.13 km/s) vacuum |
| Burn time | 165 + 335 seconds (2 burns) |
| Fuel | LOX / LH2 |
The Saturn V is a retired American super heavy-lift launch vehicle developed by NASA under the Apollo program for human exploration of the Moon. The rocket was human-rated, had three stages, and was powered by liquid fuel. Flown from 1967 to 1973, it was used for nine crewed flights to the Moon, and to launch Skylab, the first American space station.
As of 2024[update] the Saturn V remains the only launch vehicle to have carried humans beyond low Earth orbit (LEO). The Saturn V holds the record for the largest payload capacity to low Earth orbit, 311,152 lb (141,136 kg), which included unburned propellant needed to send the Apollo command and service module and Lunar Module to the Moon.
The largest production model of the Saturn family of rockets, the Saturn V was designed under the direction of Wernher von Braun at the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama; the lead contractors for construction of the rocket were Boeing, North American Aviation, Douglas Aircraft Company, and IBM. Fifteen flight-capable vehicles were built, not counting three used for ground testing. A total of thirteen missions were launched from Kennedy Space Center, nine of which carried 24 astronauts to the Moon from Apollo 8 (December 1968) to Apollo 17 (December 1972).
Contents
History
Background
In September 1945, the U.S. government brought the German rocket technologist Wernher von Braun and over 1,500 German rocket engineers and technicians to the United States in Operation Paperclip, a program authorized by President Truman. Von Braun, who had helped create the German V-2 rocket, was assigned to the Army's rocket design division. Between 1945 and 1958, his work was restricted to conveying the ideas and methods behind the V-2 to American engineers, though he wrote books and articles in popular magazines.
This approach changed in 1957, when the Soviets launched Sputnik 1 atop an R-7 ICBM, which could carry a thermonuclear warhead to the U.S. The Army and government began putting more effort towards sending Americans into space before the Soviets. They turned to von Braun's team, who had created the Jupiter series of rockets. The Juno I rocket launched the first American satellite in January 1958. Von Braun considered the Jupiter series of rockets to be a prototype of the upcoming Saturn series of rockets, and referred to it as "an infant Saturn".
Saturn development
Named after the sixth planet from the Sun, the design of the various Saturn rockets evolved from the Jupiter vehicles.
Between 1960 and 1962, the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) designed a series of Saturn rockets that could be deployed for Earth orbit and lunar missions.
NASA planned to use the Saturn C-3 as part of the Earth orbit rendezvous (EOR) method for a lunar mission, with at least two or three launches needed for a single landing on the Moon. However, the MSFC planned an even bigger rocket, the C-4, which would use four F-1 engines in its first stage, an enlarged C-3 second stage, and the S-IVB, a stage with a single J-2 engine, as its third stage. The C-4 would only need to carry out two launches to carry out an EOR lunar mission.
On January 10, 1962, NASA announced plans to build the C-5. The three-stage rocket would consist of the S-IC first stage, with five F-1 engines; the S-II second stage, with five J-2 engines; and the S-IVB third stage, with a single J-2 engine.
The C-5 would undergo component testing even before the first model was constructed. The S-IVB third stage would be used as the second stage for the C-1B, which would serve both to demonstrate proof of concept and feasibility for the C-5, but would also provide flight data critical to the development of the C-5. Rather than undergoing testing for each major component, the C-5 would be tested in an "all-up" fashion, meaning that the first test flight of the rocket would include complete versions of all three stages. By testing all components at once, far fewer test flights would be required before a crewed launch. The C-5 was confirmed as NASA's choice for the Apollo program in early 1962, and was named the Saturn V. The C-1 became the Saturn I and C-1B became Saturn IB. Von Braun headed a team at the MSFC to build a vehicle capable of launching a crewed spacecraft to the Moon. During these revisions, the team rejected the single engine of the V-2's design and moved to a multiple-engine design.
The Saturn V's final design had several key features. F-1 engines were chosen for the first stage, while new liquid hydrogen propulsion system called J-2 for the second and third stage. NASA had finalized its plans to proceed with von Braun's Saturn designs, and the Apollo space program gained speed.
The stages were designed by von Braun's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, and outside contractors were chosen for the construction: Boeing (S-IC), North American Aviation (S-II), Douglas Aircraft (S-IVB), and IBM (instrument unit).
Selection for Apollo lunar landing
Early in the planning process, NASA considered three methods for the Moon mission: Earth orbit rendezvous (EOR), direct ascent, and lunar orbit rendezvous (LOR). A direct ascent configuration would require an extremely large rocket to send a three-man spacecraft to land directly on the lunar surface. An EOR would launch the direct-landing spacecraft in two smaller parts which would combine in Earth orbit. A LOR mission would involve a single rocket launching two spacecraft: a mother ship, and a smaller, two-man landing module which would rendezvous back with the main spacecraft in lunar orbit. The lander would be discarded and the mother ship would return home.
At first, NASA dismissed LOR as a riskier option, as a space rendezvous had yet to be performed in Earth orbit, much less in lunar orbit. Several NASA officials, including Langley Research Center engineer John Houbolt and NASA Administrator George Low, argued that a lunar orbit rendezvous provided the simplest landing on the Moon with the most cost–efficient launch vehicle, and the best chance to accomplish the lunar landing within the decade. Other NASA officials became convinced, and LOR was then officially selected as the mission configuration for the Apollo program and announced by NASA administrator James E. Webb on November 7, 1962. Arthur Rudolph became the project director of the Saturn V rocket program in August 1963. He developed the requirements for the rocket system and the mission plan for the Apollo program. The first Saturn V launch lifted off from Kennedy Space Center and performed flawlessly on November 9, 1967, Rudolph's birthday. He was then assigned as the special assistant to the director of MSFC in May 1968 and subsequently retired from NASA on January 1, 1969. On July 16, 1969, the Saturn V launched Apollo 11, putting the first men on the Moon.
Launch history
| Serial number |
Mission | Launch date (UTC) |
Pad | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA-500F | Facilities integration | Used to check precise fits and test facilities operation on Pad 39A before a flight model was ready. First stage scrapped, second stage converted to S-II-F/D, third stage on display at Kennedy Space Center. | ||
| SA-500D | Dynamic testing | Used to evaluate the vehicle's response to vibrations. On display at the U.S. Space & Rocket Center, Huntsville, Alabama. | ||
| S-IC-T | All Systems Test | First stage used for static test firing at Marshall Space Flight Center. On display at Kennedy Space Center. | ||
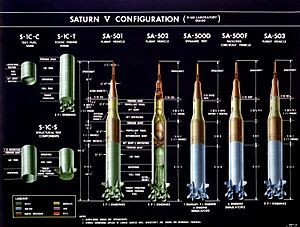
| SA-501 | Apollo 4 | November 9, 1967 12:00:01 |
39A | First uncrewed, all-up test flight; complete success. |
| SA-502 | Apollo 6 | April 4, 1968 12:00:01 |
39A | Second uncrewed test flight; J-2 engine problems caused early shutdown of two engines in second stage, and prevented third stage restart. |
| SA-503 | Apollo 8 | December 21, 1968 12:51:00 |
39A | First crewed flight; first trans-lunar injection of Apollo command and service module. |
| SA-504 | Apollo 9 | March 3, 1969 16:00:00 |
39A | Crewed low Earth orbit test of complete Apollo spacecraft with the Lunar Module (LM). |
| SA-505 | Apollo 10 | May 18, 1969 16:49:00 |
39B | Second crewed trans-lunar injection of complete Apollo spacecraft with LM; Only Saturn V launched from Pad 39B. |
| SA-506 | Apollo 11 | July 16, 1969 13:32:00 |
39A | First crewed lunar landing, at Sea of Tranquility. |
| SA-507 | Apollo 12 | November 14, 1969 16:22:00 |
39A | Vehicle was struck twice by lightning shortly after liftoff, but did not suffer serious damage. Made second crewed lunar landing, near Surveyor 3 at Ocean of Storms. |
| SA-508 | Apollo 13 | April 11, 1970 19:13:03 |
39A | Severe pogo oscillations in second stage caused early center engine shutdown; guidance compensated by burning remaining engines longer. Lunar landing mission was aborted by service module failure. |
| SA-509 | Apollo 14 | January 31, 1971 21:03:02 |
39A | Third crewed lunar landing, near Fra Mauro, Apollo 13's intended landing site. |
| SA-510 | Apollo 15 | July 26, 1971 13:34:00 |
39A | Fourth crewed lunar landing, at Hadley–Apennine. First extended Apollo mission, carrying lunar orbital Scientific Instrument Module and Lunar Roving Vehicle. |
| SA-511 | Apollo 16 | April 16, 1972 17:54:00 |
39A | Fifth crewed lunar landing, at Descartes Highlands. |
| SA-512 | Apollo 17 | December 7, 1972 05:33:00 |
39A | Only night launch. Sixth and final crewed lunar landing, at Taurus–Littrow. |
| SA-513 | Skylab 1 | May 14, 1973 17:30:00 |
39A | Uncrewed launch of the Skylab orbital workshop, which replaced the third stage, S-IVB-513, on display at Johnson Space Center. Originally designated for canceled Apollo 18. |
| SA-514 | Unused | Originally designated for canceled Apollo 18 or 19; never used. It was proposed for launching an International Skylab. This station would have been serviced by Apollo, Soyuz and later by the Space Shuttle. The first stage (S-IC-14) on display at Johnson Space Center, second and third stage (S-II-14, S-IV-14) on display at Kennedy Space Center. The S-II interstage is located at Parque de las Ciencias in Puerto Rico. | ||
| SA-515 | Unused | Originally designated for Apollo 20, never used. Later it was proposed to launch the backup Skylab station into orbit sometime between January 1975 and April 1976. That way, it could expand the Apollo–Soyuz mission by 56–90 days. The first stage was on display at Michoud Assembly Facility, until June 2016 then was moved to the INFINITY Science Center in Mississippi. The second stage (S-II-15) is on display at Johnson Space Center. The third stage was converted to a backup Skylab orbital workshop and is on display at the National Air and Space Museum. | ||
Specifications
The size and payload capacity of the Saturn V dwarfed those of all other previous rockets successfully flown at that time. With the Apollo spacecraft on top, it stood 363 feet (111 m) tall, and, ignoring the fins, was 33 feet (10 m) in diameter. Fully fueled, the Saturn V weighed 6.5 million pounds (2,900,000 kg) and had a low Earth orbit (LEO) payload capacity originally estimated at 261,000 pounds (118,000 kg), but was designed to send at least 90,000 pounds (41,000 kg) to the Moon. Later upgrades increased that capacity; on the final three Apollo lunar missions, it sent up to 95,901 lb (43,500 kg) to the Moon.
At a height of 363 feet (111 m), the Saturn V stood 58 feet (18 m) taller than the Statue of Liberty from the ground to the torch, and 48 feet (15 m) taller than the Elizabeth Tower, which houses Big Ben at the Palace of Westminster. For comparison, the Mercury-Redstone Launch Vehicle that launched Freedom 7, the first crewed American spaceflight, was approximately 11 feet (3.4 m) longer than the S-IVB stage and delivered less sea level thrust (78,000 pounds-force (350 kN)) than the Apollo command module's Launch Escape System (150,000 pounds-force (667 kN))—although the Mercury-Redstone could maintain that thrust for much longer (143.5 seconds vs. 3.2 seconds).
The Saturn V was principally designed by the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, although numerous major systems, including propulsion systems, were designed by subcontractors. The rocket used the powerful F-1 and J-2 rocket engines; during testing at Stennis Space Center, the force developed by the engines shattered the windows of nearby houses. Designers decided early on to attempt to use as much technology from the Saturn I program as possible for the Saturn V. Consequently, the S-IVB-500 third stage of the Saturn V was based on the S-IVB-200 second stage of the Saturn IB. The instrument unit that controlled the Saturn V shared characteristics with the one carried by the Saturn IB.
The Saturn V was primarily constructed of aluminum. It was also made of titanium, polyurethane, cork and asbestos. Blueprints and other plans of the rocket are available on microfilm at the Marshall Space Flight Center.
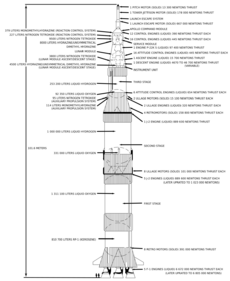
The Saturn V consisted of three stages—the S-IC first stage, S-II second stage, and S-IVB third stage—and the instrument unit. All three stages used liquid oxygen (LOX) as the oxidizer. The first stage used RP-1 for fuel, while the second and third stages used liquid hydrogen (LH2). LH2 has a higher specific energy (energy per unit mass) than RP-1, which makes it more suitable for higher-energy orbits, such as the trans-lunar injection required for Apollo missions. Conversely, RP-1 offers higher energy density (energy per unit volume) and higher thrust than LH2, which makes it more suitable for reducing aerodynamic drag and gravity losses in the early stages of launch. If the first stage had used LH2, the volume required would have been more than three times greater, which would have been aerodynamically infeasible at the time. The upper stages also used small solid-propellant ullage motors that helped to separate the stages during the launch, and to ensure that the liquid propellants were in a proper position to be drawn into the pumps.
S-IC first stage
The S-IC was built by the Boeing Company at the Michoud Assembly Facility, New Orleans, where the Space Shuttle external tanks would later be built by Lockheed Martin. Most of its mass at launch was propellant: RP-1 fuel with liquid oxygen as the oxidizer. The stage was 138 feet (42 m) tall and 33 feet (10 m) in diameter. It provided 7,750,000 lbf (34,500 kN) of thrust at sea level. The S-IC stage had a dry mass of about 303,000 pounds (137,000 kilograms); when fully fueled at launch, it had a total mass of 4,881,000 pounds (2,214,000 kilograms). The S-IC was powered by five Rocketdyne F-1 engines arrayed in a quincunx. The center engine was held in a fixed position, while the four outer engines could be hydraulically turned with gimbals to steer the rocket. In flight, the center engine was turned off about 26 seconds earlier than the outboard engines to limit acceleration. During launch, the S-IC fired its engines for 168 seconds (ignition occurred about 8.9 seconds before liftoff) and at engine cutoff, the vehicle was at an altitude of about 42 miles (67 km), was downrange about 58 miles (93 km), and was moving around 7,500 feet per second (2,300 m/s).
While not put into production, a proposed replacement for the first stage was the AJ-260x. This solid rocket motor would have simplified the design by removing the five-engine configuration and, in turn, reduced launch costs.
S-II second stage
The S-II was built by North American Aviation at Seal Beach, California. Using liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen, it had five Rocketdyne J-2 engines in a similar arrangement to the S-IC, and also used the four outer engines for control. The S-II was 81.6 feet (24.87 m) tall with a diameter of 33 feet (10 m), identical to the S-IC, and thus was the largest cryogenic stage until the launch of the Space Shuttle in 1981. The S-II had a dry mass of about 80,000 pounds (36,000 kg); when fully fueled, it weighed 1,060,000 pounds (480,000 kg). The second stage accelerated the Saturn V through the upper atmosphere with 1,100,000 pounds-force (4,900 kN) of thrust in a vacuum.
When loaded with fuel, more than 90 percent of the mass of the stage was propellant; however, the ultra-lightweight design had led to two failures in structural testing. Instead of having an intertank structure to separate the two fuel tanks as was done in the S-IC, the S-II used a common bulkhead that was constructed from both the top of the LOX tank and bottom of the LH2 tank. It consisted of two aluminum sheets separated by a honeycomb structure made of phenolic resin. This bulkhead had to be able to insulate against the 126 °F (70 °C) temperature difference between the two tanks. The use of a common bulkhead saved 7,900 pounds (3.6 t) by both eliminating one bulkhead and reducing the stage's length. Like the S-IC, the S-II was transported from its manufacturing plant to Cape Kennedy by sea.
S-IVB third stage

The S-IVB stage was built by the Douglas Aircraft Company at Huntington Beach, California. It had one Rocketdyne J-2 engine and used the same fuel as the S-II. The S-IVB used a common bulkhead to separate the two tanks. It was 58.6 feet (17.86 m) tall with a diameter of 21.7 feet (6.604 m) and was also designed with high mass efficiency, though not quite as aggressively as the S-II. The S-IVB had a dry mass of about 23,000 pounds (10,000 kg) and, when fully fueled, weighed about 262,000 pounds (119,000 kg).
The S-IVB was the only rocket stage of the Saturn V small enough to be transported by the cargo plane Aero Spacelines Pregnant Guppy.
For lunar missions it was fired twice: first for Earth orbit insertion after second stage cutoff, and a second time for translunar injection (TLI).
Instrument unit

The Saturn V's instrument unit was built by IBM and was placed on top of the rocket's third stage. It was constructed at the Space Systems Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This computer controlled the operations of the rocket from just before liftoff until the S-IVB was discarded. It included guidance and telemetry systems for the rocket. By measuring the acceleration and vehicle attitude, it could calculate the position and velocity of the rocket and correct for any deviations.
Assembly
After the construction and ground testing of each stage was completed, they were each shipped to the Kennedy Space Center. The first two stages were so massive that the only way to transport them was by barge. The S-IC, constructed in New Orleans, was transported down the Mississippi River to the Gulf of Mexico.
After rounding Florida, the stages were transported up the Intra-Coastal Waterway to the Vehicle Assembly Building (originally called the Vertical Assembly Building). This was essentially the same route which would be used later to ship Space Shuttle external tanks. The S-II was constructed in California and traveled to Florida via the Panama Canal. The third stage and Instrument Unit was carried by the Aero Spacelines Pregnant Guppy and Super Guppy, but could have been carried by barge if warranted.
Upon arrival at the Vertical Assembly Building, each stage was inspected in a horizontal position before being oriented vertically. NASA also constructed large spool-shaped structures that could be used in place of stages if a particular stage was delayed. These spools had the same height and mass and contained the same electrical connections as the actual stages.
NASA stacked (assembled) the Saturn V on a Mobile Launcher, which consisted of a Launch Umbilical Tower with nine swing arms (including the crew access arm), a "hammerhead" crane, and a water suppression system which was activated prior to engine ignition during a launch. After assembly was completed, the entire stack was moved from the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) to the launch pad using the Crawler Transporter (CT). Built by the Marion Power Shovel Company (and later used for transporting the smaller and lighter Space Shuttle, as well as the Space Launch System), the CT ran on four double-tracked treads, each with 57 "shoes". Each shoe weighed 2,000 pounds (910 kg). This transporter was also required to keep the rocket level as it traveled the 3 miles (4.8 km) to the launch site, especially at the 3 percent grade encountered at the launch pad. The CT also carried the Mobile Service Structure (MSS), which allowed technicians access to the rocket until eight hours before launch, when it was moved to the "halfway" point on the Crawlerway (the junction between the VAB and the two launch pads).
Cost
From 1964 until 1973, $6.417 billion (equivalent to $36.9 billion in 2021) was appropriated for the Research and Development and flights of the Saturn V, with the maximum being in 1966 with $1.2 billion (equivalent to $7.76 billion in 2021). That same year, NASA received its largest total budget of $4.5 billion, about 0.5 percent of the gross domestic product (GDP) of the United States at that time.
Two main reasons for the cancellation of the last three Apollo missions were the heavy investments in Saturn V and the ever-increasing costs of the Vietnam War to the U.S. in money and resources. In the time frame from 1969 to 1971 the cost of launching a Saturn V Apollo mission was between $185,000,000 to $189,000,000, of which $110 million were used for the production of the vehicle (equivalent to $1.06 billion–$1.09 billion in 2021).
Lunar mission launch sequence
The Saturn V carried all Apollo lunar missions, which were launched from Launch Complex 39 at the John F. Kennedy Space Center in Florida. After the rocket cleared the launch tower, flight control transferred to Mission Control at the Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. An average mission used the rocket for a total of just 20 minutes. Although Apollo 6 experienced three engine failures, and Apollo 13 experienced one engine shutdown, the onboard computers were able to compensate by burning the remaining engines longer to achieve parking orbit.
Range safety
In the event of an abort requiring the destruction of the rocket, the range safety officer would remotely shut down the engines and after several seconds send another command for the shaped explosive charges attached to the outer surfaces of the rocket to detonate. These would make cuts in fuel and oxidizer tanks to disperse the fuel quickly and to minimize mixing. The pause between these two actions would give time for the crew to escape via the Launch Escape Tower or (in the later stages of the flight) the propulsion system of the Service module. A third command, "safe", was used after the S-IVB stage reached orbit to irreversibly deactivate the self-destruct system. The system was also held inactive as long as the rocket was still on the launch pad.
Startup sequence

The first stage burned for about 2 minutes and 41 seconds, lifting the rocket to an altitude of 42 miles (68 km) and a speed of 6,164 miles per hour (2,756 m/s) and burning 4,700,000 pounds (2,100,000 kg) of propellant.
At 8.9 seconds before launch, the first stage ignition sequence started. The center engine ignited first, followed by opposing outboard pairs at 300-millisecond intervals to reduce the structural loads on the rocket. When thrust had been confirmed by the onboard computers, the rocket was "soft-released" in two stages: first, the hold-down arms released the rocket, and second, as the rocket began to accelerate upwards, it was slowed by tapered metal pins pulled through holes for half a second.
Once the rocket had lifted off, it could not safely settle back down onto the pad if the engines failed. The astronauts considered this one of the tensest moments in riding the Saturn V, for if the rocket did fail to lift off after release they had a low chance of survival given the large amounts of propellant. To improve safety, the Saturn Emergency Detection System (EDS) inhibited engine shutdown for the first 30 seconds of flight. If all three stages were to explode simultaneously on the launch pad, an unlikely event, the Saturn V had a total explosive yield of 543 tons of TNT or 0.543 kilotons (2,271,912,000,000 J or 155,143 lbs of weight loss), which is 0.222 kt for the first stage, 0.263 kt for the second stage and 0.068 kt for the third stage. (See Saturn V Instrument Unit) Contrary to popular myth, the noise produced was not able to melt concrete.
It took about 12 seconds for the rocket to clear the tower. During this time, it yawed 1.25 degrees away from the tower to ensure adequate clearance despite adverse winds; this yaw, although small, can be seen in launch photos taken from the east or west. At an altitude of 430 feet (130 m) the rocket rolled to the correct flight azimuth and then gradually pitched down until 38 seconds after second stage ignition. This pitch program was set according to the prevailing winds during the launch month.
The four outboard engines also tilted toward the outside so that in the event of a premature outboard engine shutdown the remaining engines would thrust through the rocket's center of mass. The Saturn V reached 400 feet per second (120 m/s) at over 1 mile (1,600 m) in altitude. Much of the early portion of the flight was spent gaining altitude, with the required velocity coming later. The Saturn V broke the sound barrier at just over 1 minute at an altitude of between 3.45 and 4.6 miles (5.55 and 7.40 km). At this point, shock collars, or condensation clouds, would form around the bottom of the command module and around the top of the second stage.
Max Q sequence
At about 80 seconds, the rocket experienced maximum dynamic pressure (max q). The dynamic pressure on a rocket varies with air density and the square of relative velocity. Although velocity continues to increase, air density decreases so quickly with altitude that dynamic pressure falls below max q.
The propellant in just the S-IC made up about three-quarters of Saturn V's entire launch mass, and it was consumed at 13,000 kilograms per second (1,700,000 lb/min). Newton's second law of motion states that force is equal to mass multiplied by acceleration, or equivalently that acceleration is equal to force divided by mass, so as the mass decreased (and the force increased somewhat), acceleration rose. Including gravity, launch acceleration was only 1+1⁄4 g, i.e., the astronauts felt 1+1⁄4 g while the rocket accelerated vertically at 1⁄4 g. As the rocket rapidly lost mass, total acceleration including gravity increased to nearly 4 g at T+135 seconds. At this point, the inboard (center) engine was shut down to prevent acceleration from increasing beyond 4 g.
When oxidizer or fuel depletion was sensed in the suction assemblies, the remaining four outboard engines were shut down. First stage separation occurred a little less than one second after this to allow for F-1 thrust tail-off. Eight small solid fuel separation motors backed the S-IC from the rest of the vehicle at an altitude of about 42 miles (67 km). The first stage continued on a ballistic trajectory to an altitude of about 68 miles (109 km) and then fell in the Atlantic Ocean about 350 miles (560 km) downrange.
The engine shutdown procedure was changed for the launch of Skylab to avoid damage to the Apollo Telescope Mount. Rather than shutting down all four outboard engines at once, they were shut down two at a time with a delay to reduce peak acceleration further.
S-II sequence
After S-IC separation, the S-II second stage burned for 6 minutes and propelled the craft to 109 miles (175 km) and 15,647 mph (25,181 km/h), close to orbital velocity.
For the first two uncrewed launches, eight solid-fuel ullage motors ignited for four seconds to accelerate the S-II stage, followed by the ignition of the five J-2 engines. For the first seven crewed Apollo missions, only four ullage motors were used on the S-II, and they were eliminated for the final four launches. About 30 seconds after first stage separation, the interstage ring dropped from the second stage. This was done with an inertially fixed attitude—orientation around its center of gravity—so that the interstage, only 3 feet 3 inches (1 m) from the outboard J-2 engines, would fall cleanly without hitting them, as the interstage could have potentially damaged two of the J-2 engines if it was attached to the S-IC. Shortly after interstage separation the Launch Escape System was also jettisoned.
About 38 seconds after the second stage ignition, the Saturn V switched from a preprogrammed trajectory to a "closed loop" or Iterative Guidance Mode. The instrument unit now computed in real time the most fuel-efficient trajectory toward its target orbit. If the instrument unit failed, the crew could switch control of the Saturn to the command module's computer, take manual control, or abort the flight.
About 90 seconds before the second stage cutoff, the center engine shut down to reduce longitudinal pogo oscillations. At around this time, the LOX flow rate decreased, changing the mix ratio of the two propellants and ensuring that there would be as little propellant as possible left in the tanks at the end of second stage flight. This was done at a predetermined delta-v.
Five level sensors in the bottom of each S-II propellant tank were armed during S-II flight, allowing any two to trigger S-II cutoff and staging when they were uncovered. One second after the second stage cut off it separated and several seconds later the third stage ignited. Solid fuel retro-rockets mounted on the interstage at the top of the S-II fired to back it away from the S-IVB. The S-II impacted about 2,600 miles (4,200 km) from the launch site.
On the Apollo 13 mission, the inboard engine suffered major pogo oscillation, resulting in an early automatic cutoff. To ensure sufficient velocity was reached, the remaining four engines were kept active for longer than planned. A pogo suppressor was fitted to later Apollo missions to avoid this, though the early fifth engine's cutoff remained to reduce g-forces.
S-IVB sequence
Unlike the two-plane separation of the S-IC and S-II, the S-II and S-IVB stages separated with a single step. Although it was constructed as part of the third stage, the interstage remained attached to the second stage. The third stage did not use much fuel to get into LEO (Low Earth Orbit), because the second stage had done most of the job.
During Apollo 11, a typical lunar mission, the third stage burned for about 2.5 minutes until first cutoff at 11 minutes 40 seconds. At this point it was 1,645.61 miles (2,648.35 km) downrange and in a parking orbit at an altitude of 118 miles (190 km) and velocity of 17,432 miles per hour (28,054 km/h). The third stage remained attached to the spacecraft while it orbited the Earth one and a half times while astronauts and mission controllers prepared for translunar injection (TLI).
For the final three Apollo flights, the temporary parking orbit was even lower (approximately 107 miles or 172 kilometers), using the Oberth effect to increase payload capacity for these missions. The Apollo 9 Earth orbit mission was launched into the nominal orbit consistent with Apollo 11, but the spacecraft were able to use their own engines to raise the perigee high enough to sustain the 10-day mission. Skylab was launched into a quite different orbit, with a 270-mile (434 km) perigee which sustained it for six years, and also a higher inclination to the equator (50 degrees versus 32.5 degrees for Apollo).
Lunar Module sequence
On Apollo 11, TLI came at 2 hours and 44 minutes after launch. The S-IVB burned for almost six minutes, giving the spacecraft a velocity close to the Earth's escape velocity of 25,053 mph (40,319 km/h). This gave an energy-efficient transfer to lunar orbit, with the Moon helping to capture the spacecraft with a minimum of CSM fuel consumption.
About 40 minutes after TLI, the Apollo command and service module (CSM) separated from the third stage, turned 180 degrees, and docked with the Lunar Module (LM) that rode below the CSM during launch. The CSM and LM separated from the spent third stage 50 minutes later, in a maneuver known as transposition, docking, and extraction.
If it were to remain on the same trajectory as the spacecraft, the S-IVB could have presented a collision hazard, so its remaining propellants were vented and the auxiliary propulsion system fired to move it away. For lunar missions before Apollo 13, the S-IVB was directed toward the Moon's trailing edge in its orbit so that the Moon would slingshot it beyond earth escape velocity and into solar orbit. From Apollo 13 onwards, controllers directed the S-IVB to hit the Moon. Seismometers left behind by previous missions detected the impacts, and the information helped map the internal structure of the Moon.
Skylab sequence
In 1965, the Apollo Applications Program (AAP) was created to look into science missions that could be performed using Apollo hardware. Much of the planning centered on the idea of a space station. Wernher von Braun's earlier (1964) plans employed a "wet workshop" concept, with a spent S-II Saturn V second stage being launched into orbit and outfitted in space. The next year AAP studied a smaller station using the Saturn IB second stage. By 1969, Apollo funding cuts eliminated the possibility of procuring more Apollo hardware and forced the cancellation of some later Moon landing flights. This freed up at least one Saturn V, allowing the wet workshop to be replaced with the "dry workshop" concept: the station (now known as Skylab) would be built on the ground from a surplus Saturn IB second stage and launched atop the first two live stages of a Saturn V. A backup station, constructed from a Saturn V third stage, was built and is now on display at the National Air and Space Museum.
Skylab was the only launch not directly related to the Apollo lunar landing program. The only significant changes to the Saturn V from the Apollo configurations involved some modification to the S-II to act as the terminal stage for inserting the Skylab payload into Earth orbit, and to vent excess propellant after engine cutoff so the spent stage would not rupture in orbit. The S-II remained in orbit for almost two years, and made an uncontrolled re-entry on January 11, 1975.
Three crews lived aboard Skylab from May 25, 1973, to February 8, 1974. Skylab remained in orbit until July 11, 1979.
Post-Apollo proposal
After Apollo, the Saturn V was planned to be the prime launch vehicle for Prospector to be launched to the Moon. Prospector was a proposed 330-kilogram (730 lb) robotic rover, similar to the two Soviet Lunokhod rovers, the Voyager Mars probes, and a scaled-up version of the Voyager interplanetary probes. Saturn V was also to have been the launch vehicle for the nuclear rocket stage RIFT test program and for some versions of the upcoming NERVA project. All of these planned uses of the Saturn V were cancelled, with cost being a major factor. Edgar Cortright, who had been the director of NASA Langley, stated decades later that "JPL never liked the big approach. They always argued against it. I probably was the leading proponent in using the Saturn V, and I lost. Probably very wise that I lost."
The canceled second production run of Saturn Vs would very likely have used the F-1A engine in its first stage, providing a substantial performance boost. Other likely changes would have been the removal of the fins (which turned out to provide little benefit when compared to their weight), a stretched S-IC first stage to support the more powerful F-1As, and uprated J-2s or an M-1 for the upper stages.
A number of alternate Saturn vehicles were proposed based on the Saturn V, ranging from the Saturn INT-20 with an S-IVB stage and interstage mounted directly onto an S-IC stage, through to the Saturn V-23(L) which would not only have five F-1 engines in the first stage, but also four strap-on boosters with two F-1 engines each, giving a total of thirteen F-1 engines firing at launch.
Lack of a second Saturn V production run killed these plans and left the United States without a super heavy-lift launch vehicle. Some in the U.S. space community came to lament this situation, as continued production could have allowed the International Space Station, using a Skylab or Mir configuration with both U.S. and Russian docking ports, to be lifted with just a handful of launches. The Saturn-Shuttle concept also could have eliminated the Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Boosters that ultimately precipitated the Challenger accident in 1986.
Proposed successors
Post-Apollo
U.S. proposals for a rocket larger than the Saturn V from the late 1950s through the early 1980s were generally called Nova. Over thirty different large rocket proposals carried the Nova name, but none were developed.
Wernher von Braun and others also had plans for a rocket that would have featured eight F-1 engines in its first stage, like the Saturn C-8, allowing a direct ascent flight to the Moon. Other plans for the Saturn V called for using a Centaur as an upper stage or adding strap-on boosters. These enhancements would have enabled the launch of large robotic spacecraft to the outer planets or the sending of astronauts to Mars. Other Saturn V derivatives analyzed included the Saturn MLV family of "Modified Launch Vehicles", which would have almost doubled the payload lift capability of the standard Saturn V and were intended for use in a proposed mission to Mars by 1980.
In 1968, Boeing studied another Saturn-V derivative, the Saturn C-5N, which included a nuclear thermal rocket engine for the third stage of the vehicle. The Saturn C-5N would carry a considerably greater payload for interplanetary spaceflight. Work on the nuclear engines, along with all Saturn V ELVs, ended in 1973.
The Comet HLLV was a massive heavy lift launch vehicle designed for the First Lunar Outpost program, which was in the design phase from 1992 to 1993 under the Space Exploration Initiative. It was a Saturn V derived launch vehicle with over twice the payload capability and would have relied completely on existing technology. All of the Comet HLLV engines were modernized versions of their Apollo counterparts and the fuel tanks would be stretched. Its main goal was to support the First Lunar Outpost program and future crewed Mars missions. It was designed to be as cheap and easy to operate as possible.
Ares family
In 2006, as part of the proposed Constellation program, NASA unveiled plans to construct two Shuttle Derived Launch Vehicles, the Ares I and Ares V, which would use some existing Space Shuttle and Saturn V hardware and infrastructure. The two rockets were intended to increase safety by specializing each vehicle for different tasks, Ares I for crew launches and Ares V for cargo launches. The original design of the heavy-lift Ares V, named in homage to the Saturn V, was 360 feet (110 m) in height and featured a core stage based on the Space Shuttle External Tank, with a diameter of 28 feet (8.4 m). It was to be powered by five RS-25 engines and two five-segment Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Boosters (SRBs). As the design evolved, the RS-25 engines were replaced with five RS-68 engines, the same engines used on the Delta IV. The switch from the RS-25 to the RS-68 was intended to reduce cost, as the latter was cheaper, simpler to manufacture, and more powerful than the RS-25, though the lower efficiency of the RS-68 required an increase in core stage diameter to 33 ft (10 m), the same diameter as the Saturn V's S-IC and S-II stages.
In 2008, NASA again redesigned the Ares V, lengthening the core stage, adding a sixth RS-68 engine, and increasing the SRBs to 5.5 segments each. This vehicle would have been 381 feet (116 m) tall and would have produced a total thrust of approximately 8,900,000 lbf (40 MN) at liftoff, more than the Saturn V or the Soviet Energia, but less than the Soviet N-1. Projected to place approximately 400,000 pounds (180 t) into orbit, the Ares V would have surpassed the Saturn V in payload capability. An upper stage, the Earth Departure Stage, would have utilized a more advanced version of the J-2 engine, the J-2X. Ares V would have placed the Altair lunar landing vehicle into low Earth orbit. An Orion crew vehicle launched on Ares I would have docked with Altair, and the Earth Departure Stage would then send the combined stack to the Moon.
Space Launch System
After the cancellation of the Constellation program – and hence Ares I and Ares V – NASA announced the Space Launch System (SLS) heavy-lift launch vehicle for beyond low Earth orbit space exploration. The SLS, similar to the original Ares V concept, is powered by four RS-25 engines and two five-segment SRBs. Its Block 1 configuration can lift approximately 209,000 pounds (95 t) to LEO. The Block 1B configuration will add the Exploration Upper Stage, powered by four RL10 engines, to increase payload capacity. An eventual Block 2 variant will upgrade to advanced boosters, increasing LEO payload to at least 290,000 pounds (130 t).
One proposal for advanced boosters would use a derivative of the Saturn V's F-1, the F-1B, and increase SLS payload to around 330,000 pounds (150 t) to LEO. The F-1B is to have better specific impulse and be cheaper than the F-1, with a simplified combustion chamber and fewer engine parts, while producing 1,800,000 lbf (8.0 MN) of thrust at sea level, an increase over the approximate 1,550,000 lbf (6.9 MN) achieved by the mature Apollo 15 F-1 engine,
Saturn V displays
- There are two displays at the U.S. Space & Rocket Center in Huntsville:
- SA-500D is on horizontal display made up of its S-IC-D, S-II-F/D and S-IVB-D. These were all test stages not meant for flight. This vehicle was displayed outdoors from 1969 to 2007, was restored, and is now displayed in the Davidson Center for Space Exploration.
- Vertical display (replica) built in 1999 located in an adjacent area.
- There is one at the Johnson Space Center made up of the first stage from SA-514, the second stage from SA-515, and the third stage from SA-513 (replaced for flight by the Skylab workshop). With stages arriving between 1977 and 1979, this was displayed in the open until its 2005 restoration when a structure was built around it for protection. This is the only display Saturn consisting entirely of stages intended to be launched.
- Another one at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex, made up of S-IC-T (test stage) and the second and third stages from SA-514. It was displayed outdoors for decades, then in 1996 was enclosed for protection from the elements in the Apollo/Saturn V Center.
- The S-IC stage from SA-515, originally at the Michoud Assembly Facility, New Orleans, is now on display at the Infinity Science Center in Mississippi.
- The S-IVB stage from SA-515 was converted for use as a backup for Skylab, and is on display at the National Air and Space Museum in Washington, D.C.
-
Complete Saturn V rocket display. Temporary exposition at the Kennedy Space Center.
-
Saturn V display, Johnson Space Center
-
SA-500D (S-IC-D, S-II-F/D and S-IVB-D), U.S. Space & Rocket Center, Huntsville
-
S-IC-T (test stage) and second and third stages from SA-514, Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex
-
S-IVB stage from SA-515, converted for use as Skylab B, National Air and Space Museum.
-
Saturn V main rockets, Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex
Discarded stages
On September 3, 2002, astronomer Bill Yeung discovered a suspected asteroid, which was given the discovery designation J002E3. It appeared to be in orbit around the Earth, and was soon discovered from spectral analysis to be covered in white titanium dioxide, which was a major constituent of the paint used on the Saturn V. Calculation of orbital parameters led to tentative identification as being the Apollo 12 S-IVB stage. Mission controllers had planned to send Apollo 12's S-IVB into solar orbit after separation from the Apollo spacecraft, but it is believed the burn lasted too long, and hence did not send it close enough to the Moon, so it remained in a barely stable orbit around the Earth and Moon. In 1971, through a series of gravitational perturbations, it is believed to have entered in a solar orbit and then returned into weakly captured Earth orbit 31 years later. It left Earth orbit again in June 2003.
See also
 In Spanish: Saturno V para niños
In Spanish: Saturno V para niños
- Comparison of orbital launchers families
- Comparison of orbital launch systems
- Space exploration
- Comet HLLV (a Saturn-derived launch vehicle design from the 1990s)