Radiation facts for kids
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium.
This includes:
- electromagnetic radiation such as radio waves, visible light, and x-rays
- particle radiation such as α, β, and neutron radiation
- acoustic radiation such as ultrasound, sound
- seismic waves.
Radiation may also refer to the energy, waves, or particles being radiated.
Contents
Types of Radiation
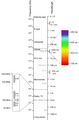
Many people are already familiar with different kinds of electromagnetic radiation/light. Scientists categorize this type of radiation based on its wavelength and frequency. Some kinds of electromagnetic radiation are:
- Ionizing radiation comes from radioactive materials and x-ray machines and non-ionizing radiation (usually electromagnetic radiation) comes from other sources. Ionizing radiation carries more than 10 eV (electronvolt), which is enough to ionize atoms and molecules, and break chemical bonds. This is important for its harmfulness to living organisms. Non-ionizing radiation does not cause microscopic damage, but some types can cause chemical changes or make things hotter.
- Radio waves: This is the kind of electromagnetic radiation with the highest wavelength. Radio waves are used to send and receive communications.
- Micro-waves: This is a special kind of radio wave that is used by a microwave oven to warm up food. Microwaves are also used for communications, as weapons, and to move electrical power from one place to another.
- Radar waves: This is also a kind of radio wave that is used to detect air planes in the sky and ships in the ocean. Radar is also used to see changes in weather.
- Infrared waves: Most objects at room temperature let off infrared radiation. Although humans cannot see it, special types of cameras can pick up this kind of radiation. Usually, the hotter something is, the more infrared radiation it lets off, which means that these special cameras can see hot things, even behind walls.
- Visible light: This is the radiation that we see all around us as what most people call "light."
- Ultraviolet light: This is a type of radiation with more energy than visible light that gives people a sunburn. Ultraviolet light is also used to kill bacteria and to make some kinds of invisible ink visible.
- X-rays and Gamma rays: These are extremely strong rays that are commonly used in medicine to photograph the interior of the body and treat cancer. However, in too large amounts, they are very dangerous to life.
Danger from radiation
Ionising radiation is radiation that carries enough energy to free electrons from atoms or molecules.
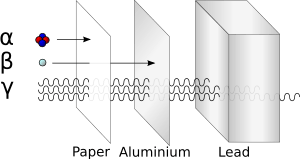
Only certain types of radiation are harmful to humans. For example, ultraviolet radiation can give people sunburns. X-rays and gamma rays can make a person sick, or even die, depending on the dose they get. Some types of particle radiation can also make people sick and lead to burns. If radiation does not carry high enough levels of energy, though, then these changes will not happen when something is hit by the radiation. This is referred to as non-ionizing radiation, which is not as dangerous.
One can distinguish between various types of radiation by looking at the source of the radiation, its wavelength (if the radiation is electromagnetic), the amount of energy being carried, any particles involved, etc. Radioactive material is a material which emits radiation. Uranium and plutonium are examples of radioactive materials. The atoms they are made of tend to fall apart and give off different kinds of radiation, like gamma rays and lots of particle radiation.
Ionising radiation by type
Ionising radiation can kill living things. It can cause genetic mutations, as shown by H.J. Muller. It can destroy cells in the body which divide, and thus indirectly kill a person.
- Alpha radiation, a type of particle radiation made up of the nuclei of helium atoms.
- Beta radiation, another type of particle radiation made up of high energy electrons or positrons.
- Neutron radiation, yet another type of particle radiation made up of high energy neutrons.
- Gamma radiation (Gamma rays), a type of radiation made up of high energy photons.
- X-ray radiation (X-rays), a type of radiation also made up of photons but which typically contain less energy than gamma rays.
Non-ionizing radiation by type
- Ultraviolet radiation, also known as UV.
- Infrared radiation
- Microwave radiation, familiar to those who use microwave ovens.
- Radio or Television waves.
- Visible light
- Gravitational radiation, a predicted consequence of general relativity.
Related pages
- Background radiation
- Cosmic microwave background radiation, 3K blackbody radiation that fills the Universe
- Radiation poisoning - destructive effects on life forms
- Radiation hardening - making devices resistant to failure in high radiation environments
- Radioactive contamination
- Radioactive decay
- Radiation accidents
Images for kids
-
Some kinds of ionizing radiation can be detected in a cloud chamber.
-
Gamma radiation detected in an isopropanol cloud chamber.
-
Alpha particle detected in an isopropanol cloud chamber
-
Electrons (beta radiation) detected in an isopropanol cloud chamber
See also
 In Spanish: Radiación para niños
In Spanish: Radiación para niños