Niagara County, New York facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Niagara County
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|

Niagara County Clerks Office
|
|||
|
|||
Location within the U.S. state of New York
|
|||
 New York's location within the U.S. |
|||
| Country | |||
| State | |||
| Founded | March 11, 1808 | ||
| Seat | Lockport | ||
| Largest city | Niagara Falls | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 1,140 sq mi (3,000 km2) | ||
| • Land | 522 sq mi (1,350 km2) | ||
| • Water | 617 sq mi (1,600 km2) 54% | ||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||
| • Total | 212,666 | ||
| • Density | 407.1/sq mi (157.2/km2) | ||
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) | ||
| Congressional districts | 24th, 26th | ||
Niagara County is in the U.S. state of New York. As of the 2020 census, the population was 212,666. The county seat is Lockport. The county name is from the Iroquois word Onguiaahra; meaning the strait or thunder of waters. The county is part of the Western New York region of the state.
Niagara County is part of the Buffalo–Niagara Falls metropolitan area, and across the Canada–US border is the province of Ontario.
It is the location of Niagara Falls and Fort Niagara, and has many parks and lake shore recreation communities. In the summer of 2008, Niagara County celebrated its 200th birthday with the first settlement of the county, of Niagara Falls.
Contents
History
When counties were established in the New York colony in 1683, the present Niagara County was part of Albany County. Prior to the British, the area was part of New Netherland.
Albany was an enormous county, including the northern part of New York State as well as all of the present State of Vermont and, in theory, extending westward to the Pacific Ocean. This county was reduced in size on July 3, 1766, by the creation of Cumberland County, and further on March 16, 1770, by the creation of Gloucester County, both containing territory now in Vermont.
On March 12, 1772, what was left of Albany County was split into three parts, one remaining under the name Albany County. One of the other pieces, Tryon County, contained the western portion (and thus, since no western boundary was specified, theoretically still extended west to the Pacific). The eastern boundary of Tryon County was approximately five miles west of the present city of Schenectady, and the county included the western part of the Adirondack Mountains and the area west of the West Branch of the Delaware River. The area then designated as Tryon County now includes 37 counties of New York State. The county was named for William Tryon, colonial governor of New York.
In the years prior to 1776, most of the Loyalists in Tryon County fled to Canada including the likes of local judge John Butler and militia commander Sir John Johnson. In 1784, following the peace treaty that ended the American Revolutionary War, the name of Tryon County was changed to honor the general, Richard Montgomery, who had captured several places in Canada and died attempting to capture the city of Quebec, replacing the name of the hated British governor.
In 1789, Ontario County was split off from Montgomery. In turn, Genesee County was created from Ontario County in 1802.
Niagara County was created from Genesee County in 1808. It was, however, larger than the present Niagara County even though it consisted of only the Town of Cambria.
From 1814 to 1817, records of Cattaraugus County were divided between Belmont (the seat of Allegany County) and Buffalo (then in Niagara County). Niagara County governed the western portion of Cattaraugus County, then known as the town of Perry.
In 1821, Erie County was created from Niagara County.
The county has a number of properties on the National Register of Historic Places.
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 1,139 square miles, of which 522 square miles (1,350 km2) is land and 617 square miles (1,600 km2) (54%) is water.
Niagara County is in the most western part of New York State, just north of the city Buffalo and1,140 square miles (3,000 km2) bordering Lake Ontario on its northern border, and the Niagara River Canada on its western border.
The county's primary geographic feature is Niagara Falls, the riverbed of which has eroded seven miles south over the past 12,000 years since the last ice age. The Niagara River and Niagara Falls, are in effect, the drainage ditch for four of the Great Lakes which constitute the world's largest supply of fresh water. The water flows north from Lake Erie, then through the Niagara River, goes over Niagara Falls, and then on to Lake Ontario and the St. Lawrence River, eventually emptying into the North Atlantic Ocean. Today, tourists and visitors to the Falls see a diminished flow of water over the Falls, since a portion of the flow has been diverted for hydroelectric power purposes. Both the American and Canadian side of the Niagara River have massive electrical power plants.
The Niagara Gorge is the path Niagara Falls has taken over thousands of years as it continues to erode. Niagara Falls started at the Niagara Escarpment which cuts Niagara County in half in an east–west direction. North of the Escarpment lies the Lake Plain, which is a fertile flatland used to grow grapes, apples, peaches and other fruits and vegetables. The grape variety Niagara, source of most American white grape juice but not esteemed for wine, was first grown in the county, in 1868. Viticulture, or wine culture has begun to take place, with several wineries below the escarpment. This has helped to improve the depressed economy of the region.
Adjacent counties and areas
- Orleans County - east
- Genesee County - southeast
- Erie County - south
- Regional Municipality of Niagara, Ontario, Canada - west
Major highways
State protected areas
- De Veaux Woods State Park, north of the City of Niagara Falls.
- Devil's Hole State Park, immediately north of the City of Niagara Falls.
- Fort Niagara State Park, located at the mouth of the Niagara River.
- Earl W. Brydges Artpark State Park, in the Town of Lewiston.
- Four Mile Creek State Park, on the shore of Lake Ontario.
- Golden Hill State Park, on the shore of Lake Ontario.
- Hartland Swamp Wildlife Management Area—a conservation area in the Town of Hartland.
- Joseph Davis State Park, along the Niagara River.
- Niagara Reservation State Park, in the City of Niagara Falls.
- Reservoir State Park, south of the power reservoir.
- Tonawanda Wildlife Management Area, partly in the Town of Royalton.
- Wilson-Tuscarora State Park, on the shore of Lake Ontario.
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1810 | 8,971 | — | |
| 1820 | 22,990 | 156.3% | |
| 1830 | 18,482 | −19.6% | |
| 1840 | 31,132 | 68.4% | |
| 1850 | 42,276 | 35.8% | |
| 1860 | 50,399 | 19.2% | |
| 1870 | 50,437 | 0.1% | |
| 1880 | 54,173 | 7.4% | |
| 1890 | 62,491 | 15.4% | |
| 1900 | 74,961 | 20.0% | |
| 1910 | 92,036 | 22.8% | |
| 1920 | 118,705 | 29.0% | |
| 1930 | 149,329 | 25.8% | |
| 1940 | 160,110 | 7.2% | |
| 1950 | 189,992 | 18.7% | |
| 1960 | 242,269 | 27.5% | |
| 1970 | 235,720 | −2.7% | |
| 1980 | 227,354 | −3.5% | |
| 1990 | 220,756 | −2.9% | |
| 2000 | 219,846 | −0.4% | |
| 2010 | 216,469 | −1.5% | |
| 2020 | 212,666 | −1.8% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 1790-1960 1900-1990 1990-2000 2010-2019 |
|||
As of the census of 2010, there were 216,469 people, 87,846 households, and 58,593 families residing in the county. The population density was 420 inhabitants per square mile (160/km2). There were 95,715 housing units at an average density of 183 units per square mile (71/km2). The racial makeup of the county was 90.70% White, 6.15% Black or African American, 0.94% Native American, 0.58% Asian, 0.02% Pacific Islander, 0.40% from other races, and 1.21% from two or more races. 1.33% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race. 23.6% were of German, 18.1% Italian, 11.3% Irish, 11.2% Polish and 8.3% English ancestry. 94.5% spoke English, 1.6% Spanish and 1.0% Italian as their first language.
There were 87,846 households, out of which 30.90% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 50.30% were married couples living together, 12.30% had a female householder with no husband present, and 33.30% were non-families. 28.60% of all households were made up of individuals, and 12.00% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.45 and the average family size was 3.03.
In the county, the population was spread out, with 24.70% under the age of 18, 8.50% from 18 to 24, 28.40% from 25 to 44, 23.10% from 45 to 64, and 15.40% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 38 years. For every 100 females there were 93.30 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 89.50 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $38,136, and the median income for a family was $47,817. Males had a median income of $37,468 versus $24,668 for females. The per capita income for the county was $19,219. About 8.20% of families and 10.60% of the population were below the poverty line, including 15.00% of those under age 18 and 7.30% of those age 65 or over.
2020 Census
| Race | Num. | Perc. |
|---|---|---|
| White (NH) | 173,691 | 82.0% |
| Black or African American (NH) | 16,206 | 7.62% |
| Native American (NH) | 2,294 | 1.1% |
| Asian (NH) | 2,439 | 1.2% |
| Pacific Islander (NH) | 45 | 0.02% |
| Other/Mixed (NH) | 10,173 | 5.0% |
| Hispanic or Latino | 7,818 | 4.0% |
Education
Niagara University is located in Lewiston, New York. Niagara County Community College is located in Sanborn, New York. Many Niagara County residents also attend Erie and other Western New York County Schools. In the Buffalo Metro area there are more than 20 public and private colleges and universities offering programs in technical and vocational training, graduate, and professional studies.
K-12 school districts
School districts include:
- Barker Central School District
- Lewiston-Porter Central School District
- Lockport City School District
- Newfane Central School District
- Niagara Falls City School District
- Niagara-Wheatfield Central School District
- North Tonawanda City School District
- Royalton-Hartland Central School District
- Starpoint Central School District
- Wilson Central School District
Communities
Larger settlements
| # | Location | Population | Type | Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Niagara Falls | 50,193 | City | Greater Niagara |
| 2 | North Tonawanda | 31,568 | City | Greater Niagara |
| 3 | Lockport | 21,165 | City | Southeast |
| 4 | South Lockport | 8,234 | CDP | Southeast |
| 5 | Newfane | 3,822 | CDP | Lake Shore |
| 6 | Lewiston | 2,701 | Village | Greater Niagara |
| 7 | Youngstown | 1,935 | Village | Greater Niagara |
| 8 | Middleport | 1,840 | Village | Southeast |
| 9 | Sanborn | 1,645 | CDP | Greater Niagara |
| 10 | Rapids | 1,636 | CDP | Southeast |
| 11 | Ransomville | 1,419 | CDP | Lake Shore |
| 12 | Wilson | 1,264 | Village | Lake Shore |
| 13 | Gasport | 1,248 | CDP/Hamlet | Southeast |
| 14 | Olcott | 1,241 | CDP | Lake Shore |
| 15 | Barker | 533 | Village | Lake Shore |
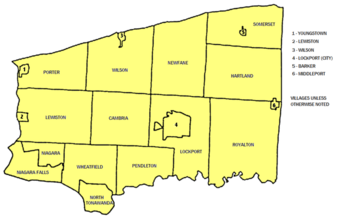
Towns
Hamlets
- Nashville
- Orangeport
- Pekin
CDPs
- Newfane
- Niagara University
- Olcott
- Ransomville
- Rapids
- Sanborn
- South Lockport
Indian reservations
See also
 In Spanish: Condado de Niágara para niños
In Spanish: Condado de Niágara para niños