Hylidae facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Hylidae |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Red-eyed Tree Frog, Agalychnis callidryas | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: |
Hylidae
Rafinesque, 1815
|
| Genera | |
|
See text. |
|
 |
|
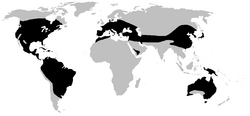
| Distribution of Hylidae (in black) | |
Hylidae is a family of tree frogs. Some of the Hylids are semi-aquatic while others will be territorial frogs.
Contents
Characteristics
Most hylids has forward-facing eyes that gives them binocular vision. These hylids are arboreal species. Non-aboreal species do not have any of these advantages. The Cyclorana species are burrowing frogs. They spend most of their time underground. Hylids will eat on insects and other invertebrates. Larger species can eat small vertebrates.
Hylids will lay their eggs in ponds. Some will lay their eggs in puddles that are found in the holes of trees. Others will lay their eggs on plants, if water is near. The tadpoles will drop from the plants and into the pond when they hatch. In South America, female hylids will carry the eggs on her back until they hatch.
Species
The European tree frog (Hyla arborea) lives in middle and Southern Europe. They can also be found in Asia and North Africa. These species are noisy during a rain storm. In North America, there are many species of the Hylidae family. These include Hyla versicolor (Grey Tree Frog) and the Hyla cinerea (American Green Tree Frog). The spring peeper (Pseudacris crucifer) can also be found in Eastern United States. The spring peeper will make loud noises during the spring and summer time.
The word "tree frog" is a popular name for several of the Hylidae. For an example the Hyla versicolor is the name of the changeable tree frog, Trachycephalus lichenatus is the name of the lichened tree frog, and Trachycephalus marmoratus is the name of the marbled tree frog. However, the name "tree frog" is not "unique" to this family. The word "tree frog" is used more often for many species of the Rhacophoridae.
Taxonomy


The Hylidae family is divided into the following subfamilies and genera:
- Hylidae
- Subfamily Pelodryadinae (Austro-Papuan tree frogs)
- Litoria
- Nyctimystes
- Pelodryas
- Subfamily Phyllomedusinae (Leaf frogs)
- Agalychnis
- Cruziohyla
- Hylomantis – Rough Leaf Frogs
- Pachymedusa – Mexican Leaf Frogs
- Phasmahyla – Shining Leaf Frogs
- Phrynomedusa – Colored Leaf Frogs
- Phyllomedusa
- Subfamily Hylinae
- Acris – Cricket Frogs
- Anotheca – Spiny-headed Treefrogs
- Aparasphenodon – Casque-headed Frogs
- Aplastodiscus – Canebreak Treefrogs
- Argenteohyla – Argentinian Frogs
- Bokermannohyla
- Bromeliohyla
- Charadrahyla
- Corythomantis – Casque-headed Treefrog
- Dendropsophus
- Duellmanohyla – Brook Frogs
- Ecnomiohyla
- Exerodonta
- Hyla – Common Treefrogs
- Hyloscirtus
- Hypsiboas – Gladiator Frogs
- Isthmohyla
- Itapotihyla
- Lysapsus
- Megastomatohyla
- Myersiohyla
- Nyctimantis – Brown-eyed Treefrogs
- Osteocephalus – Slender-legged Treefrogs
- Osteopilus – Cuban Treefrogs
- Phyllodytes – Heart-tongued Frogs
- Plectrohyla – Spike-thumb Frogs
- Pseudacris – Chorus Frogs
- Pseudis – Swimming Frogs
- Ptychohyla – Stream Frogs
- Scarthyla – Madre de Dios Treefrogs
- Scinax – Snouted Treefrogs
- Smilisca – Burrowing Frogs
- Sphaenorhynchus – Lime Treefrogs
- Tepuihyla – Amazon Treefrogs
- Tlalocohyla
- Trachycephalus – Casque-headed Treefrogs
- Triprion – Shovel-headed Treefrogs
- Xenohyla
See also
 In Spanish: Ranas arborícolas comunes para niños
In Spanish: Ranas arborícolas comunes para niños




