Ormond Beach, Florida facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Ormond Beach, Florida
|
|
|---|---|

Ormond Beach City Hall
|
|
| Nickname(s):
Birthplace of Speed
|
|

Location in Volusia County and the state of Florida
|
|
| Country | |
| State | |
| County | Volusia |
| Settled by Native Timucuans (Nocoroco) | c. early 1500s |
| Settled by American colonizers (New Britain) |
c. 1860s-1870s |
| Incorporated (Town of Ormond) |
April 22, 1880 |
| Incorporated (City of Ormond Beach) |
April 25, 1950 |
| Government | |
| • Type | Commission-Manager |
| Area | |
| • City | 38.91 sq mi (100.78 km2) |
| • Land | 34.78 sq mi (90.09 km2) |
| • Water | 4.13 sq mi (10.69 km2) |
| Elevation | 7 ft (2 m) |
| Population
(2020)
|
|
| • City | 43,080 |
| • Density | 1,238.50/sq mi (478.18/km2) |
| • Urban | 349,064 (109th U.S.) |
| • Metro | 609,939 (90th U.S.) |
| Time zone | UTC−05:00 (Eastern (EST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−04:00 (EDT) |
| ZIP Codes |
32174-32176
|
| Area code(s) | 386 |
| FIPS code | 12-53150 |
| GNIS feature ID | 0307388 |
Ormond Beach is a city in Volusia County, Florida, United States. The population was 43,080 at the 2020 census. Ormond Beach lies directly north of Daytona Beach and is a principal city of the Deltona–Daytona Beach–Ormond Beach, FL Metropolitan Statistical Area. The city is known as the birthplace of speed, as early adopters of motorized cars flocked to its hard-packed beaches for yearlong entertainment, since paved roads were not yet commonplace. Ormond Beach lies in Central Eastern Florida.
Contents
History
The Timucuan town of Nocoroco was located where the Tomoka River joins the Halifax River, just north of present-day Ormond Beach, when Álvaro Mexía passed through it in 1605 on a mission to establish relations between Spanish Florida and the Surruque and Ais peoples of the coast of what are now Volusia and Brevard counties. Little is known of what happened to inhabitants of the area after Mexía's visit.
The city is named for James Ormond I, an Anglo-Irish-Scottish sea captain commissioned by King Ferdinand VII of Spain to bring Franciscan settlers to this part of Florida. Ormond had served Britain and Spain in the Napoleonic Wars as a ship captain, and was rewarded for his services to Spain by King Ferdinand VII. Ormond later worked for the Scottish Indian trade company of Panton, Leslie & Company, and his armed brig was called the "Somerset". After returning to Spanish control, in 1821, Florida was acquired from Spain by the United States, but hostilities during the Second Seminole War delayed settlement until after 1842. In 1875, the community was founded as New Britain by inhabitants from New Britain, Connecticut, but would be incorporated on April 22, 1880, as the Town of Ormond for its early plantation owner.
With its hard, white beach, Ormond became popular for the wealthy seeking relief from northern winters during the Floridian boom in tourism following the Civil War. The St. Johns and Halifax Railway arrived in 1886, and the first bridge across the Halifax River was built in 1887. John Anderson and James Downing Price opened the Ormond Hotel on January 1, 1888. Henry Flagler bought the hotel in 1890 and expanded it to accommodate 600 guests. It would be one in a series of Gilded Age hotels catering to passengers aboard his Florida East Coast Railway, which had purchased the St. Johns & Halifax Railroad. Once a well-known landmark which was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1980, the hotel was razed in 1992.
On December 5, 1896, the Nathan F. Cobb, a wooden schooner built in 1890, ran aground on a sandbar off Ormond.
One of Flagler's guests at the Ormond Hotel was his former business partner at the Standard Oil Company, John D. Rockefeller. He arrived in 1914 and after four seasons at the hotel bought an estate called The Casements, that would be Rockefeller's winter home during the latter part of his life. Sold by his heirs in 1939, it was purchased by the city in 1973 and now serves as a cultural center. It is the community's best-known historical structure.
Beginning in 1902, some of the first automobile races were held on the compacted sand from Ormond south to Daytona Beach. Pioneers in the industry, including Ransom Olds with his Pirate Racer, and Alexander Winton, tested their inventions. The American Automobile Association brought timing equipment in 1903 and the area acquired the nickname the "Birthplace of Speed." In 1907, Glenn Curtiss set an unofficial world record of 136.36 miles per hour (219.45 km/h), on a 40 hp (30 kW) 269 cu in (4,410 cc) Curtiss V-8 motorcycle. Lee Bible, in the record-breaking, but fatal, White Triplex, was less fortunate. Driving on the beach is still permitted on some stretches.
The municipality was officially renamed as the City of Ormond Beach following a referendum held on April 25, 1950.
Ormond Beach has four downtown riverfront parks and a beachfront park along with 37 other parks and gardens large and small. The historic shopping district located along Granada Boulevard from A1A to Orchard Street is home to dozens of locally owned shops and restaurants along with historic and cultural sites.
Geography

The approximate coordinates for the City of Ormond Beach is located at 29°17′11″N 81°04′30″W / 29.286405°N 81.074882°W (29.286405, –81.074882).
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 39.0 square miles (101.0 km2), of which 31.9 square miles (82.7 km2) is land, and 7.1 square miles (18.3 km2) (18.12%) is water. Drained by the Tomoka River, Ormond Beach is located on the Halifax River lagoon and the Atlantic Ocean.
Climate
The climate in this area is characterized by hot, humid summers and generally mild winters. According to the Köppen climate classification, the City of Ormond Beach has a humid subtropical climate zone (Cfa).
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1890 | 239 | — | |
| 1900 | 595 | 149.0% | |
| 1910 | 780 | 31.1% | |
| 1920 | 1,292 | 65.6% | |
| 1930 | 1,517 | 17.4% | |
| 1940 | 1,914 | 26.2% | |
| 1950 | 3,418 | 78.6% | |
| 1960 | 8,658 | 153.3% | |
| 1970 | 14,063 | 62.4% | |
| 1980 | 21,436 | 52.4% | |
| 1990 | 29,721 | 38.6% | |
| 2000 | 36,301 | 22.1% | |
| 2010 | 38,137 | 5.1% | |
| 2020 | 43,080 | 13.0% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census | |||
2010 and 2020 census
| Race | Pop 2010 | Pop 2020 | % 2010 | % 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White (NH) | 33,920 | 35,455 | 88.94% | 82.30% |
| Black or African American (NH) | 1,196 | 1,669 | 3.14% | 3.87% |
| Native American or Alaska Native (NH) | 56 | 76 | 0.15% | 0.18% |
| Asian (NH) | 856 | 1,305 | 2.24% | 3.03% |
| Pacific Islander or Native Hawaiian (NH) | 13 | 13 | 0.03% | 0.03% |
| Some other race (NH) | 55 | 146 | 0.14% | 0.34% |
| Two or more races/Multiracial (NH) | 462 | 1,567 | 1.21% | 3.64% |
| Hispanic or Latino (any race) | 1,579 | 2,849 | 4.14% | 6.61% |
| Total | 38,137 | 43,080 |
As of the 2020 United States census, there were 43,080 people, 18,554 households, and 11,121 families residing in the city.
As of the 2010 United States census, there were 38,137 people, 16,617 households, and 10,408 families residing in the city.
Notable people
- Paul America, actor
- Adelbert Ames, the last surviving general officer of the Civil War, who died at age 97, in 1933
- Lisa Andersen, pro surfer
- Ben Brainard, stand-up comedian and social media personality
- Shirley Chisholm, U.S. Congress member, U.S. presidential candidate
- David Allan Coe, musician
- Bryan Collyer, racing driver
- Phil Dalhausser, 2008 Olympic gold medalist in beach volleyball
- Jacob deGrom, MLB pitcher for the Texas Rangers
- Jimmy Foster, racing driver
- Alan Gustafson, NASCAR Cup Series crew chief for Hendrick Motorsports
- Brian Kelley, musician, member of Florida Georgia Line
- Paul LePage, politician
- Frederick Dana Marsh, artist
- John D. Rockefeller, billionaire industrialist
- Freelan Oscar Stanley and Francis Edgar Stanley, co-owners of the Stanley Motor Carriage Company
- Corey Walden, professional basketball player, 2019 Israeli Basketball Premier League MVP
- Harry Wendelstedt, baseball umpire
Sites of interest
Historic places
- Anderson-Price Memorial Library Building
- The Casements
- Dix House
- Bulow Creek State Park
- Ormond Memorial Art Museum and Gardens
- North Peninsula State Park
- Tomoka State Park
Transportation
Airports
The Ormond Beach Municipal Airport is the main airport in Ormond Beach. For more international travel, commuters would be required to drive to the Daytona Beach International Airport.
Major Roads
 I-95 (SR 9 / Interstate 95) is the main north–south interstate highway along the east coast of the state. Two interchanges exist within the city. The first is at Exit 268, also known as Florida State Road 40 and the second is at Exit 273, also known as US 1 (see below).
I-95 (SR 9 / Interstate 95) is the main north–south interstate highway along the east coast of the state. Two interchanges exist within the city. The first is at Exit 268, also known as Florida State Road 40 and the second is at Exit 273, also known as US 1 (see below).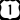 US 1 (SR 5 / Ridgewood Avenue) is the main local road through Ormond Beach, running north–south. It served as the main north–south highway in the state and the eastern half of the county until I-95 was built. The route enters the city from the south at the border with Holly Hill, Florida and leaves just north after the interchange with Interstate 95.
US 1 (SR 5 / Ridgewood Avenue) is the main local road through Ormond Beach, running north–south. It served as the main north–south highway in the state and the eastern half of the county until I-95 was built. The route enters the city from the south at the border with Holly Hill, Florida and leaves just north after the interchange with Interstate 95. SR A1A (North Atlantic Avenue) is the state prefixed and suffixed, scenic coastal alternate route to US 1, which also includes some county road spurs and extensions.
SR A1A (North Atlantic Avenue) is the state prefixed and suffixed, scenic coastal alternate route to US 1, which also includes some county road spurs and extensions.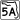 SR 5A (Nova Road) is the state suffixed alternate route of SR 5.
SR 5A (Nova Road) is the state suffixed alternate route of SR 5.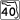 SR 40 (Granada Boulevard)
SR 40 (Granada Boulevard)
Railroad
The main railroad line through Ormond Beach is the Florida East Coast Railway, which had a station within the city. Ormond Beach contained a connection to the former Ormond Hotel, which was accessed via the St. Johns and Halifax Railway. Passenger service ended in during the strike of 1963. Freight service continues to operate along the Florida East Coast Railway, but makes no stops within Ormond Beach.
Media
Newspapers
- Daytona Beach News-Journal, daily newspaper covering the greater Daytona Beach area
- Hometown News, community newspaper in print on Fridays and daily on the Internet
- The Ormond Beach Observer, a weekly newspaper published in print on Thursdays and daily online, part of the Observer Media Group
- Ormond Local Pulse, a daily newsletter published daily by email and on the internet Focusing on local news for Ormond Beach and Ormond-By-The-Sea
Radio stations
AM
- WELE, 1380 AM, Ormond Beach, News/Talk
FM
- WAVX-LP, 107.1 FM, Ormond Beach, Contemporary Christian
- WHOG-FM, 95.7 FM, Ormond Beach, Classic Rock
Economy
Business
Ormond Beach is an active commercial and residential market in the Deltona-Daytona Beach-Ormond Beach MSA. Manufacturers enjoy a healthy business climate and engage in global marketing.
Ormond Beach Business Park and Airpark, a foreign trade zone, is home to 29 companies that provide more than 2,000 jobs.
Recent studies show the workforce to be educated, productive, and competitive with 10 percent underemployed. Seven colleges and universities and the Advanced Technology Center support business needs with career advancement, workforce development, and research. Education, health care, and government are the largest employment sectors within the area.
Among the corporations that call Ormond Beach home are:
- Costa Del Mar Headquarters (eye care products)
- First Green Bank
- Florida Production Engineering (automotive)
- Hawaiian Tropic - Tanning Research Laboratories (skin care products)
- ABB Thomas & Betts/Homac (electrical connectors, utility products)
- Hudson Technologies (deep draw manufacturer)
- Microflex Inc.
- U.S. Food Service (distributor)
- Vital Aire (health care)
Shopping
- Historic Ormond Beach/Granada Blvd.
- Ormond Mall
- Ormond Town Square
- River Gate Shopping Center
- South Forty Shopping Center
- The Trails Shopping Center
- Wal-Mart Super Center
- Tanger Outlets
- Granada Plaza
See also
 In Spanish: Ormond Beach para niños
In Spanish: Ormond Beach para niños






