Javanese language facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Javanese |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basa Jawa | ||||
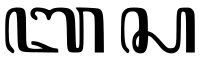
Basa (language) written in the Javanese script
|
||||
| Native to | Java (Indonesia) | |||
| Ethnicity | Javanese (Mataram, Osing, Tenggerese, Boyanese, Samin, Cirebonese, Banyumasan, Javanese Surinamese, etc) | |||
| Native speakers | 94 million (2013) | |||
| Language family |
Default
|
|||
| Dialects | Javanese dialects | |||
| Writing system | Latin script Javanese script Pegon alphabet |
|||
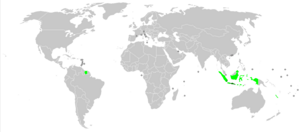
Dark green: areas where Javanese is the majority language. Light green: where it is a minority language.
|
||||
|
||||
Javanese is the language of the Javanese people from the central and eastern parts of the island of Java, in Indonesia. There are also pockets of Javanese speakers in the northern coast of western Java. It is the native language of more than 98 million people (more than 42% of the total population of Indonesia).
Javanese is one of the Austronesian languages, but it is not particularly close to other languages and is difficult to classify. Its closest relatives are the neighbouring languages such as Sundanese, Madurese and Balinese. Most speakers of Javanese also speak Indonesian, the standardized form of Malay spoken in Indonesia, for official and commercial purposes as well as a means to communicate with non-Javanese-speaking Indonesians.
There are speakers of Javanese in Malaysia (concentrated in the states of Selangor and Johor) and Singapore. Some people of Javanese descent in Suriname (the Dutch colony of Suriname until 1975) speak a creole descendant of the language.
Speakers
The language is spoken in Yogyakarta, Central and East Java, as well as on the north coast of West Java. It is also spoken elsewhere by the Javanese people in other provinces of Indonesia, which are numerous due to the government-sanctioned transmigration program in the late 20th century, including Lampung, Jambi, and North Sumatra provinces. In Suriname, creolized Javanese is spoken among descendants of plantation migrants brought by the Dutch during the 19th century. In Madura, Bali, Lombok, and the Sunda region of West Java, it is also used as a literary language. It was the court language in Palembang, South Sumatra, until the palace was sacked by the Dutch in the late 18th century.
Javanese is written with the Latin script, Javanese script, and Arabic script. In the present day, the Latin script dominates writings, although the Javanese script is still taught as part of the compulsory Javanese language subject in elementary up to high school levels in Yogyakarta, Central and East Java.
Javanese is the tenth largest language by native speakers and the largest language without official status. It is spoken or understood by approximately 100 million people. At least 45% of the total population of Indonesia are of Javanese descent or live in an area where Javanese is the dominant language. All seven Indonesian presidents since 1945 have been of Javanese descent. It is therefore not surprising that Javanese has had a deep influence on the development of Indonesian, the national language of Indonesia.
There are three main dialects of the modern language: Central Javanese, Eastern Javanese, and Western Javanese. These three dialects form a dialect continuum from northern Banten in the extreme west of Java to Banyuwangi Regency in the eastern corner of the island. All Javanese dialects are more or less mutually intelligible.
Images for kids
-
Susuhunan Pakubuwono X of Surakarta. Surakarta has been a center of Javanese culture, and its dialect is regarded as the most "refined".
-
A modern bilingual text in Portuguese and Javanese in Yogyakarta.
See also
 In Spanish: Idioma javanés para niños
In Spanish: Idioma javanés para niños





