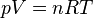Ideal gas law facts for kids
The ideal gas law is the equation of a possible ideal gas, first made by Benoît Paul Émile Clapeyron in 1834.
The state or amount of an amount of gas is found by using its pressure, volume, and temperature in the equation:
where
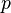 is the absolute pressure of the gas,
is the absolute pressure of the gas,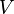 is the volume of the gas,
is the volume of the gas,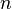 is the number of moles of gas,
is the number of moles of gas,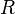 is the universal gas constant,
is the universal gas constant,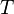 is the absolute temperature.
is the absolute temperature.
Images for kids
-
Molecular collisions within a closed container (a propane tank) are shown (right). The arrows represent the random motions and collisions of these molecules. The pressure and temperature of the gas are directly proportional: As temperature increases, the pressure of the propane gas increases by the same factor. A simple consequence of this proportionality is that on a hot summer day, the propane tank pressure will be elevated, and thus propane tanks must be rated to withstand such increases in pressure.
See also
 In Spanish: Ley de los gases ideales para niños
In Spanish: Ley de los gases ideales para niños