Edible mushroom facts for kids

Edible mushrooms are the fleshy and edible fruit bodies of several species of macrofungi (fungi which bear fruiting structures that are large enough to be seen with the naked eye). They can appear either below ground (hypogeous) or above ground (epigeous) where they may be picked by hand. Edibility may be defined by criteria that include absence of poisonous effects on humans and desirable taste and aroma. Edible mushrooms are consumed for their nutritional and culinary value. Mushrooms, especially dried shiitake, are sources of umami flavor. Especially tasty and desired mushrooms are referred as "choice edible".
Edible mushrooms include many fungal species that are either harvested wild or cultivated. Easily cultivated and common wild mushrooms are often available in markets, and those that are more difficult to obtain (such as the prized truffle, matsutake and morel) may be collected on a smaller scale by private gatherers. Some preparations may render certain poisonous mushrooms fit for consumption.
Before assuming that any wild mushroom is edible, it should be identified. Accurate determination and proper identification of a species is the only safe way to ensure edibility, and the only safeguard against possible accident. Some mushrooms that are edible for most people can cause allergic reactions in some individuals, and old or improperly stored specimens can cause food poisoning. Great care should therefore be taken when eating any fungus for the first time, and only small quantities should be consumed in case of individual allergies. Deadly poisonous mushrooms that are frequently confused with edible mushrooms and responsible for many fatal poisonings include several species of the genus Amanita, particularly Amanita phalloides, the death cap. Even normally edible species of mushrooms may be dangerous, as mushrooms growing in polluted locations can accumulate pollutants, such as heavy metals.
Despite long-term use in folk medicine, there is no scientific evidence that consuming "medicinal mushrooms" cures or lowers the risk of human diseases.
Contents
History of mushroom use
Mycophagy the act of consuming mushrooms, dates back to ancient times. Edible mushroom species have been found in association with 13,000-year-old archaeological sites in Chile. Ötzi, the mummy of a man who lived between 3400 and 3100 BCE in Europe, was found with two types of mushroom. The Chinese value mushrooms for supposed medicinal properties as well as for food. Ancient Romans and Greeks, particularly the upper classes, used mushrooms for culinary purposes. Food tasters were employed by Roman emperors to ensure that mushrooms were safe to eat.
| Mushroom and truffle production – 2019 | |
|---|---|
| Country | (millions of tonnes) |
| 8.94 | |
| 0.47 | |
| 0.38 | |
| 0.36 | |
| 0.30 | |
| World | 11.90 |
| Source: FAOSTAT of the United Nations | |
Production
In 2019, world production of commercial mushrooms and recorded truffle collection reported to the Food and Agriculture Organization was 11.9 million tonnes, led by China with 75% of the total (table).
Culinary uses
Commercially cultivated
Mushroom cultivation has a long history, with over twenty species commercially cultivated. Mushrooms are cultivated in at least 60 countries. A fraction of the many fungi consumed by humans are currently cultivated and sold commercially. Commercial cultivation is important ecologically, as there have been concerns of depletion of larger fungi such as chanterelles in Europe, possibly because the group has grown popular, yet remains a challenge to cultivate.
- Agaricus bisporus dominates the edible mushroom market in North America and Europe, in several forms. It is an edible basidiomycete mushroom native to grasslands in Europe and North America. As it ages, this mushroom turns from small, white and smooth to large and light brown. In its youngest form, it is known as the 'common mushroom', 'button mushroom', 'cultivated mushroom', and 'champignon mushroom'. Its fully mature form is known as 'portobello'. Its semi-mature form is known variously as 'cremini', 'baby-bella', 'Swiss brown' mushroom, 'Roman brown' mushroom, 'Italian brown' mushroom, or 'chestnut' mushroom.
- Pleurotus species, the oyster mushrooms, are commonly grown at industrial scale.
- Lentinula edodes, the Shiitake mushroom
- Auricularia auricula-judae, wood ear or jelly ear mushroom
- Volvariella volvacea, the paddy straw mushroom or straw mushroom
- Flammulina velutipes, the enoki mushroom, golden needle mushroom, seafood mushroom, lily mushroom, winter mushroom, velvet foot, velvet shank or velvet stem
- Tremella fuciformis, the snow fungus, snow ear, silver ear fungus and white jelly mushroom
- Hypsizygus tessellatus, aka Hypsizygus marmoreus, the beech mushroom, also known in its white and brown varieties as Bunapi-shimeji and Buna-shimeji, respectively
- Stropharia rugosoannulata, the wine cap mushroom, burgundy mushroom, garden giant mushroom or king stropharia
- Cyclocybe aegerita, the pioppino, velvet pioppini, poplar or black poplar mushroom
- Hericium erinaceus, the lion's mane, monkey head, bearded tooth, satyr's beard, bearded hedgehog, or pom pom mushroom.
Commercially harvested wild edibles
Some species are difficult to cultivate; others (particularly mycorrhizal species) have not yet been successfully cultivated. Some of these species are harvested from the wild, and can be found in markets. When in season they can be purchased fresh, and many species are sold dried as well. The following species are commonly harvested from the wild:
- Boletus edulis or edible Boletus, native to Europe, known in Italian as fungo porcino (plural 'porcini') (pig mushroom), in German as Steinpilz (stone mushroom), in Russian as Russian: Белый гриб, tr. Bely grib (white mushroom), in Albanian as (wolf mushroom), in French as the cèpe and in the UK as the penny bun. It is also known as the king bolete, and is renowned for its delicious flavor. It is sought after worldwide, and can be found in a variety of culinary dishes.
- Calbovista subsculpta commonly known as the sculptured giant puffball is a common puffball of the Rocky Mountains and Pacific Coast ranges of western North America. The puffball is more or less round with a diameter of up to 15 cm (6 in), white becoming brownish in age, and covered with shallow pyramid-shaped plates or scales. It fruits singly or in groups along roads and in open woods at high elevations, from summer to autumn. It is considered a choice edible species while its interior flesh (the gleba) is still firm and white. As the puffball matures, its insides become dark brown and powdery from mature spores.
- Calvatia gigantea the giant puffball. Giant puffballs are considered a choice edible species and are commonly found in meadows, fields, and deciduous forests usually in late summer and autumn. It is found in temperate areas throughout the world. They can reach diameters up to 150 cm (60 in) and weights of 20 kg (45 lb). The inside of mature Giant puffballs is greenish brown, whereas the interior of immature puffballs is white. The large white mushrooms are edible when young.
- Cantharellus cibarius (the chanterelle), The yellow chanterelle is one of the best and most easily recognizable mushrooms, and can be found in Asia, Europe, North America and Australia. There are poisonous mushrooms which resemble it, though these can be confidently distinguished if one is familiar with the chanterelle's identifying features.
- Craterellus tubaeformis, the tube chanterelle, yellowfoot chanterelle or yellow-leg
- Clitocybe nuda, blewit (or blewitt)
- Cortinarius caperatus, the Gypsy mushroom
- Craterellus cornucopioides, Trompette de la mort (trumpet of death) or horn of plenty
- Grifola frondosa, known in Japan as maitake (also "hen of the woods" or "sheep’s head"), a large, hearty mushroom commonly found on or near stumps and bases of oak trees, and believed to have Macrolepiota procera properties.
- Gyromitra esculenta (the false morel) is prized by the Finns. This mushroom is deadly poisonous if eaten raw, but highly regarded when parboiled (see below).
- Hericium erinaceus, a tooth fungus; also called "lion's mane mushroom"
- Hydnum repandum, sweet tooth fungus, hedgehog mushroom or hedgehog fungus, urchin of the woods
- Lactarius deliciosus, saffron milk cap, consumed around the world and prized in Russia
- Morchella species, (morel family) morels belong to the ascomycete grouping of fungi. They are usually found in open scrub, woodland or open ground in late spring. When collecting this fungus, care must be taken to distinguish it from the poisonous false morels, including Gyromitra esculenta. The morel must be cooked before eating.
- Morchella conica var. deliciosa
- Morchella esculenta var. rotunda
- Pleurotus species are sometimes commercially harvested despite ease of cultivation.
- Tricholoma matsutake, the matsutake, a mushroom highly prized in Japanese cuisine.
- Tuber, species, (the truffle), Truffles have long eluded the modern techniques of domestication known as trufficulture. Although the field of trufficulture has greatly expanded since its inception in 1808, several species still remain uncultivated. Domesticated truffles include
- Tuber aestivum, black summer truffle
- Tuber borchii
- Tuber brumale
- Tuber indicum, Chinese black truffle
- Tuber macrosporum, smooth black truffle
- Tuber mesentericum, the Bagnoli truffle
-
Chanterelles in the wild
-
Baskets of mixed culinary mushrooms at the San Francisco Ferry Building
-
Black Périgord truffle, cut in half
Other edible wild species
Many wild species are consumed around the world. The species which can be identified "in the field" (without use of special chemistry or a microscope) and therefore safely eaten vary widely from country to country, even from region to region. This list is a sampling of lesser-known species that are reported as edible.
- Agaricus arvensis (Horse Mushroom)
- Agaricus silvaticus (Pinewood Mushroom)
- Amanita caesarea (Caesar's Mushroom)
- Armillaria mellea (Honey mushroom)
- Boletus badius (Bay Bolete)
- Calocybe gambosa (St George's mushroom)
- Calvatia utriformis (Lycoperdon caelatum)
- Chroogomphus species (pine-spikes or spike-caps)
- Clavariaceae species (coral fungus family)
- Clavulinaceae species (coral fungus family)
- Coprinus comatus, the Shaggy mane, Shaggy Inkcap or Lawyer's Wig. Must be cooked as soon as possible after harvesting or the caps will first turn dark and unappetizing, then deliquesce and turn to ink. Not found in markets for this reason.
- Corn smut economically important pathogens of cereals. Known in Mexico as huitlacoche, where it is considered a delicacy. Corn smuts can be used as filings in quesadillas, tacos and soups.
- Cortinarius variicolor
- Cyttaria espinosae
- Fistulina hepatica (beefsteak polypore or the ox tongue)
- Flammulina velutipes (Velvet Shank or Winter Fungus)
- Hygrophorus chrysodon
- Kalaharituber pfeilii
- Lactarius deterrimus (Orange Milkcap)
- Lactarius salmonicolor
- Lactarius subdulcis (mild milkcap)
- Lactarius volemus (Fishy Milkcap). Also known as "Weeping Milkcap".
- Laetiporus sulphureus (Sulphur shelf). Also known by names such as the "chicken mushroom", "chicken fungus", the sulphur shelf is a distinct bracket fungus popular among mushroom hunters.
- Leccinum aurantiacum (Red-capped scaber stalk)
- Leccinum scabrum (Birch bolete)
- Leccinum versipelle (Orange Birch Bolete / Boletus testaceoscaber)
- Macrolepiota procera (Parasol Mushroom); globally, it is widespread in temperate regions
- Marasmius oreades (Fairy Ring Champignon)
- Polyporus mylittae
- Polyporus squamosus (Dryad's saddle and Pheasant's back mushroom)
- Ramariaceae species (coral fungus family)
- Rhizopogon luteolus
- Russula, some members of this genus, such as R. laeta, are edible
- Sparassis crispa, also known as "cauliflower mushroom"
- Suillus bovinus
- Suillus granulatus (Weeping Bolete). Also known as "Granulated Bolete".
- Suillus luteus (Slippery Jack)
- Suillus tomentosus
- Tricholoma terreum
Conditionally-edible species

- Amanita fulva (Tawny Grisette) must be cooked before eating.
- Amanita muscaria is edible if parboiled to leach out toxins, fresh mushrooms cause vomiting, twitching, drowsiness, and hallucinations due to the presence of muscimol. Although present in A. muscaria, ibotenic acid is not in high enough concentration to produce any physical or psychological effects unless massive amounts are ingested.
- Amanita rubescens (The Blusher) must be cooked before eating.
- Coprinopsis atramentaria (Coprinus atramentarius - Common Inkcap) is edible without special preparation, however, consumption with alcohol is toxic due to the presence of coprine. Some other Coprinus spp. share this property.
- Gyromitra esculenta (False Morel - Turban, Brain Mushroom) is eaten by some after it has been parboiled, however, many mycologists do not recommend it. Raw Gyromitra are toxic due to the presence of gyromitrin, and it is not known whether all of the toxin can be removed by parboiling.
- Lactarius spp. Apart from Lactarius deliciosus (Saffron Milkcap), which is universally considered edible, other Lactarius spp. that are considered toxic elsewhere in the world are eaten in some Eastern European countries and Russia after pickling or parboiling.
- Lepista saeva (Field Blewit, Blue Leg, or Tricholoma personatum) must be cooked before eating.
- Morchella esculenta (Morel) must be cooked before eating.
- Verpa bohemica is considered choice by some—it even can be found for sale as a "morel"—but cases of toxicity have been reported. Verpas appear to contain monomethylhydrazine and similar precautions apply to them as Gyromitra species.
Nutrients
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |
|---|---|
| Energy | 93 kJ (22 kcal) |
|
3.3 g
|
|
|
0.3 g
|
|
|
Protein
|
3.1 g
|
| Vitamins | Quantity
%DV†
|
| Vitamin A equiv. |
0%
0 μg |
| Thiamine (B1) |
7%
0.08 mg |
| Riboflavin (B2) |
33%
0.4 mg |
| Niacin (B3) |
23%
3.6 mg |
| Pantothenic acid (B5) |
30%
1.5 mg |
| Vitamin B6 |
8%
0.1 mg |
| Folate (B9) |
4%
17 μg |
| Vitamin B12 |
0%
0 μg |
| Choline |
4%
17.3 mg |
| Vitamin D |
1%
7 IU |
| Vitamin E |
0%
0 mg |
| Vitamin K |
0%
0 μg |
| Minerals | Quantity
%DV†
|
| Calcium |
0%
3 mg |
| Copper |
16%
0.32 mg |
| Iron |
4%
0.5 mg |
| Magnesium |
3%
9 mg |
| Manganese |
2%
0.05 mg |
| Phosphorus |
12%
86 mg |
| Potassium |
11%
318 mg |
| Selenium |
13%
9.3 μg |
| Zinc |
5%
0.52 mg |
| Other constituents | Quantity |
| Water | 92 g |
| †Percentages estimated using US recommendations for adults. | |
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |
|---|---|
| Energy | 117 kJ (28 kcal) |
|
5.3 g
|
|
|
0.5 g
|
|
|
Protein
|
2.2 g
|
| Vitamins | Quantity
%DV†
|
| Vitamin A equiv. |
0%
0 μg |
| Thiamine (B1) |
9%
0.1 mg |
| Riboflavin (B2) |
25%
0.3 mg |
| Niacin (B3) |
28%
4.5 mg |
| Pantothenic acid (B5) |
44%
2.2 mg |
| Vitamin B6 |
8%
0.1 mg |
| Folate (B9) |
5%
18 μg |
| Vitamin B12 |
0%
0 μg |
| Choline |
4%
19.9 mg |
| Vitamin D |
4%
21 IU |
| Vitamin E |
0%
0 mg |
| Vitamin K |
0%
0 μg |
| Minerals | Quantity
%DV†
|
| Calcium |
1%
6 mg |
| Copper |
25%
0.5 mg |
| Iron |
13%
1.7 mg |
| Magnesium |
3%
12 mg |
| Manganese |
5%
0.1 mg |
| Phosphorus |
12%
87 mg |
| Potassium |
12%
356 mg |
| Selenium |
19%
13.4 μg |
| Zinc |
9%
0.9 mg |
| Other constituents | Quantity |
| Water | 91.1 g |
| †Percentages estimated using US recommendations for adults. | |
A commonly eaten mushroom is the white mushroom (Agaricus bisporus). In a 100-gram (3+1⁄2-ounce) reference serving, Agaricus mushrooms provide 92 kilojoules (22 kilocalories) of food energy and are 92% water, 3% carbohydrates, 3% protein, and 0.3% fat (table). They contain high levels (20% or more of the Daily Value, DV) of riboflavin, niacin, and pantothenic acid (24–33% DV), with moderate content of phosphorus (table). Otherwise, raw white mushrooms generally have low amounts of essential nutrients (table). Although cooking (by boiling) lowers mushroom water content only 1%, the contents per 100 grams for several nutrients increase appreciably, especially for dietary minerals (table for boiled mushrooms).
The content of vitamin D is absent or low unless mushrooms are exposed to sunlight or purposely treated with artificial ultraviolet light (see below), even after harvesting and processed into dry powder.
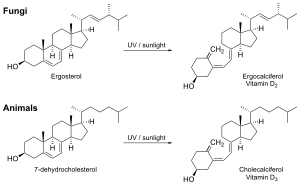
Vitamin D
Mushrooms exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light produce vitamin D2 before or after harvest by converting ergosterol, a chemical found in large concentrations in mushrooms, to vitamin D2. This is similar to the reaction in humans, where vitamin D3 is synthesized after exposure to sunlight.
Testing showed an hour of UV light exposure before harvesting made a serving of mushrooms contain twice the U.S. Food and Drug Administration's daily recommendation of vitamin D, and 5 minutes of artificial UV light exposure after harvesting made a serving of mushrooms contain four times the FDA's daily recommendation of vitamin D. Analysis also demonstrated that natural sunlight produced vitamin D2.
The ergocalciferol, vitamin D2, in UV-irradiated mushrooms is not the same form of vitamin D as is produced by UV-irradiation of human or animal skin, fur, or feathers (cholecalciferol, vitamin D3). Although vitamin D2 clearly has vitamin D activity in humans and is widely used in food fortification and in nutritional supplements, vitamin D3 is more commonly used in dairy and cereal products.
Use in traditional medicine
Medicinal mushrooms are mushrooms or extracts from mushrooms that are thought to be treatments for diseases, yet remain unconfirmed in mainstream science and medicine, and so are not approved as drugs or medical treatments. Such use of mushrooms therefore falls into the domain of traditional medicine for which there is no direct high-quality clinical evidence of efficacy.
Preliminary research on mushroom extracts has been conducted to determine if anti-disease properties exist, such as for polysaccharide-K or lentinan. Some extracts have widespread use in Japan, Korea and China, as potential adjuvants for radiation treatments and chemotherapy.
-
Chicken of the woods (Laetiporus sulphureus)
-
Common Morel (Morchella esculenta)
Safety concerns
Some wild species are toxic, or at least indigestible, when raw. The safety of consuming Reishi mushrooms has not been adequately demonstrated, as of 2019. Reishi mushrooms may cause side effects including dryness of the mouth or throat, itchiness, rash, stomach upset, diarrhea, headache, or allergic reactions. Failure to identify poisonous mushrooms and confusing them with edible ones has resulted in death.
Gallery
-
Stuffed mushrooms prepared using portabello mushrooms
See also
 In Spanish: Seta comestible para niños
In Spanish: Seta comestible para niños