Faraday cage facts for kids
A Faraday cage or Faraday shield is an enclosure made from material that conducts electricity. It is used to block electric fields. The Faraday cage is named after the English scientist Michael Faraday, who invented it in 1836.
An electrical field outside the cage causes electric charges in the cage's conducting material to move around and cancel the field's effect inside the cage. It protects sensitive electronic equipment from external radio frequency interference (RFI).
Faraday cages are also used to enclose devices that produce RFI, such as radio transmitters, to prevent their radio waves from interfering with other nearby equipment. They are also used to protect people and equipment against actual electric currents such as lightning strikes and electrostatic discharges. The enclosing cage conducts current round the outside of the enclosed space and none passes though the inside space.
Images for kids
-
Faraday bags are a type of Faraday cage made of flexible metallic fabric. They are typically used to block remote wiping or alteration of wireless devices recovered in criminal investigations, but may also be used by the general public to protect against data theft or to enhance digital privacy.
-
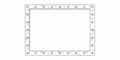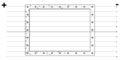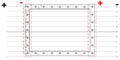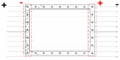
Animation showing how a Faraday cage (box) works. When an external electrical field (arrows) is applied, the electrons (little balls) in the metal move to the left side of the cage, giving it a negative charge, while the remaining unbalanced charge of the nuclei give the right side a positive charge. These induced charges create an opposing electric field that cancels the external electric field throughout the box.
-
SLC-40 with SpaceX Falcon 9 launch infrastructure. The four towers surrounding the rocket are lightning arresters, acting like a giant Faraday cage
See also
 In Spanish: Jaula de Faraday para niños
In Spanish: Jaula de Faraday para niños