Petrochemical facts for kids

Petrochemicals (also known as petroleum distillates) are chemical products derived from petroleum. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable sources such as corn, palm fruit or sugar cane.
The two most common petrochemical classes are olefins (including ethylene and propylene) and aromatics (including benzene, toluene and xylene isomers).
Oil refineries produce olefins and aromatics by fluid catalytic cracking of petroleum fractions. Chemical plants produce olefins by steam cracking of natural gas liquids like ethane and propane. Aromatics are produced by catalytic reforming of naphtha. Olefins and aromatics are the building-blocks for a wide range of materials such as solvents, detergents, and adhesives. Olefins are the basis for polymers and oligomers used in plastics, resins, fibers, elastomers, lubricants, and gels.
Global ethylene and propylene production are about 115 million tonnes and 70 million tonnes per annum, respectively. Aromatics production is approximately 70 million tonnes. The largest petrochemical industries are located in the USA and Western Europe; however, major growth in new production capacity is in the Middle East and Asia. There is substantial inter-regional petrochemical trade.
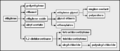
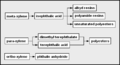
Primary petrochemicals are divided into three groups depending on their chemical structure:
- Olefins includes Ethene, Propene, Butenes and butadiene. Ethylene and propylene are important sources of industrial chemicals and plastics products. Butadiene is used in making synthetic rubber.
- Aromatics includes Benzene, toluene and xylenes, as a whole referred to as BTX and primarily obtained from petroleum refineries by extraction from the reformate produced in catalytic reformers using Naphtha obtained from petroleum refineries. Benzene is a raw material for dyes and synthetic detergents, and benzene and toluene for isocyanates MDI and TDI used in making polyurethanes. Manufacturers use xylenes to produce plastics and synthetic fibers.
- Synthesis gas is a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen used to make ammonia and methanol. Ammonia is used to make the fertilizer urea and methanol is used as a solvent and chemical intermediate. Steam crackers are not to be confused with steam reforming plants used to produce hydrogen and ammonia.
- Methane, ethane, propane and butanes obtained primarily from natural gas processing plants.
- Methanol and formaldehyde.
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Producto petroquímico para niños
In Spanish: Producto petroquímico para niños