Lysozyme facts for kids
A lysozyme is a part of the innate immune system. They are enzymes which are in mucus secretions like saliva. They protect against infection by chopping up the bacteria, viruses and fungi which infect animals.
The name 'lysozyme' was coined in 1922 by Alexander Fleming (1881–1955), the discoverer of penicillin. Fleming first observed the antibacterial action of lysozyme when he treated bacterial cultures with nasal mucus from a patient suffering from a common cold.
Lysozyme is in a number of secretions, such as tears, saliva, milk, and mucus. It is also present in cytoplasmic granules of macrophages and granulocyte neutrophils.
The enzyme works by attacking polymers in the cell walls of bacteria, especially Gram-positive bacteria like Bacillus and Streptococcus.
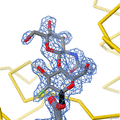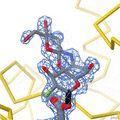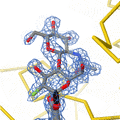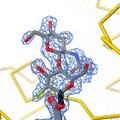
Lysozyme was the second protein structure, and the first enzyme structure, solved by X-ray diffraction methods. It was the first enzyme to be fully sequenced that contains all twenty common amino acids. It was also the first enzyme to have a detailed, specific mechanism suggested for its action. This work led to an explanation of how enzymes speed up a chemical reaction by their physical structures.
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Lisozima para niños
In Spanish: Lisozima para niños