Khadija bint Khuwaylid facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Khadijah bint Khuwaylid
Mother of the Believers |
|
|---|---|
| خَدِيجَة بِنْت خُوَيْلِد | |
| Born | c. 555 or 567 |
| Died | 10 Ramadan BH 3 c. 619 (aged 63–64) Mecca, Hejaz
|
| Resting place | Jannat al-Mu'alla, Mecca |
| Other names | Khadīja al-Kubra |
| Known for | First wife of Muhammad |
| Title |
|
| Spouse(s) |
|
| Children | Sons:
Daughters:
|
| Parents |
|
| Relatives | Grandsons:
Granddaughters:
Cousin:
|
| Family | Banu Asad (by birth) Ahl al-Bayt (by marriage) |
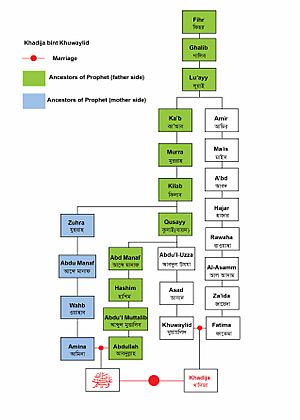
Khadijah bint Khuwaylid (Arabic: خَدِيجَة بِنْت خُوَيْلِد, romanized: Khadīja bint Khuwaylid, c. 555 – November 619 CE) was the first wife and the first follower of Muhammad. Khadija was the daughter of Khuwaylid ibn Asad, a leader of the Quraysh tribe in Makkah and a successful businesswoman.
Khadija is often referred to by Muslims as "The Mother of Believers". In Islam, she is an important female figure as one of the four 'ladies of heaven', alongside Asiya, Maryam, and her daughter Fatimah. Muhammad was monogamously married to her for 25 years.
Contents
Family
Khadija's mother, Fatima bint Za'idah, who died in 575, was a member of the Amir ibn Luayy clan of the Quraysh and a third cousin of Muhammad's mother.
Khadija's father, Khuwaylid ibn Asad, was a merchant and leader. According to some accounts, he died c. 585 in the Sacrilegious War, but according to others, he was still alive when Khadija married Muhammad in 595. Khuwaylid also had a sister named Ume Habib binte Asad.
Profession
Khadija was a very successful merchant. It is said that when the Quraysh's trade caravan travellers gathered to embark upon their summer journey to Syria or winter journey to Yemen, Khadija's caravan equaled the caravans of all other traders of the Quraysh put together. Khadija was given many honorifics, including 'The Pious One', 'Princess of Quraysh' (Ameerat-Quraysh), and 'Khadija the Great' (Khadija al-Kubra). It is said that she fed and clothed the poor, assisted her relatives financially, and provided marriage portions for poor relations. Khadija was said to have neither believed in nor worshipped idols, which was atypical for pre-Islamic Arabian culture.
Khadija did not travel with her trade caravans; instead, she employed others to trade on her behalf for a commission. In 595 Khadija needed a co-worker for a transaction in Syria. She hired Muhammad ibn Abdullah, then 25 years old, for the trade in Syria, sending word that she would pay to double her usual commission. With the permission of Abu Talib ibn Muttalib, his uncle, Muhammad was sent to Syria with one of Khadija's servants. This caravan experience earned Muhammad the honorifics of al-Sadiq ('the Truthful') and I'll-Amin ('the Trustworthy' or 'the Honest').
She sent one of her servants, Maysarah, to assist him. Upon returning, Maysarah gave accounts of the honourable way in which Muhammad had conducted his business, bringing back twice as much profit as Khadija had expected.
Differing views on previous marriages
Sunni version
Khadija married three times and had children from all her marriages. While the order of her marriages is debated, it is generally believed that she first married Atiq ibn 'A'idh ibn' Abdullah Al-Makhzumi, followed by Malik ibn Nabash ibn Zargari ibn at-Tamimi. To Atiq, Khadija bore a daughter named Hindah. This marriage left Khadija a widow. With Malik, she had two daughters, who were named Hala and Hind. Malik also left Khadija a widow, dying before his business became a success. Khadija, subsequently proposed to Muhammad.
Shia version
Ibn Shahrashub quoted from al-Sayyid al-Murtada in al-Shafi and al-Shaykh al-Tusi in al-Talkhis, that Khadija was a virgin when she married Muhammad. Considering the cultural and intellectual situation in Hijaz, and the high position and status Khadija al-Kubra enjoyed, among other people, it is improbable that she would have married men from Banu Tamim or Banu Makhzum (the two 'low' tribes). Some believe the two children attributed to Khadija were the children of Hala, Khadija's sister. After the death of Hala's husband, Khadija took care of Hala and (after Hala's own death) Hala's children.
Marriage to Muhammad
Khadija entrusted a friend named Nafisa to approach Muhammad and ask if he would consider marriage. When Muhammad hesitated because he had no money to support a wife, Nafisa asked if he would consider marriage to a woman who had the means to provide for herself. Muhammad agreed to meet with Khadija, and after this meeting they consulted their respective uncles. The uncles agreed to the marriage, and Muhammad's uncles accompanied him to make a formal proposal to Khadija. It is disputed whether it was Hamza ibn Abdul-Muttalib, Abu Talib, or both who accompanied Muhammad on this errand. Khadija's uncle accepted the proposal, and the marriage took place. At the time of the marriage Muhammad was around 23 to 25 years old. Khadija was 40 years old at that time according to some sources. However, other sources claim that she was aged approximately 28 or 30 during the marriage.
Children
Muhammad and Khadija may have had six or eight children. (Sources disagree about number of children: Al-Tabari names eight; the earliest biography of Muhammad by Ibn Ishaq, names seven children; most sources only identify six).
Their first son was Qasim, who died after his third birthday (hence Muhammad's kunya Abu Qasim). Khadija then gave birth to their daughters Zaynab, Ruqayyah, Kulthum and Fatima; and lastly to their son Abd Allah. Abd Allah was known as at-Tayyib ('the Good') and at-Tahir ('the Pure'). Abd-Allah also died in childhood.
Two other children also lived in Khadija's household: Ali ibn Abi Talib, the son of Muhammad's uncle; and Zayd ibn Harithah, a boy from the Udhra tribe who had been kidnapped and sold into slavery. Zayd was a slave in Khadija's household for several years, until his father came to Mecca to take him home. Muhammad insisted that Zayd be given a choice about where he lived, and Zayd decided to remain where he was, after which Muhammad legally adopted Zayd as his own son.
Becoming the first follower of Muhammad
According to the traditional Sunni narrative, when Muhammad reported his first revelation from the Angel Gabriel (Jibril), Khadija was the first person to accept Al-Haqq The Truth i.e. she accepted Islam. After his experience in the cave of Hira, Muhammad returned home to Khadija in a state of terror, pleading for her to cover him with a blanket. After calming down, he described the encounter to Khadija, who comforted him with the words that Allah would surely protect him from any danger, and would never allow anyone to revile him as he was a man of peace and reconciliation and always extended the hand of friendship to all. According to some sources, it was Khadija's cousin, Waraqah ibn Nawfal, who confirmed Muhammad's prophethood soon afterwards.
Yahya ibn `Afeef is quoted saying that he once came, during the period of Jahiliyyah (before the advent of Islam), to Mecca to be hosted by 'Abbas ibn 'Abd al-Muttalib, one of Muhammad's uncles mentioned above. 'When the sun started rising', he said, 'I saw a man who came out of a place not far from us, faced the Kaaba and started performing his prayers. He hardly started before being joined by a young boy who stood on his right side, then by a woman who stood behind them. When he bowed down, the young boy and the woman bowed, and when he stood up straight, they, too, did likewise. When he prostrated, they, too, prostrated.' He expressed his amazement at that, saying to Abbas: 'This is quite strange, O Abbas!' 'Is it, really?' responded al-Abbas. 'Do you know who he is?' Abbas asked his guest, who answered in the negative. 'He is Muhammad ibn Abdullah, my nephew. Do you know who the young boy is?' he asked again. 'No, indeed', answered the guest. 'He is Ali son of Abu Talib. Do you know who the woman is?' The answer came again in the negative, to which Abbas said, 'She is Khadija bint Khuwaylid, my nephew's wife.' This incident is included in the books of both Ahmad ibn Hanbal and Al-Tirmidhi, each detailing it in his own Ṣaḥīḥ.
Khadija was supportive of Muhammad's prophetic mission, always helping in his work, proclaiming his message and belittling any opposition to his prophecies. It was her encouragement that helped Muhammad believe in his mission and spread Islam. Khadija also invested her wealth in the mission. When the polytheists and aristocrats of the Quraysh harassed the Muslims, she used her money to ransom Muslim slaves and feed the Muslim community.
In 616, the Quraysh declared a trade boycott against the Hashim clan. They attacked, imprisoned and beat the Muslims, who sometimes went for days without food or drink. Khadija continued to maintain the community until the boycott was lifted in late 619 or early 620.
Death

Khadija died in 'Ramadan of the year 10 after the Prophethood', i.e., in November 619 CE. Muhammad later called this tenth year the 'Year of Sorrow', as his uncle and protector Abu Talib also died at this time. Khadija is said to have been about 65 years old at the time of her death. She was buried in Jannat al-Mu'alla cemetery, in Mecca, Saudi Arabia.
Another report from Muhammad bin Ishaq says that 'Abu Talib and Khadija bint Khuwaylid died in the same year. This was three years before the emigration of the Messenger of Allah (Muhammad) to Medina. Khadija was buried in al-Hajun. The Messenger of Allah buried her in her grave. She was 40 years old when the Messenger of Allah married her.'
In the years immediately following Khadija's death, Muhammad faced persecution from opponents of his message and also from some who originally followed him but had now turned back. Hostile tribes ridiculed him. Muhammad migrated to Yathrib (Medina) after Khadija's death.
Children and relatives
Sons
- Qasim ibn Muhammad, died in 601, after his third birthday.
- Abd-Allah ibn Muhammad, died in childhood in 615
Daughters
- Fatimah (605–632), although it is sometimes asserted that she was born during the first year of Muhammad's mission (610–611). She had the by-name 'The mother of her father', as she took over, caring for her father and being a support to her father once her mother died. She married Ali, who became the fourth caliph in 656. (According to early debate after the death of Muhammad, some would argue that Ali would be the proper succession to Muhammad.) Ali and Fatimah moved to a small village in Ghoba after the marriage, but later moved back to Medina to live next door to Muhammad. Muhammad forbade Ali to take additional wives, because 'What caused pain to his daughter grieved him as well.' Fatima died six months after her father died. All of Muhammad's surviving descendants are by Fatima's children. Muhammad loved her two sons Hassan and Husayn, who would continue his heritage.
- Zaynab (599–629). She married her maternal cousin Abu al-As before al-Hijra. Later lived with Muhammad. Her husband accepted Islam before her death in 629
- Ruqayyah (601–624). She was first married to Utbah ibn Abi Lahab and then to the future third caliph, Uthman.
- Umm Kulthum (603–630). She was first married to Utaybah bin Abi Lahab and then, after the death of her sister Ruqayyah, to Uthman. She was childless.
Sunni view
The Sunni scholar Yusuf ibn abd al-Barr says: "His children born of Khadīja are four daughters; there is no difference of opinion about that."
The Quran (33:59) says:
Shia view
According to some Shi'ite sources, Khadija and Muhammad adopted two daughters of Halah, a sister of Khadija.
- Hind bint Atiq. She married her paternal cousin, Sayfi ibn Umayya, and they had one son, Muhammad ibn Sayfi.
- Zaynab bint Abi Hala, who probably died in infancy.
The adopted daughters attributed to Muhammad, by Shia sources, are:
- Zaynab (599–629). She married her maternal cousin Abu al-Aas ibn al-Rabee before al-Hijra. Later lived with Muhammad. Her husband accepted Islam before her death in 629
- Ruqayyah (601–624). She was first married to Utbah ibn Abu Lahab and then to the future third caliph Uthman ibn Affan.
- Umm Kulthum (603–630). She was first married to Utaybah bin Abu Lahab and then, after the death of her sister Ruqayyah, to Uthman ibn Affan. She was childless.
Cousins
- Ibn Umm Maktum
- Waraqah ibn Nawfal was the son of Nawfal b. Asad b. ʿAbd al-ʿUzzā b. Ḳuṣayy and Hind bt. Abī Kat̲h̲īr. Waraqah had been proposed to marry Khadija bint Khuwaylid, but the marriage never took place. Waraqah is noteworthy because he converted from polytheism to Christianity before Muhammad's revelation. Ibn Ishaq claims that Waraqah is also important because he plays a role in legitimizing Muhammad's revelation.
'There has come to him', Waraḳa says, 'the greatest law that came to Moses; surely he is the prophet of this people.'
Her important descendants
| Quraysh tribe (detailed tree) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Waqida bint Amr | Abd Manaf ibn Qusai | Ātikah bint Murrah | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nawfal ibn Abd Manaf | ‘Abd Shams | Barra | Hala | Muṭṭalib ibn Abd Manaf | Hashim | Salma bint Amr | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Umayya ibn Abd Shams | ʿAbd al-Muṭṭalib | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Harb | Abū al-ʿĀs | ʿĀminah | ʿAbdallāh | Hamza | Abī Ṭālib | Az-Zubayr | al-ʿAbbās | Abū Lahab | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ʾAbī Sufyān ibn Harb | al-Ḥakam | ʿUthmān | ʿAffān | MUHAMMAD (Family tree) |
Khadija bint Khuwaylid | ʿAlī (Family tree) |
Khawlah bint Ja'far | ʿAbd Allāh | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Muʿāwiyah I | Marwān I | ʿUthmān ibn ʿAffān | Ruqayyah | Fatimah | Muhammad ibn al-Hanafiyyah | ʿAli ibn ʿAbdallāh | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sufyanids | Marwanids | al-Ḥasan | al-Ḥusayn (Family tree) |
Abu Hashim (Imām of al-Mukhtār and Hashimiyya) |
Muhammad "al-Imām" (Abbasids) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ibrāhim "al-Imām" | al-Saffāḥ | al-Mansur | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
 In Spanish: Jadiya para niños
In Spanish: Jadiya para niños