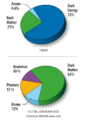Dark energy facts for kids
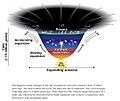
Dark energy is the name given to the force that is believed to be making the universe larger. Distant galaxies appear to be moving away from us at high speed: the idea is that the universe is getting bigger and has been since the Big Bang. Measurements are now accurate enough to allow astronomers to tell that these galaxies seem to be accelerating away from us. The universe is expanding at an increasing rate.
This faster and faster expansion is not understood by scientists. There are many ideas for what might be causing the rapid expansion. However, at the moment, cosmologists who study it do not have an answer. It is as if there was something there in empty space providing a repulsive force (Anti-gravity) that makes the universe expand. This has been named dark energy.
As of 2021, there are active areas of cosmology research to understand the fundamental nature of dark energy. The best current measurements indicate that dark energy contributes 68% of the total energy in the present-day observable universe. The mass–energy of dark matter and ordinary (baryonic) matter contributes 26% and 5%, respectively, and other components such as neutrinos and photons contribute a very small amount.
Dark energy's density is very low: 6×10−10 J/m3 (~7×10−30 g/cm3), much less than the density of ordinary matter or dark matter within galaxies. However, it dominates the universe because it is uniform across space.
The term "dark energy", echoing Fritz Zwicky's "dark matter" from the 1930s, was coined by Michael Turner in 1998.
In February of 2023, University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa researchers hypothesized that the expansion of the universe, coupled with the expansion of black holes produces dark energy. This is called cosmological coupling.
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Energía oscura para niños
In Spanish: Energía oscura para niños