- This page was last modified on 16 October 2023, at 16:53. Suggest an edit.
Na+/K+-ATPase facts for kids
Na+/K+-ATPase is an enzyme found in the plasma membrane. It is sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphatase, also known as the 'Na+/K+ pump', 'sodium-potassium pump', or simply 'sodium pump', for short. It was first discovered by Jens Christian Skou who won a Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1997.
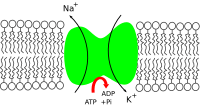
The enzyme moves Na+ (sodium) ions out of the cell and replaces them with K+ (potassium) ions. This keeps the Na+ ions outside of the cell membrane, and keeps the K+ ions on the inside of the cell membrane. The process works in the opposite direction of diffusion.
For every three sodium ions that get pumped out of the cell, two potassium ions get pumped into the cell. One phosphate group is still bound to the pump.
Images for kids
-
The Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase, as well as effects of diffusion of the involved ions maintain the resting potential across the membranes.
-
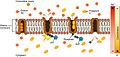
The sodium–potassium pump is found in many cell (plasma) membranes. Powered by ATP, the pump moves sodium and potassium ions in opposite directions, each against its concentration gradient. In a single cycle of the pump, three sodium ions are extruded from and two potassium ions are imported into the cell.
See also
 In Spanish: Bomba sodio-potasio para niños
In Spanish: Bomba sodio-potasio para niños