Botany facts for kids
Botany is the study of plants. It is a science. It is a branch of biology, and is also called plant biology. It is sometimes called phytology. Scientists who study botany are called botanists. They study how plants work.
Branches of Botany
- Agronomy—Application of plant science to crop production
- Bryology—Mosses, liverworts, and hornworts
- Forestry—Forest management and related studies
- Horticulture—Cultivated plants
- Micropaleontology—Pollen and spores
- Mycology—Fungi
- Paleobotany—Fossil plants
- Phycology—Algae
- Phytochemistry—Plant secondary chemistry and chemical processes
- Phytopathology—Plant diseases
- Plant anatomy—Cell and tissue structure
- Plant ecology—Role of plants in the environment
- Plant genetics—Genetic inheritance in plants
- Plant morphology—Structure and life cycles
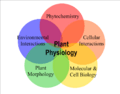
- Plant physiology—Life functions of plants
- Plant systematics—Classification and naming of plants
Notable botanists
- Ibn al-Baitar (d. 1248), Andalusian-Arab scientist, botanist, pharmacist, physician, and author of one of the largest botanical encyclopedias.
- Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon (1707–1788) was a French naturalist who held the position of Intendant of the Jardin du Roi ('King's Garden'). Buffon published thirty-five volumes of his Histoire naturelle during his lifetime, and nine more volumes were published after his death.
- Luther Burbank (1849–1926), American botanist, horticulturist, and a pioneer in agricultural science.
- Charles Darwin (1809–1882) wrote eight important books on botany after he published the Origin of Species.
- Al-Dinawari (828–896), Kurdish botanist, historian, geographer, astronomer, mathematician, and founder of Arabic botany.
- Conrad Gessner (1516–1565) was a Swiss naturalist and bibliographer.
- Joseph Dalton Hooker (1817–1911), English botanist and explorer. Second winner of Darwin Medal.
- Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778), Swedish botanist, physician and zoologist who laid the foundations for the modern scheme of Binomial nomenclature. He is known as the father of modern taxonomy, and is also considered one of the fathers of modern ecology.
- Gregor Mendel (1822–1884), Augustinian priest and scientist, and is often called the father of genetics for his study of the inheritance of traits in pea plants.
- John Ray (1627–1705) was an English naturalist, the father of English natural history.
- G. Ledyard Stebbins (1906–2000) was an American botanist and geneticist. He was one of the leading evolutionary biologists of the 20th century.
- Eduard Strasburger (1844–1912) was a Polish-German professor who was one of the most famous botanists of the 19th century.
- Nikolai Vavilov (1887–1943) was a Russian botanist and geneticist. He showed how and where crop plants evolved. He studied and improved wheat, corn, and other cereal crops.
Images for kids
-
The fruit of Myristica fragrans, a species native to Indonesia, is the source of two valuable spices, the red aril (mace) enclosing the dark brown nutmeg.
-
An engraving of the cells of cork, from Robert Hooke's Micrographia, 1665
-
The nodules of Medicago italica contain the nitrogen fixing bacterium Sinorhizobium meliloti. The plant provides the bacteria with nutrients and an anaerobic environment, and the bacteria fix nitrogen for the plant.
-
Thale cress, Arabidopsis thaliana, the first plant to have its genome sequenced, remains the most important model organism.
-
Transverse section of a fossil stem of the Devonian vascular plant Rhynia gwynne-vaughani
-
A nineteenth-century illustration showing the morphology of the roots, stems, leaves and flowers of the rice plant Oryza sativa
-
A botanist preparing a plant specimen for mounting in the herbarium
See also
 In Spanish: Botánica para niños
In Spanish: Botánica para niños