List of extreme points of Canada facts for kids
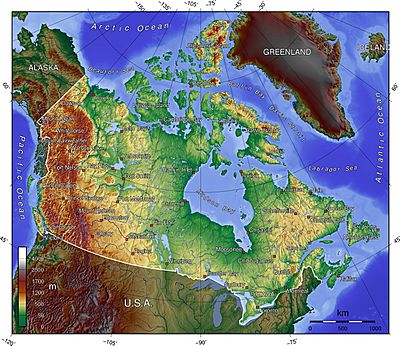
The following lists include extreme and significant points of the geography of Canada.
Contents
All Canada
- Northernmost point — Cape Columbia, Ellesmere Island, Nunavut 83°6′41″N 69°57′30″W / 83.11139°N 69.95833°W
- Southernmost point — South point of Middle Island, Ontario, in Lake Erie 41°40′53″N 82°40′56″W / 41.68139°N 82.68222°W
- Easternmost point — Cape Spear, Newfoundland 47°31′25″N 52°37′10″W / 47.52361°N 52.61944°W
- Westernmost point — Boundary Peak 187, Yukon 60°18′23″N 141°0′7″W / 60.30639°N 141.00194°W
Non-insular (mainland) Canada
- Northernmost point — Zenith Point, Nunavut 72°0′0″N 94°38′59″W / 72.00000°N 94.64972°W
- Southernmost point — Point Pelee, Ontario 41°54′33″N 82°30′32″W / 41.90917°N 82.50889°W
- Easternmost point — Cape Saint Charles, Labrador 52°13′3″N 55°37′15″W / 52.21750°N 55.62083°W
- Westernmost point — Boundary Peak 187, Yukon 60°18′23″N 141°0′7″W / 60.30639°N 141.00194°W
Highest points
- Mount Logan Yukon 60°34′33″N 140°24′10″W / 60.57583°N 140.40278°W — highest Canadian summit at 5,959 m (19,551 ft)
- Barbeau Peak, Ellesmere Island, Nunavut 81°54′30″N 75°1′30″W / 81.90833°N 75.02500°W — highest Canadian island summit and highest summit of the Canadian Arctic at 2,616 m (8,583 ft)
Lowest points
- Coastline — lowest Canadian surface point at sea level
- Great Slave Lake bottom, Northwest Territories 61°40′N 114°00′W / 61.667°N 114.000°W — lowest fresh water point of North America at −458 m (−1,503 feet)
Islands
- Baffin Island, Nunavut 63°33′N 65°26′W / 63.550°N 65.433°W — most extensive Canadian island at 507,451 km2 (195,928 square miles)
- Ellesmere Island, Nunavut 81°55′36″N 74°59′12″W / 81.92667°N 74.98667°W — tallest Canadian island at 2,616 m (8,583 ft)
- Island of Newfoundland, Newfoundland and Labrador 49°N 56°W / 49°N 56°W — most extensive Canadian Atlantic island at 108,860 km2 (42,031 square miles)
- Vancouver Island, British Columbia 49°30′N 125°30′W / 49.500°N 125.500°W — most extensive Canadian Pacific island at 31,285 km2 (12,079 square miles)
- Manitoulin Island in Lake Huron, Ontario 45°46′N 82°12′W / 45.767°N 82.200°W — most extensive lake island on Earth at 2,766 km2 (1,068 square miles)
Lakes
- Lake Superior, Ontario 47°45′N 87°30′W / 47.750°N 87.500°W — most voluminous lake of Western Hemisphere at 11,600 km3 (2,800 cubic miles)
- Great Slave Lake, Northwest Territories 61°40′N 114°00′W / 61.667°N 114.000°W — deepest lake of Western Hemisphere at 614 m (2,014 ft)
- Lake Michigan–Huron, Ontario 45°49′N 84°45′W / 45.817°N 84.750°W — by some considerations the most extensive lake of Western Hemisphere and the most extensive freshwater lake on Earth at 117,400 km2 (45,300 sq mi)
- Nettilling Lake on Baffin Island, Nunavut 66°30′N 70°50′W / 66.500°N 70.833°W — most extensive lake on an island on Earth at 5,066 km2 (1,956 square miles)
- Lake Manitou on Manitoulin Island in Lake Huron, Ontario 45°46′42″N 81°59′30″W / 45.77833°N 81.99167°W — most extensive lake on an island in a lake on Earth at 104 km2 (40 square miles)
- Upper Dumbell Lake on Ellesmere Island Nunavut 82°28′N 062°30′W / 82.467°N 62.500°W — most northern lake, there are more northern lakes but they are all unnamed and are only shown on detailed maps.
Rivers
- Yukon River, British Columbia, Yukon, and Alaska 62°35′55″N 164°47′40″W / 62.59861°N 164.79444°W — longest Bering Sea main stem river at 3,185 km (1,979 miles)
- Nelson River, Manitoba 57°5′5″N 92°30′8″W / 57.08472°N 92.50222°W — longest Hudson Bay main stem river at 2,575 km (1,600 miles)
- Columbia River, British Columbia 46°14′39″N 124°3′29″W / 46.24417°N 124.05806°W — longest Canadian Pacific Ocean main stem river at 2,000 km (1,243 miles)
- Mackenzie River, Northwest Territories 68°56′23″N 136°10′22″W / 68.93972°N 136.17278°W — longest Canadian Arctic Ocean main stem river at 1,738 km (1,080 miles)
- Saint Lawrence River, Ontario and Quebec 49°40′N 64°30′W / 49.667°N 64.500°W — longest Canadian Atlantic Ocean main stem river at 965 km (600 miles)
Extreme distances
- Greatest driving distance between any two points via the Canadian road network (including the Trans-Canada Highway Ferry): 9262 km from L'Anse Aux Meadows, Newfoundland and Labrador to Tuktoyatuk, Northwest Territories.
- Greatest driving distance between any two points via the Canadian road network (excluding the Trans-Canada Highway Ferry): 9156 km from Old Fort, Quebec to Tuktoyatuk, Northwest Territories.
See also
- Geography of Canada
- Extreme points of North America
- Extreme points of Canadian provinces
- Extreme communities of Canada
- Nordicity
- Remote and isolated community

All content from Kiddle encyclopedia articles (including the article images and facts) can be freely used under Attribution-ShareAlike license, unless stated otherwise. Cite this article:
List of extreme points of Canada Facts for Kids. Kiddle Encyclopedia.