History of the Earth facts for kids
The history of the Earth describes the most important events and fundamental stages in the development of the planet Earth from its formation to the present day.
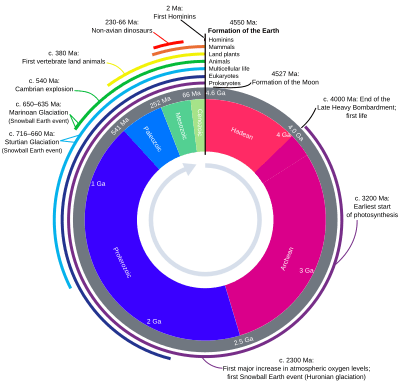
The age of the Earth is about 4.56 billion years. Nearly all branches of science have helped us understand the main events of the Earth's past. The Earth is about one third the age of the universe.
Contents
Hadean
Origin

The formation of Earth occurred as part of the formation of the Solar System. It started as a large rotating cloud of dust and gas. This cloud, the solar nebula, was composed of hydrogen and helium produced in the Big Bang, as well as heavier elements produced in supernovas. Then, about 4.68×109 years ago, the solar nebula began to contract, rotate and gain angular momentum. This may have been triggered by a star in the region exploding as a supernova, and sending a shock wave through the solar nebula.
As the cloud rotated, it became a flat disc perpendicular to its axis of rotation. Most of the mass concentrated in the middle and began to heat up. Meanwhile, the rest of the disc began to break up into rings, with gravity causing matter to condense around dust particles. Small fragments collided to become larger fragments, including one collection about 150 million kilometers from the center: this would become the Earth. As the Sun condensed and heated, nuclear fusion started, and the solar wind cleared out most of the material in the disc, which had not yet condensed, into larger bodies.
Moon
The Earth's relatively large natural satellite, the Moon, is unique. During the Apollo program, rocks from the Moon's surface were brought to Earth. Radiometric dating of these rocks has shown the Moon to be 4527 ± 10 million years old, about 30 to 55 million years younger than other bodies in the solar system. New evidence suggests the Moon formed even later, 4.48±0.02 Ga, or 70–110 Ma after the start of the Solar System. Another notable feature is the relatively low density of the Moon, which must mean it does not have a large metallic core, like all other terrestrial bodies in the solar system. The Moon has a bulk composition closely resembling the Earth's mantle and crust together, without the Earth's core. This has led to the giant impact hypothesis: the idea that the Moon was formed during a giant impact of the proto-Earth with another protoplanet.
The impactor, sometimes named Theia, is thought to have been a little smaller than the current planet Mars. Theia finally collided with Earth about 4.533 Ga. Models reveal that when an impactor this size struck the proto-Earth at a low angle and relatively low speed (8–20 km/sec), much material from the mantles (and proto-crusts) of the proto-Earth and the impactor was ejected into space, where much of it stayed in orbit around the Earth. This material would eventually form the Moon. However, the metallic cores of the impactor would have sunk through the Earth's mantle to fuse with the Earth's core, depleting the Moon of metallic material. The giant impact hypothesis thus explains the Moon's abnormal composition. The ejecta in orbit around the Earth could have condensed into a single body within a couple of weeks. Under the influence of its own gravity, the ejected material became a more spherical body: the Moon.
The radiometric ages show the Earth existed already for at least 10 million years before the impact, enough time to allow for differentiation of the Earth's primitive mantle and core. Then, when the impact occurred, only material from the mantle was ejected, leaving the Earth's core of heavy elements untouched.
The impact had some important consequences for the young Earth. It released an enormous amount of energy, causing both the Earth and Moon to be completely molten. Immediately after the impact, the Earth's mantle was vigorously convecting, the surface was a large magma ocean. The planet's first atmosphere must have been completely blown away by the enormous amount of energy released. The impact is also thought to have changed Earth’s axis to produce the large 23.5° axial tilt that is responsible for Earth’s seasons (a simple, ideal model of the planets’ origins would have axial tilts of 0° with no recognizable seasons). It may also have sped up Earth’s rotation.
Archean
Archean Earth
At the beginning of the Archaean, the Earth's heat flow was nearly three times higher than it is today, and was still twice the current level by the beginning of the Proterozoic. Thus, tectonic and volcanic activity were considerably more active than they are today; the Earth's crust was not only thinner than is today, but probably broken up into many more tectonic plates, with numerous hot spots, rift valleys, and transform faults. The existence of plate tectonics in this eon is disputed: it is an active area of modern research.p297-302
There were no large continents until late in the Archean; small protocontinents were the norm, prevented from coalescing into larger units by the high rate of geologic activity. These felsic protocontinents probably formed at hot spots rather than subduction zones, from a variety of sources: mafic magma melting more felsic rocks, partial melting of mafic rock, and from the metamorphic alteration of felsic sedimentary rocks.p297-301
The Archean atmosphere apparently lacked free oxygen. Temperatures appear to have been near modern levels, although astronomers think that the sun was about one-third dimmer. This is thought to reflect larger amounts of greenhouse gases than later in Earth history.
Archean geology
The oldest rock formations exposed on the surface of the Earth are Archean or slightly older. Archean rocks are known from Greenland, the Canadian Shield, western Australia, and southern Africa. Although the first continents formed during this eon, rock this age makes up only 7% of the world's current cratons; even allowing for erosion and destruction of past formations, evidence suggests that only 5-40% of the present continental crust formed during the Archean.p301
In contrast to the Proterozoic, Archean rocks are often heavily metamorphized deep-water sediments, such as greywackes, mudstones, volcanic sediments, and banded iron formations. Greenstone belts are typical Archean formations, consisting of alternating high and low-grade metamorphic rocks. The high-grade rocks were derived from volcanic island arcs, while the low-grade metamorphic rocks represent deep-sea sediments eroded from from the neighboring island arcs and deposited in a forearc basin. In short, greenstone belts represent sutured protocontinents.p302-3
Archean life
Fossils of cyanobacterial mats (stromatolites) are found throughout the Archean—becoming especially common late in the eon—while a few other probable bacterial fossils are known from chert beds.p307 In addition to bacteria, microfossils of the extremophilic archaea have also been identified.
There are no known eukaryote fossils.p306, 323 No fossil evidence yet exists for viruses.
Proterozoic
The Proterozoic record
The geologic record of the Proterozoic is much better than that for the preceding Archaean. In contrast to the deep-water deposits of the Archean, the Proterozoic features many strata that were laid down in extensive, shallow epicontinental seas; furthermore, many of these rocks are less metamorphosed than Archean-age ones, and plenty are in fact unaltered.p315 Study of these rocks show that the eon featured rapid continental accretion (unique to the Proterozoic), supercontinent cycles, and wholly-modern orogenic activity.p315/8; 329/32
The first known glaciations occurred during the Proterozoic. One ice age began shortly after the beginning of the eon. There were at least four during the Neoproterozoic, climaxing with the "Snowball Earth" of the Varangian glaciation.p320; 325
The build-up of oxygen
One of the most important events of the Proterozoic was the accumulation of oxygen in the Earth's atmosphere. Though oxygen was undoubtedly released by photosynthesis well back in Archean times, it could not build up to any significant degree until chemical sinks--unoxidized sulfur and iron—had been filled; until roughly 2.3 billion years ago, oxygen was probably only 1 to 2% of its current level.(Stanley, 323) Banded iron formations, which provide most of the world's iron ore, were also a prominent chemical sink; most accumulation ceased after 1.9 billion years ago, either due to an increase in oxygen or a more thorough mixing of the oceanic water column.p324
Red beds, which are coloured by haematite, indicate an increase in atmospheric oxygen after 2 billion years ago; they are not found in older rocks.(Stanley, 324) The oxygen build-up was probably due to two factors: a filling of the chemical sinks, and an increase in carbon burial, which stored organic compounds which would have otherwise been oxidized by the atmosphere.p325
Proterozoic life
The first advanced single-celled and multi-cellular life roughly coincides with the oxygen accumulation; this may have been due to an increase in the oxidized nitrates that eukaryotes use, as opposed to cyanobacteria.(Stanley, 325) It was also during the Proterozoic that the first symbiotic relationship between mitochondria (for animals and protists) and chloroplasts (for plants) and their hosts evolved.
Eukaryotes such as acritarchs blossomed, as did cyanobacteria; in fact, stromatolites reached their greatest abundance and diversity during the Proterozoic, peaking roughly 1.2 billion years ago.
Classically, the boundary between the Proterozoic and the Paleozoic was set at the base of the Cambrian period when the first fossils of animals known as trilobites appeared. In the second half of the 20th century, a number of fossil forms have been found in Proterozoic rocks, but the boundary of the Proterozoic has remained fixed at the base of the Cambrian—currently placed at 542 Ma.
Phanerozoic
Paleozoic

The Paleozoic covers the time from the first appearance of abundant, hard-shelled fossils to the time when the continents were beginning to be dominated by large, relatively sophisticated reptiles and relatively modern plants.
The upper (youngest) boundary is set at a major extinction event 250 million years later, known as the Permian–Triassic extinction event. Modern practice sets the older boundary at the first appearance of a distinctive trace fossil called Phycodes pedum.
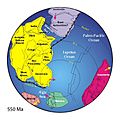
Geologically, the Paleozoic starts shortly after the breakup of a supercontinent called Rodinia and at the end of a global ice age (Snowball Earth). Throughout the early Palaeozoic, the Earth's landmass was broken up into a substantial number of relatively small continents. Toward the end of the era, the continents gathered together into a supercontinent called Pangaea, which included most of the Earth's land area.
At the start of the era, life was confined to bacteria, algae, sponges and a variety of somewhat enigmatic forms known collectively as the Ediacaran fauna. A large number of body plans appeared nearly simultaneously at the start of the era—a phenomenon known as the Cambrian Explosion.
There is some evidence that simple life may already have invaded the land at the start of the Palaeozoic, but substantial plants and animals did not take to the land until the Silurian and did not thrive until the Devonian. Although primitive vertebrates are known near the start of the Palaeozoic, animal forms were dominated by invertebrates until the mid-Palaeozoic. Fish populations exploded in the Devonian. During the late Palaeozoic, great forests of primitive plants thrived on land forming the great coal beds of Europe and eastern North America. By the end of the era, the first large, sophisticated reptiles and the first modern plants (conifers) had developed.
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic covers the time when life was dominated by large sophisticated reptiles. The lower (oldest) boundary is set by the P/Tr extinction event. The upper (youngest) boundary is set at the K/T extinction event.
Geologically, the Mesozoic starts with almost all the Earth's land collected into a supercontinent called Pangaea. During the era, Pangaea split into the northern continent Laurasia and the southern continent Gondwana. Laurasia then split into North America and Eurasia. Gondwana broke up progressively into continents: South America, Africa, Madagascar, India, Australia and Antarctica.
The Mesozoic is known as the Age of Dinosaurs. It also saw the development of early birds and mammals and, later, flowering plants (angiosperms). At the end of the Mesozoic, all the major body plans of modern life were in place, though in some cases – notably the mammals – the forms that existed at the end of the Cretaceous were relatively primitive.
Cainozoic
The Cainozoic is the age of mammals. During the Cainozoic, mammals diverged from a few small, simple, generalized forms into a diverse collection of terrestrial, marine, and flying animals. Flowering plants and birds also evolved substantially in the Cainozoic.
Geologically, the Cainozoic is the era when continents moved into their current positions. Africa and Australasia split from Gondwana to drift north, and India collided with Southeast Asia; Antarctica moved into its current position over the South Pole; the Atlantic Ocean widened and, late in the era, South America became attached to North America.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Lithified stromatolites on the shores of Lake Thetis, Western Australia. Archean stromatolites are the first direct fossil traces of life on Earth.
-
A banded iron formation from the 3.15 Ga Moodies Group, Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa. Red layers represent the times when oxygen was available; gray layers were formed in anoxic circumstances.
-
A 580 million year old fossil of Spriggina floundensi, an animal from the Ediacaran period. Such life forms could have been ancestors to the many new forms that originated in the Cambrian Explosion.
-
Trilobites first appeared during the Cambrian period and were among the most widespread and diverse groups of Paleozoic organisms.
-
Artist's conception of Devonian flora
-
Tiktaalik, a fish with limb-like fins and a predecessor of tetrapods. Reconstruction from fossils about 375 million years old.
-
Astronaut Bruce McCandless II outside of the Space Shuttle Challenger in 1984
See also
 In Spanish: Historia de la Tierra para niños
In Spanish: Historia de la Tierra para niños
 | Audre Lorde |
 | John Berry Meachum |
 | Ferdinand Lee Barnett |