Chariot facts for kids
A chariot is a type of carriage driven by a charioteer using primarily horses to provide rapid motive power. Chariots were used by armies as transport or mobile archery platforms, for hunting or for racing, and as a conveniently fast way to travel for many ancient people.
The word "chariot" comes from the Latin carrus, itself a loanword from Gaulish. A chariot of war or one used in military parades was called a car. In ancient Rome and some other ancient Mediterranean civilizations, a biga required two horses, a triga three, and a quadriga four.
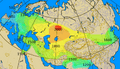
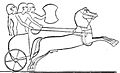
The horse chariot was a fast, light, open, two-wheeled conveyance drawn by two or more horses that were hitched side by side, and was little more than a floor with a waist-high guard at the front and sides. It was initially used for ancient warfare during the Bronze and Iron Ages; but, after its military capabilities had been superseded by cavalry, as horses were gradually bred to be bigger, the chariot was used for travel, in processions, for games, and in races.
Ancient Greek myths says that Poseidon, god of the sea, and Athena, goddess of wisdom, created the chariot together. Poseidon created the horses like waves, and Athena made the chariot. The two gods worked together.
Images for kids
-
Han dynasty bronze models of cavalry and chariots
-
Chariot detail at Airavatesvara Temple built by Rajaraja Chola II of the Chola Empire in the 12th century CE.
-
Stone chariot at Hampi, built under the Vijayanagara Empire, early 16th century CE.
-
A golden chariot made during Achaemenid Empire (550–330 BCE).
-
Ramses II fighting from a chariot at the Battle of Kadesh with two archers, one with the reins tied around the waist to free both hands (relief from Abu Simbel)
-
The Charioteer of Delphi was dedicated to the god Apollo in 474 BCE by the tyrant of Gela in commemoration of a Pythian racing victory at Delphi.
-
Two female charioteers from Tiryns 1200 BCE
-
A petroglyph in a double burial, c. 1000 BCE (the Nordic Bronze Age)
-
A winner of a Roman chariot race
-
A mosaic of the Kasta Tomb in Amphipolis depicting the abduction of Persephone by Pluto, 4th century BCE.
-
The goddess Nike riding on a two-horse chariot, from an Apulian patera (tray), Magna Graecia, 4th century BCE.
-
Procession of chariots on a Late Geometric amphora from Athens (c. 720–700 BCE).
-
Sculpture by Thomas Thornycroft of Boudica and her daughters in her chariot, addressing her troops before the battle.
-
Procession of chariots and warriors on the Vix krater (c. 510), a vessel of Archaic Greek workmanship found in a Gallic burial.
-
Modern reconstruction of a Hussite war wagon.
-
Chariot burial of Zheng
-
Bronze Chinese charioteer from the Warring States period (403–221 BCE).
-
Powerful landlord in chariot (Eastern Han, 25–220 CE, Anping County, Hebei).
See also
 In Spanish: Carro de guerra para niños
In Spanish: Carro de guerra para niños