Luftwaffe facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Luftwaffe |
|
|---|---|

Emblem of the Luftwaffe (variant)
|
|
| Active | 1933–1946 |
| Country | |
| Allegiance | |
| Type | Air force |
| Role | Aerial warfare |
| Size | Aircraft 119,871 (total production) Personnel 3,400,000 (total in service at any time for 1939–45) |
| Part of | Wehrmacht |
| Engagements | Spanish Civil War World War II |
| Insignia | |
| Balkenkreuz (fuselage and wing undersurfaces) | 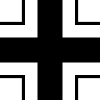 |
| Balkenkreuz (upper wing surfaces) | 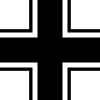 |
| Swastika (fin flash 1939–1945, white border omitted during late war) |  |
The Luftwaffe is the name for the air force of Germany.
Contents
History
This was the name for the air force of Germany during the Third Reich when Adolf Hitler was in power (between 1933 and 1945) and was also the name for the air force during the era of the Cold War when Germany was divided into two: East Germany and West Germany. This meant that the Luftwaffe was the air force of West Germany between 1955 and 1990. In 1990, these two countries became one country again, so the Luftwaffe has been the air force of the united (together) Germany since 1990. Luftwaffe means Air force in English.
The early years including World War I

Germany first had aeroplanes in its army in 1910, four years before the start of World War I in 1914. At that time, aeroplanes had no guns. They were being used for reconnaissance duties, that is, they would fly over the battlefield to see what the enemy was doing and fly back so that the pilots could tell their generals what they knew. The generals used that information to plan the fighting. Before aeroplanes, balloons had been used.
During World War I, Germany used a few kinds of aeroplane to fight its war, such as fighters, bombers and reconnaissance aeroplanes, but the fighter aeroplanes became very famous because of its brave pilots. The most famous German pilot of World War I was Manfred von Richthofen, also known as "The Red Baron."
Germany also used airships called "Zeppelins". They were named after Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin, who had built the first airships in 1900, but he had wanted them to carry cargo and passengers, not bombs. He died in 1917, but people still use his name when they remember the German airships of World War I. (In fact, the Zeppelin company is still making airships today, but these are much smaller now.)
After the war
In November 1918, the "Allies", or the Allied forces (which included Britain and France) won the war, and Germany had to sign the Treaty of Versailles. It was told that it could not have any military aeroplanes at all because it was blamed for starting the war in 1914. Germany therefore had to destroy all its military aeroplanes as a punishment, so until 1933 it had no air force at all.
Between the two world wars
For many years, Germany pretended to have no army pilots because the German army generals did not like the idea of not having any aeroplanes. At first, pilots would pretend to be training to become airline pilots but this was not much use because they really needed to fly fighters and bombers. The Treaty of Versailles did not allow Germany to have them, so Germany had to ask for help from Russia, its former (and future) enemy.
In 1924, German army pilots started to fly Russian fighters and bombers at a secret training school near the Russian city of Lipetsk. These pilots would then become the first ones to fly for the new German air force, the Luftwaffe, when Hitler said that it now existed. The training school closed in 1933.
In 1935, Adolf Hitler finally told the world that Germany had a new air force, even if the Treaty of Versailles forbade Germany from having one. Hitler was defying the Allies, who had won World War I, but they did not do anything about this, because many people still remembered the war in 1914-1918. They were frightened by the idea of war and did not want another one.
The Spanish Civil War of 1936-1939 gave the Germans the opportunity to test its new aircraft, pilots and weapons in battle. Hitler sent many aeroplanes and pilots over to Spain because he wanted to support Francisco Franco, who wanted to get rid of the Spanish government. Amongst the aeroplanes were fighters called the Messerschmitt Bf 109 and dive-bombers called the Junkers Ju 87 ‘Stuka”.
Aftermath of the German airforce
The world now remembers one mission that the German air force carried out during the war. German bombers attacked the city of Guernica in the Basque region of northeast Spain, and many civilians (people who were not soldiers) died in the attack. Many governments and people around the world were horrified by the attack. The artist Pablo Picasso painted a painting called Guernica that has become very famous. People see the painting as a symbol of the horror of war. A copy of the painting hangs in the United Nations building in New York City.
World War II
The new airforce in action

The German air force was the strongest in the world when World War II broke out in September 1939. It supported the army on the ground and the aircraft were very effective at defeating all opposition, since the German armed forces, the Wehrmacht, had practised a very new and very fast way to defeat their enemies. This was called Blitzkrieg or Lightning War. The French and the British were prepared for a trench war. It was impossible to fight back.
Results
Within a year, Germany had conquered Poland, Denmark, Norway, Luxembourg, Belgium, and France. Britain supported the countries attacked by Germany but found herself on her own by June 1940 when Germany had conquered most of western Europe.

Problems
As the war went on, things began to go badly wrong for the Luftwaffe. The leadership of the Luftwaffe began to become quite bad, as generals were arguing about what the air force should be doing and blaming each other when the Luftwaffe was unable to stop the British from attacking German aircraft factories and other industrial targets in large numbers during the night. The RAF had lost many planes when attacking by day.
Not only that, but Germany was suffering a shortage of materials needed to build the aeroplanes. Things got worse for the Germans when the USA joined the war in December 1941, because the Americans brought thousands of bombers to the United Kingdom, and they attacked Germany from there. Soon, hundreds of American and British bombers were attacking Germany every day and night.
Ground fighting
Germany could not hope to win the war on the ground. Since Russia was so huge, the government set up factories hundreds of miles away from the fighting in order to build aeroplanes, tanks, guns and other weapons for the Russian Army. This meant that the Russians would eventually start to push the Germans back west, especially after they defeated the Germans in great battles near the city of Kursk and in the city of Stalingrad itself. The Germans had failed to conquer the city of Leningrad, too.
On January 1 1945 the Luftwaffe launched a desperate plan called operation 'Bodenplatte' (Baseplate), a dawn air attack aimed at multiple Allied air bases in Belgium & Holland. Over 800 German aircraft were rounded up with many veteran pilots retired from combat duty pressesd back into service.
The plan cost more than it was worth, with over 280 German planes lost and 213 irreplaceble pilots killed or captured. As with the fog of war, over 100 German planes were shot down by their own ground fire who were not in on the plan.
Trivia
Germany became famous as the country, which flew the first jet aeroplanes. In 1944, the Luftwaffe started to use the world’s first jet fighter plane, the Messerschmitt Me-262, even if the engines sometimes did not work properly. Once again, the shortage of the materials needed to build the plane as well as the continuing bombing of Germany meant that not as many Me-262s were built as Germany would have liked. Even so, Germany also built and flew the world's first jet bomber, the Arado Ar 234, the world’s first fighter plane powered by a rocket, the Messerschmitt Me-163, the world’s first "cruise missile", the V-1, and the world’s first ballistic missile, the V-2.
After the war the allies were quite impressed with Germany's technical know how & gleaned all they could from the vast array of Luftwaffe aircraft strewn across Germany.
The Cold War and afterwards
Once again, the Allies prohibited Germany from having an air force. The Russians were in the eastern half of Germany, and this half became East Germany. The British, French and Americans were in the western half, and this half became West Germany. These became countries in their own right, and East Germany became a Russian puppet state. In case a new war started with Russia and East Germany as enemies, the Western Allies finally allowed West Germany to join the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO), an organization of western countries which wanted there to be peace throughout the world. NATO allowed West Germany to have an air force because the country was right next to East Germany.
First use
Germany used military aircraft in war for the first time since 1945 when they supported British aircraft in the war in Kosovo in 1999, but many people still believed that Germany should never again go to war because of what had happened in the two world wars.
Images for kids
-
Junkers Ju 87 Ds over the Eastern Front, winter 1943–44
-
Defendants in the dock during the Nuremberg trials. The main target of the prosecution was Hermann Göring (at the left edge on the first row of benches), considered to be the most important surviving Nazi official after Hitler's death.
-
Ruins of Guernica, 1937
See also
 In Spanish: Luftwaffe (Wehrmacht) para niños
In Spanish: Luftwaffe (Wehrmacht) para niños














