Phobos-Grunt facts for kids
| Phobos-Grunt Фобос-Грунт |
|
|---|---|
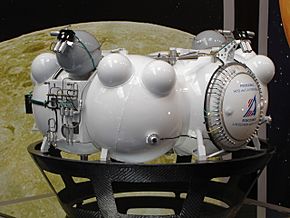 A model of Phobos-Grunt's base section |
|
| Organization: | Russian Federal Space Agency |
| Mission type: | Orbiter, lander, sample return |
| Flyby of: | Phobos |
| Satellite of: | Mars |
| Launch date: | 8 November 2011 |
| Launch vehicle: | Zenit rocket |
| Launch site: | Baikonur Cosmodrome |
| Mass: | 8120 kg |
Quick facts for kids edit |
|
Phobos-Grunt (also spelled Fobos-Grunt, also called Phobos Sample Return Mission) was an unmanned Russian spacecraft. It was an attempted sample return mission to Phobos, a moon of the planet Mars. Scientists intended Phobos-Grunt to orbit and study Mars. It was meant to look at Mars' atmosphere and dust storms, plasma and radiation. Then, Phobos-Grunt should have landed on Phobos and returned a 200 g soil sample to Earth.
The spacecraft was the first Russian interplanetary mission since Mars 96. It was launched on 8 November 2011 (UTC), aboard a Zenit rocket, at Baikonur Cosmodrome. It was sent with the Chinese spacecraft Yinghuo-1 and with the Living Interplanetary Flight Experiment.
The name Phobos-Grunt (Russian: Фобос-Грунт) is Russian for Phobos-Soil.
Information
=Images for kids
Images for kids
-
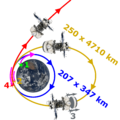
Modules -- A: lander, B: return module, C: reentry vehicle (not shown). Major components -- 1: solar panels, 2: reaction wheels, 3: landing gear, 4: robotic sample arm (second arm not shown), 6: sample transfer container, 7: attitude control thrusters, 8 and 10: fuel and helium tanks, 9: return module solar panels. Scientific instruments (some instruments are not visible from this angle or are not present on the model) -- a: Termofob thermodetector, b: GRAS-F seismogravimeter; c: METEOR-F cosmic dust detector, d: GAP (Gas Analytic Package) pyrolizer/thermal-differential analyzer, e: GAP chromatograph; f: GAP mass spectrometer, g: LAZMA mass spectrometer, h: MANAGA mass spectrometer, i: FPMS dust detector
-
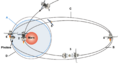
Phobos-Grunt around Mars: (1) Arrival of Phobos-Grunt, (2) Insertion maneuver in orbit around Mars, (3) Drop of the Fregat stage and separation of the probe and Yinghuo-1, (4) Maneuver for to raise the periapsis, (5) Yinghuo 1 starts his mission on the first orbit, (6) Maneuver to place himself in an orbit close to that of Phobos; (A) Orbit of Phobos, (B) Orbit of insertion of Phobos-Grunt and Yinghuo-1, (C) Orbit with raised periapsis, (D) Quasi-synchronous orbit with Phobos.
See also
 In Spanish: Fobos-Grunt para niños
In Spanish: Fobos-Grunt para niños