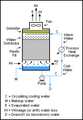
Cooling towers are towers that are used to transfer waste heat to the atmosphere. Cooling towers may use the evaporation of water to remove heat and cool the working fluid to near the wet-bulb air temperature. They may also use only air to cool the working fluid to near the dry-bulb air temperature. Cooling towers are used in oil refineries, petrochemical plants and power stations, especially nuclear power stations. In a nuclear power plant, the cooling tower is isolated from the nuclear reactor by a heat exchanger, and the steam from the cooling tower is not radioactive. The cooling tower is usually the tallest and most visible part of a nuclear power plant, much taller than the reactor building or turbine hall.
Images for kids
-
A typical evaporative, forced draft open-loop cooling tower rejecting heat from the condenser water loop of an industrial chiller unit
-
Forced draft wet cooling towers (height: 34 meters) and natural draft wet cooling tower (height: 122 meters) in Westfalen, Germany.
-
A 1902 engraving of "Barnard's fanless self-cooling tower", an early large evaporative cooling tower that relied on natural draft and open sides rather than a fan; water to be cooled was sprayed from the top onto the radial pattern of vertical wire-mesh mats.
-
Two HVAC cooling towers on the rooftop of a shopping center (Darmstadt, Hesse, Germany)
-
FRP cooling tower installed on roof top
-
Cell of a cross-flow type cooling tower with fill material, and circulating water visible
-
Industrial cooling towers for a power plant
-
Industrial cooling towers for fruit processing
-
Field erected cooling tower
-
Field-erected cooling towers
-
-
-
Access stairs at the base of a massive hyperboloid cooling tower give a sense of its scale (UK).
-
Mechanical draft crossflow cooling tower used in an HVAC application
-
Showers inside cooling tower
-
Forced-draft counter-flow package-type cooling tower
-
Fan-induced draft, counter-flow cooling tower
-
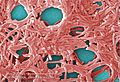
Legionella pneumophila (5000 × magnification)
-
A multitude of microscopic organisms such as bacterial colonies, fungi, and algae can easily thrive within the moderately high temperatures present inside a cooling tower.
-
Fill plates at the bottom of the Iru Power Plant cooling tower (Estonia). Tower is shut down, revealing numerous water spray heads.
-
Fog produced by Eggborough power station
-
Flue gas stack inside a natural draft wet cooling tower
-
Flue gas stack connection into a natural draft wet cooling tower
-
Large hyperboloid cooling towers made of structural steel for a power plant in Kharkiv (Ukraine)
See also
 In Spanish: Torre de refrigeración para niños
In Spanish: Torre de refrigeración para niños

 In Spanish: Torre de refrigeración para niños
In Spanish: Torre de refrigeración para niños