History of Chicago facts for kids
Chicago has played a central role in American economic, cultural and political history. Since the 1850s Chicago has been one of the dominant metropolises in the Midwestern United States, and has been the largest city in the Midwest since the 1880 census. The area's recorded history begins with the arrival of French explorers, missionaries and fur traders in the late 17th century and their interaction with the local Pottawatomie Native Americans. Jean Baptiste Point du Sable was the first permanent non-indigenous settler in the area, having a house at the mouth of the Chicago River in the late 18th century. There were small settlements and a U.S. Army fort, but the soldiers and settlers were all driven off in 1812. The modern city was incorporated in 1837 by Northern businessmen and grew rapidly from real estate speculation and the realization that it had a commanding position in the emerging inland transportation network, based on lake traffic and railroads, controlling access from the Great Lakes into the Mississippi River basin.
Despite a fire in 1871 that destroyed the Central Business District, the city grew exponentially, becoming the nation's rail center and the dominant Midwestern center for manufacturing, commerce, finance, higher education, religion, broadcasting, sports, jazz, and high culture. The city was a magnet for European immigrants—at first Germans, Irish and Scandinavians, then from the 1890s to 1914, Jews, Czechs, Poles and Italians. They were all absorbed in the city's powerful ward-based political machines. Many joined militant labor unions, and Chicago became notorious for its violent strikes, but respected for its high wages.
Large numbers of African Americans migrated from the South starting in the World War I era as part of the Great Migration. Mexicans started arriving after 1910, and Puerto Ricans after 1945. The Cook County suburbs grew rapidly after 1945, but the Democratic party machine kept both the city and suburbs under control, especially under mayor Richard J. Daley, who was chairman of the Cook County Democratic Party. Deindustrialization after 1970 closed the stockyards and most of the steel mills and factories, but the city retained its role as a financial and transportation hub. Increasingly it emphasized its service roles in medicine, higher education, and tourism. The city formed the political base for leaders such as Stephen A. Douglas in the 1850s, Adlai Stevenson in the 1950s, and Barack Obama in recent years.
Pre-1830
Early native settlements
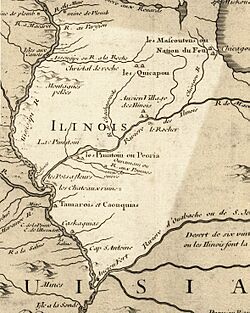
At its first appearance in records by explorers, the Chicago area was inhabited by a number of Algonquian peoples, including the Mascouten and Miami. The name "Chicago" is derived from a French rendering of the Native American word shikaakwa, known to botanists as Allium tricoccum, from the Miami-Illinois language. The first known reference to the site of the current city of Chicago as "Checagou" was by Robert de LaSalle around 1679 in a memoir. Henri Joutel, in his journal of 1688, noted that the wild garlic, called "chicagoua", grew abundantly in the area. According to his diary of late September 1687:
when we arrived at the said place called Chicagou which, according to what we were able to learn of it, has taken this name because of the quantity of garlic which grows in the forests in this region.
The tribe was part of the Miami Confederacy, which included the Illini and Kickapoo. In 1671, Potawatomi guides first took the French trader Nicolas Perrot to the Miami villages near the site of present-day Chicago. Pierre François Xavier de Charlevoix would write in 1721 that the Miami had a settlement in what is now Chicago around 1670. Chicago's location at a short canoe portage (the Chicago Portage) connecting the Great Lakes with the Mississippi River system attracted the attention of many French explorers, notably Louis Jolliet and Jacques Marquette in 1673. The Jesuit Relations indicate that by this time, the Iroquois tribes of New York had driven the Algonquian tribes entirely out of Lower Michigan and as far as this portage, during the later Beaver Wars.
René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle, who traversed the Kankakee and Illinois Rivers south of Chicago in the winter of 1681–82, identified the Des Plaines River as the western boundary of the Miami. In 1683, La Salle built Fort St. Louis on the Illinois River. Almost two thousand Miami, including Weas and Piankeshaws, left the Chicago area to gather on the opposite shore at the Grand Village of the Illinois, seeking French protection from the Iroquois. In 1696, French Jesuits led by Jean-François Buisson de Saint-Cosme built the Mission of the Guardian Angel to Christianize the local Wea and Miami people. Shortly thereafter, Augustin le Gardeur de Courtemanche visited the settlement on behalf of the French government, seeking peace between the Miami and Iroquois. Miami chief Chichikatalo accompanied de Courtemanche to Montreal.
The Algonquian tribes began to retake the lost territory in the ensuing decades, and in 1701, the Iroquois formally abandoned their claim to their "hunting grounds" as far as the portage to England in the Nanfan Treaty, which was finally ratified in 1726. This was largely a political maneuver of little practicality, as the English then had no presence in the region whatsoever, the French and their Algonquian allies being the dominant force in the area. A writer in 1718 noted at the Was had a village in Chicago, but had recently fled due to concerns about approaching Ojibwes and Pottawatomis. The Iroquois and Meskwaki probably drove out all Miami from the Chicago area by the end of the 1720s. The Pottawatomi assumed control of the area, but probably did not have any major settlements in Chicago. French and allied use of the Chicago portage was mostly abandoned during the 1720s because of continual Native American raids during the Fox Wars.
There was also a Michigamea chief named Chicago who may have lived in the region. In the 1680s, the Illinois River was called the Chicago River.
First non-native settlements

The first settler in Chicago was Jean Baptiste Point du Sable, a Frenchman of European and African descent, who built a farm at the mouth of the Chicago River in 1788 to 1790. He left Chicago in 1800. In 1968, Point du Sable was honored at Pioneer Court as the city's founder and featured as a symbol.
In 1795, following the Northwest Indian War, some Native Americans ceded the area of Chicago to the United States for a military post in the Treaty of Greenville. The US built Fort Dearborn in 1803 on the Chicago River. It was destroyed by Indian forces during the War of 1812 in the Battle of Fort Dearborn, and many of the inhabitants were killed or taken prisoner. The fort had been ordered to evacuate. During the evacuation soldiers and civilians were overtaken near what is today Prairie Avenue. After the end of the war, the Potawatomi ceded the land to the United States in the 1816 Treaty of St. Louis. (Today, this treaty is commemorated in Indian Boundary Park.) Fort Dearborn was rebuilt in 1818 and used until 1837.
Growth of the city
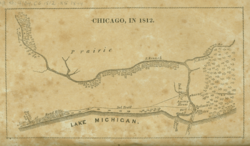
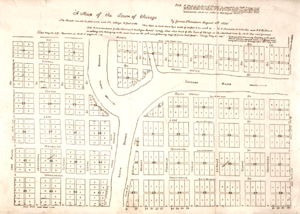
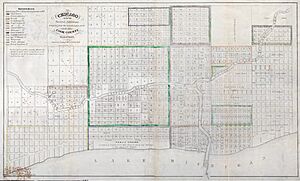
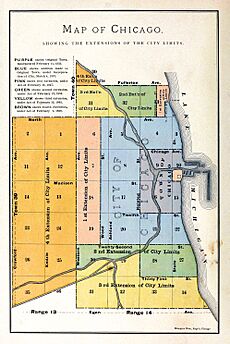
In 1829, the Illinois legislature appointed commissioners to locate a canal and lay out the surrounding town. The commissioners employed James Thompson to survey and plat the town of Chicago, which at the time had a population of less than 100. Historians regard the August 4, 1830, filing of the plat as the official recognition of a location known as Chicago.
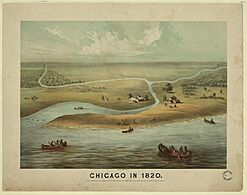
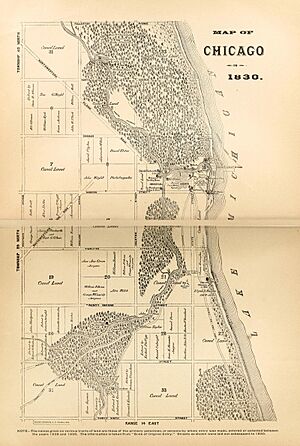
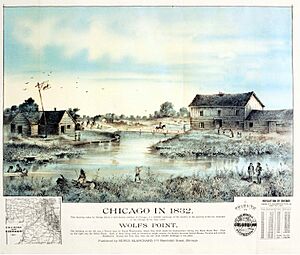
Yankee entrepreneurs saw the potential of Chicago as a transportation hub in the 1830s and engaged in land speculation to obtain the choicest lots. On August 12, 1833, the Town of Chicago was incorporated with a population of 350. The Chippewa, Odawa and Potawatomi ceded land in Illinois, Wisconsin and Michigan in the 1833 Treaty of Chicago and were forced to move west of the Mississippi River by 1838. On July 12, 1834, the Illinois from Sackets Harbor, New York, was the first commercial schooner to enter the harbor, a sign of the Great Lakes trade that would benefit both Chicago and New York state. Chicago was granted a city charter by the State of Illinois on March 4, 1837; it was part of the larger Cook County. By 1840 the boom town had a population of over 4,000.
After 1830, the rich farmlands of northern Illinois attracted Yankee settlers. Yankee real estate operators created a city overnight in the 1830s. To open the surrounding farmlands to trade, the Cook County commissioners built roads south and west. The latter crossed the "dismal Nine-mile Swamp," the Des Plaines River, and went southwest to Walker's Grove, now the Village of Plainfield. The roads enabled hundreds of wagons per day of farm produce to arrive and so the entrepreneurs built grain elevators and docks to load ships bound for points east through the Great Lakes. Produce was shipped through the Erie Canal and down the Hudson River to New York City; the growth of the Midwest farms expanded New York City as a port.
In 1837, Chicago held its first mayoral election and elected William B. Ogden as its inaugural mayor.
Emergence as a transportation hub
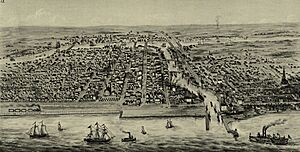
In 1848, the opening of the Illinois and Michigan Canal allowed shipping from the Great Lakes through Chicago to the Mississippi River and the Gulf of Mexico. The first rail line to Chicago, the Galena & Chicago Union Railroad, was completed the same year. Chicago would go on to become the transportation hub of the United States, with its road, rail, water, and later air connections. Chicago also became home to national retailers offering catalog shopping such as Montgomery Ward and Sears, Roebuck and Company, which used the transportation lines to ship all over the nation.
By the 1850s, the construction of railroads made Chicago a major hub and over 30 lines entered the city. The main lines from the East ended in Chicago, and those oriented to the West began in Chicago and so by 1860, the city had become the nation's trans-shipment and warehousing center. Factories were created, most famously the harvester factory that was opened in 1847 by Cyrus Hall McCormick. It was a processing center for natural resource commodities extracted in the West. The Wisconsin forests supported the millwork and lumber business; the Illinois hinterland provided the wheat. Hundreds of thousands of hogs and cattle were shipped to Chicago for slaughter, preserved in salt, and transported to eastern markets. By 1870, refrigerated cars allowed the shipping of fresh meat to cities in the East.
The prairie bog nature of the area provided a fertile ground for disease-carrying insects. In springtime, Chicago was so muddy from the high water that horses could scarcely move. Comical signs proclaiming "Fastest route to China" or "No Bottom Here" were placed to warn people of the mud.
Travelers reported Chicago was the filthiest city in America. The city created a massive sewer system. In the first phase, sewage pipes were laid across the city above ground and used gravity to move the waste. The city was built in a low-lying area subject to flooding. In 1856, the city council decided that the entire city should be elevated four to five feet by using a newly available jacking-up process. In one instance, the five-story Brigg's Hotel, weighing 22,000 tons, was lifted while it continued to operate. Observing that such a thing could never have happened in Europe, the British historian Paul Johnson cites the astounding feat as a dramatic example of American determination and ingenuity based on the conviction that anything material is possible.
Immigration and population in 19th century
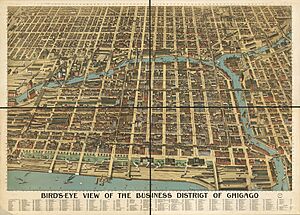
Although originally settled by Yankees in the 1830s, the city in the 1840s had many Irish Catholics come as a result of the Great Famine. Later in the century, the railroads, stockyards, and other heavy industry of the late 19th century attracted a variety of skilled workers from Europe, especially Germans, English, Swedes, Norwegians, and Dutch. A small African-American community formed, led by activist leaders like John Jones and Mary Richardson Jones, who established Chicago as a stop on the Underground Railroad.
In 1840, Chicago was the 92nd city in the United States by population. Its population grew so rapidly that 20 years later, it was the ninth city. In the pivotal year of 1848, Chicago saw the completion of the Illinois and Michigan Canal, its first steam locomotives, the introduction of steam-powered grain elevators, the arrival of the telegraph, and the founding of the Chicago Board of Trade. By 1857, Chicago was the largest city in what was then called the Northwest. In 20 years, Chicago grew from 4,000 people to over 90,000. Chicago surpassed St. Louis and Cincinnati as the major city in the West and gained political notice as the home of Stephen Douglas, the 1860 presidential nominee of the Northern Democrats. The 1860 Republican National Convention in Chicago nominated the home-state candidate Abraham Lincoln. The city's government and voluntary societies gave generous support to soldiers during the American Civil War.
Many of the newcomers were Irish Catholic and German immigrants. Their neighborhood saloons, a center of male social life, were attacked in the mid-1850s by the local Know-Nothing Party, which drew its strength from evangelical Protestants. The new party was anti-immigration and anti-liquor and called for the purification of politics by reducing the power of the saloonkeepers. In 1855, the Know-Nothings elected Levi Boone mayor, who banned Sunday sales of liquor and beer. His aggressive law enforcement sparked the Lager Beer Riot of April 1855, which erupted outside a courthouse in which eight Germans were being tried for liquor ordinance violations. After 1865, saloons became community centers only for local ethnic men, as reformers saw them as places that incited riotous behavior and moral decay. Salons were also sources of musical entertainment. Francis O'Neill, an Irish immigrant who later became police chief, published compendiums of Irish music that were largely collected from other newcomers playing in saloons.
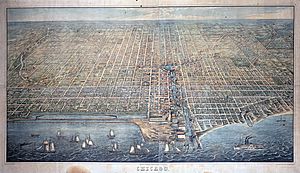
By 1870, Chicago had grown to become the nation's second-largest city and one of the largest cities in the world. Between 1870 and 1900, Chicago grew from a city of 299,000 to nearly 1.7 million and was the fastest-growing city in world history. Chicago's flourishing economy attracted huge numbers of new immigrants from Eastern and Central Europe, especially Jews, Poles, and Italians, along with many smaller groups. Many businesspeople and professionals arrived from the eastern states. Relatively few new arrivals came from Chicago's rural hinterland. The exponential growth put increasing pollution on the environment, as hazards to public health impacted everyone.
Gilded Age
Most of the city burned in the 1871 Great Chicago Fire. The damage from the fire was immense since 300 people died, 18,000 buildings were destroyed, and nearly 100,000 of the city's 300,000 residents were left homeless. Several key factors exacerbated the spread of the fire. Most of Chicago's buildings and sidewalks were then constructed of wood. Also, the lack of attention to proper waste disposal practices, which was sometimes deliberate to favor certain industries, left an abundance of flammable pollutants in the Chicago River along which the fire spread from the south to the north. The fire led to the incorporation of stringent fire-safety codes, which included a strong preference for masonry construction.
The Danish immigrant Jens Jensen arrived in 1886 and soon became a successful and celebrated landscape designer. Jensen's work was characterized by a democratic approach to landscaping, which was informed by his interest in social justice and conservation, and a rejection of antidemocratic formalism. Among Jensen's creations were four Chicago city parks, most famously Columbus Park. His work also included garden design for some of the region's most influential millionaires.
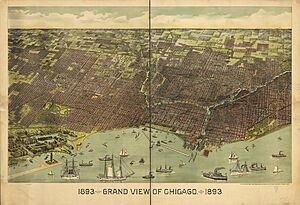
The World's Columbian Exposition of 1893 was constructed on former wetlands at the present location of Jackson Park along Lake Michigan in Chicago's Hyde Park neighborhood. The land was reclaimed according to a design by the landscape architect Frederick Law Olmsted. The temporary pavilions, which followed a classical theme, were designed by a committee of the city's architects under the direction of Daniel Burnham. It was called the "White City" for the appearance of its buildings.
The Exposition drew 27.5 million visitors; is considered among the most influential world's fairs in history; and affected art, architecture, and design throughout the nation. The classical architectural style contributed to a revival of Beaux Arts architecture that borrowed from historical styles, but Chicago was also developing the original skyscraper and organic forms based in new technologies. The fair featured the first and until recently the largest Ferris wheel ever built.
The soft, swampy ground near the lake proved unstable ground for tall masonry buildings. That was an early constraint, but builders developed the innovative use of steel framing for support and invented the skyscraper in Chicago, which became a leader in modern architecture and set the model nationwide for achieving vertical city densities.
Developers and citizens began immediate reconstruction on the existing Jeffersonian grid. The building boom that followed saved the city's status as the transportation and trade hub of the Midwest. Massive reconstruction using the newest materials and methods catapulted Chicago into its status as a city on par with New York and became the birthplace of modern architecture in the United States.
Rise of industry and commerce

Chicago became the center of the nation's advertising industry after New York City. Albert Lasker, known as the "father of modern advertising", made Chicago his base from 1898 to 1942. As head of the Lord and Thomas agency, Lasker devised a copywriting technique that appealed directly to the psychology of the consumer. Women, who seldom smoked cigarettes, were told that if they smoked Lucky Strikes, they could stay slender. Lasker's use of radio, particularly with his campaigns for Palmolive soap, Pepsodent toothpaste, Kotex products, and Lucky Strike cigarettes, not only revolutionized the advertising industry but also significantly changed popular culture.
Gambling
In Chicago, like other rapidly growing industrial centers with large immigrant working-class neighborhoods, gambling was a major issue. The city's elite upper-class had private clubs and closely-supervised horse racing tracks. The middle-class reformers like Jane Addams focused on the workers, who discovered freedom and independence in gambling that were a world apart from their closely-supervised factory jobs and gambled to validate risk-taking aspect of masculinity, betting heavily on dice, card games, policy, and cock fights. By the 1850s, hundreds of saloons had offered gambling opportunities, including off-track betting on the horses.
20th century
Chicago's manufacturing and retail sectors, fostered by the expansion of railroads throughout the upper Midwest and East, grew rapidly and came to dominate the Midwest and greatly influence the nation's economy. The Chicago Union Stock Yards dominated the packing trade. Chicago became the world's largest rail hub, and one of its busiest ports by shipping traffic on the Great Lakes. Commodity resources, such as lumber, iron and coal, were brought to Chicago and Ohio for processing, with products shipped both East and West to support new growth.
Lake Michigan—the primary source of fresh water for the city—became polluted from the rapidly growing industries in and around Chicago; a new way of procuring clean water was needed. In 1885 the civil engineer Lyman Edgar Cooley proposed the Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal. He envisioned a deep waterway that would dilute and divert the city's sewage by funneling water from Lake Michigan into a canal, which would drain into the Mississippi River via the Illinois River. Beyond presenting a solution for Chicago's sewage problem, Cooley's proposal appealed to the economic need to link the Midwest with America's central waterways to compete with East Coast shipping and railroad industries.
Strong regional support for the project led the Illinois legislature to circumvent the federal government and complete the canal with state funding. The opening in January 1900 met with controversy and a lawsuit against Chicago's appropriation of water from Lake Michigan. By the 1920s the lawsuit was divided between the states of the Mississippi River Valley, who supported the development of deep waterways linking the Great Lakes with the Mississippi, and the Great Lakes states, which feared sinking water levels might harm shipping in the lakes. In 1929 the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in support of Chicago's use of the canal to promote commerce, but ordered the city to discontinue its use for sewage disposal.
New construction boomed in the 1920s, with notable landmarks such as the Merchandise Mart and art deco Chicago Board of Trade Building completed in 1930. The Wall Street Crash of 1929, the Great Depression and diversion of resources into World War II led to the suspension for years of new construction.
The Century of Progress International Exposition was the name of the World's Fair held on the Near South Side lakefront from 1933 to 1934 to celebrate the city's centennial. The theme of the fair was technological innovation over the century since Chicago's founding. More than 40 million people visited the fair, which symbolized for many hope for Chicago and the nation, then in the midst of the Great Depression.
The demographics of the city were changing in the early 20th century as black southern families migrated out of the south, but while cities like Chicago empathized with the condition of impoverished white children, black children were mostly excluded from the private and religious institutions that provided homes for such children. Those that did take in black dependent children were overcrowded and underfunded. Between 1899 and 1945 many of the city's black children found themselves in the juvenile court system. The 1899 Juvenile Court Act, supported by Progressive reformers, created a class of dependants for orphans and other children lacking "proper parental care or guardianship" but the court's designations of "delinquency" and "dependency" were racialized{{{1}}} so black children were far more likely to be labeled as delinquents.
Politics in the late 19th and early 20th centuries

During the election of April 23, 1875, the voters of Chicago chose to operate under the Illinois Cities and Villages Act of 1872. Chicago still operates under this act, in lieu of a charter. The Cities and Villages Act has been revised several times since, and may be found in Chapter 65 of the Illinois Compiled Statutes.
Late-19th-century big city newspapers such as the Chicago Daily News - founded in 1875 by Melville Stone - ushered in an era of news reporting that was, unlike earlier periods, in tune with the particulars of community life in specific cities. Vigorous competition between older and newer-style city papers soon broke out, centered on civic activism and sensationalist reporting of urban political issues and the numerous problems associated with rapid urban growth. Competition was especially fierce between the Chicago Times (Democratic), the Chicago Tribune (Republican), and the Daily News (independent), with the latter becoming the city's most popular paper by the 1880s. The city's boasting lobbyists and politicians earned Chicago the nickname "Windy City" in the New York press. The city adopted the nickname as its own.
-
State Street c. 1907
-
Oak Street Beach, 1925
1930s
Labor unions
After 1900 Chicago was a heavily unionized city, apart from the factories (which were non-union until the 1930s). The Industrial Workers of the World was founded in Chicago in June 1905 at a convention of 200 socialists, anarchists, and radical trade unionists from all over the United States. The Railroad brotherhoods were strong, as were the crafts unions affiliated with the American Federation of Labor. The AFL unions operated through the Chicago Federation of Labor to minimize jurisdictional conflicts, which caused many strikes as two unions battled to control a work site.
The unionized teamsters in Chicago enjoyed an unusually strong bargaining position when they contended with employers around the city, or supported another union in a specific strike. Their wagons could easily be positioned to disrupt streetcars and block traffic. In addition, their families and neighborhood supporters often surrounded and attacked the wagons of nonunion teamsters who were strikebreaking. When the teamsters used their clout to engage in sympathy strikes, employers decided to coordinate their antiunion efforts, claiming that the teamsters held too much power over commerce in their control of the streets. The teamsters' strike in 1905 represented a clash both over labor issues and the public nature of the streets. To the employers, the streets were arteries for commerce, while to the teamsters, they remained public spaces integral to their neighborhoods.
World War II
On December 2, 1942, the world's first controlled nuclear reaction was conducted at the University of Chicago as part of the top secret Manhattan Project.
During World War II, the steel mills in the city of Chicago alone accounted for 20% of all steel production in the United States and 10% of global production. The city produced more steel than the United Kingdom during the war, and surpassed Nazi Germany's output in 1943 (after barely missing in 1942).
The city's diversified industrial base made it second only to Detroit in the value—$24 billion—of war goods produced. Over 1,400 companies produced everything from field rations to parachutes to torpedoes, while new aircraft plants employed 100,000 in the construction of engines, aluminum sheeting, bombsights, and other components. The Great Migration, which had been on pause due to the Depression, resumed at an even faster pace as the 1910 - 1930 period, as hundreds of thousands of black Americans arrived in the city to work in the steel mills, railroads, and shipping yards.
Postwar
Returning World War II veterans and immigrants from Europe (in particular displaced persons from Eastern Europe) created a postwar economic boom and led to the development of huge housing tracts on Chicago's Northwest and Southwest sides. The city was extensively photographed during the postwar years by street photographers such as Richard Nickel and Vivian Maier.
In the 1950s, the postwar desire for new and improved housing, aided by new highways and commuter train lines, caused many middle and higher income Americans to begin to move from the inner-city of Chicago to the suburbs. Changes in industry after 1950, with restructuring of the stockyards and steel industries, led to massive job losses in the city for working-class people. The city population shrank by nearly 700,000. The City Council devised "Plan 21" to improve neighborhoods and focused on creating "Suburbs within the city" near downtown and the lakefront. It built public housing to try to improve housing standards in the city. As a result, many poor were uprooted from newly created enclaves of Black, Latino, and poor people in neighborhoods such as Near North, Wicker Park, Lakeview, Uptown, Cabrini–Green, West Town and Lincoln Park. The passage of civil rights laws in the 1960s also affected Chicago and other northern cities. In the 1960s and the 1970s, many middle- and upper-class Americans continued to move from the city for better housing and schools in the suburbs.
Office building resumed in the 1960s. When completed in 1974, the Sears Tower, now known as the Willis Tower, was at 1451 feet the world's tallest building. It was designed by the famous Chicago firm of Skidmore, Owings & Merrill, which designed many of the city's other famous buildings.
-
Chicago Picasso, a 1967 sculpture in Daley Plaza. Pablo Picasso refused the $100,000 fee and donated it to the people of Chicago.
Mayor Richard J. Daley served 1955–1976, dominating the city's machine politics by his control of the Cook County Democratic Central Committee, which selected party nominees, who were usually elected in the Democratic stronghold. Daley took credit for building four major expressways focused on the Loop, and city-owned O'Hare Airport (which became the world's busiest airport, displacing Midway Airport's prior claims). Several neighborhoods near downtown and the lakefront were gentrified and transformed into "suburbs within the city". He held office during the unrest of the 1960s, some of which was provoked by the police department's discriminatory practices. In the Lincoln Park, Lakeview, Wicker Park and Humboldt Park communities, the Young Lords under the leadership of Jose Cha Cha Jimenez marched and held sit ins to protest the displacement of Latinos and the poor. After the assassination of Martin Luther King Jr. in 1968, major riots of despair resulted in the burning down of sections of the black neighborhoods of the South and West sides. Protests against the Vietnam War at the 1968 Democratic National Convention, held in Chicago, resulted in street violence, with televised broadcasts of the Chicago police's beating of unarmed protesters.
In 1979, Jane Byrne, the city's first woman mayor, was elected, winning the Democratic primary due to a citywide outrage about the ineffective snow removal across the city. In 1983, Harold Washington became the first black mayor of Chicago. Richard M. Daley, son of Richard J. Daley, became mayor in 1989, and was repeatedly reelected until he declined to seek re-election in 2011. He sparked debate by demolishing many of the city's vast public housing projects, which had deteriorated and were holding too many poor and dysfunctional families. Concepts for new affordable and public housing have changed to include many new features to make them more viable: smaller scale, environmental designs for public safety, mixed-rate housing, etc. New projects during Daley's administration have been designed to be environmentally sound, more accessible and better for their occupants.
21st century
Chicago earned the title of "City of the Year" in 2008 from GQ for contributions in architecture and literature, its world of politics, and the downtown's starring role in the Batman movie The Dark Knight. The city was rated by Moody's as having the most balanced economy in the United States due to its high level of diversification.
Flag
Four historical events are commemorated by the four red stars on Chicago's flag: The United States' Fort Dearborn, established at the mouth of the Chicago River in 1803; the Great Chicago Fire of 1871, which destroyed much of the city; the World Columbian Exposition of 1893, by which Chicago celebrated its recovery from the fire; and the Century of Progress World's Fair of 1933–1934, which celebrated the city's centennial. The flag's two blue stripes symbolize the north and south branches of the Chicago River, which flows through the city's downtown. The three white stripes represent the North, West and South sides of the city, Lake Michigan being the east side.
See also
- American urban history
- Bibliography of Chicago history
- Chicago in the 1930s
- Ethnic groups in Chicago; the larger groups have articles such as Poles in Chicago and History of African Americans in Chicago
- History of education in Chicago
- Political history of Chicago
- Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Chicago
- Timeline of Chicago history