Liquid crystal facts for kids
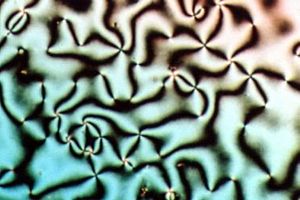
Liquid crystals are special substances that are usually liquid, but that show certain properties of a solid crystal. A liquid crystal (LC) may flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be rotated in a crystal-like way. There are many different types of liquid crystal phases. Different phases are different because their optical properties are different. Using a microscope and a polarized light source, different liquid crystal phases will have different textures. This is also shown in the image.
The contrasting areas in the texture each correspond to a domain where the LC molecules are rotated in a different direction. Within a domain, however, the molecules are well ordered. LC materials may not always be in an LC phase (just as water is not always in the liquid phase: it may also be found in the solid and gaseous phase).
Applications of liquid crystals
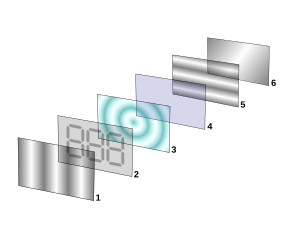
Liquid crystals find wide use in liquid crystal displays, which rely on the optical properties of certain liquid crystalline substances in the presence or absence of an electric field. In a typical device, a liquid crystal layer (typically 4 μm thick) sits between two polarizers that are crossed (oriented at 90° to one another). The liquid crystal alignment is chosen so that its relaxed phase is a twisted one (see Twisted nematic field effect). This twisted phase reorients light that has passed through the first polarizer, allowing its transmission through the second polarizer (and reflected back to the observer if a reflector is provided). The device thus appears transparent. When an electric field is applied to the LC layer, the long molecular axes tend to align parallel to the electric field thus gradually untwisting in the center of the liquid crystal layer. In this state, the LC molecules do not reorient light, so the light polarized at the first polarizer is absorbed at the second polarizer, and the device loses transparency with increasing voltage. In this way, the electric field can be used to make a pixel switch between transparent or opaque on command. Color LCD systems use the same technique, with color filters used to generate red, green, and blue pixels. Chiral smectic liquid crystals are used in ferroelectric LCDs which are fast-switching binary light modulators. Similar principles can be used to make other liquid crystal based optical devices.
Liquid crystal tunable filters are used as electrooptical devices, e.g., in hyperspectral imaging.
Thermotropic chiral LCs whose pitch varies strongly with temperature can be used as crude liquid crystal thermometers, since the color of the material will change as the pitch is changed. Liquid crystal color transitions are used on many aquarium and pool thermometers as well as on thermometers for infants or baths. Other liquid crystal materials change color when stretched or stressed. Thus, liquid crystal sheets are often used in industry to look for hot spots, map heat flow, measure stress distribution patterns, and so on. Liquid crystal in fluid form is used to detect electrically generated hot spots for failure analysis in the semiconductor industry.
Liquid crystal lenses converge or diverge the incident light by adjusting the refractive index of liquid crystal layer with applied voltage or temperature. Generally, the liquid crystal lenses generate a parabolic refractive index distribution by arranging molecular orientations. Therefore, a plane wave is reshaped into a parabolic wavefront by a liquid crystal lens. The focal length of liquid crystal lenses could be continuously tunable when the external electric field can be properly tuned. Liquid crystal lenses are a kind of adaptive optics. Imaging system can be benefited with focusing correction, image plane adjustment, or changing the range of depth-of-field or depth of focus. Liquid crystal lens is one of the candidates to develop vision correction device for myopia and presbyopia eyes (e.g., tunable eyeglass and smart contact lenses).
Liquid crystal lasers use a liquid crystal in the lasing medium as a distributed feedback mechanism instead of external mirrors. Emission at a photonic bandgap created by the periodic dielectric structure of the liquid crystal gives a low-threshold high-output device with stable monochromatic emission.
Polymer dispersed liquid crystal (PDLC) sheets and rolls are available as adhesive backed Smart film which can be applied to windows and electrically switched between transparent and opaque to provide privacy.
Many common fluids, such as soapy water, are in fact liquid crystals. Soap forms a variety of LC phases depending on its concentration in water.
Images for kids
-
Phase transition between a nematic (left) and smectic A (right) phases observed between crossed polarizers. The black color corresponds to isotropic medium.
-
A planar cell, filled with achiral LC host doped with an optically active Tröger base analog, placed between a pair of parallel (A) and crossed (B) linear polarizers. This doped mesogenic phase forms self-organized helical superstructures, that allow specific wavelengths of light pass through the crossed polarizers, and selectively reflects a particular wavelength of light.
See also
 In Spanish: Cristal líquido para niños
In Spanish: Cristal líquido para niños