Plant anatomy facts for kids
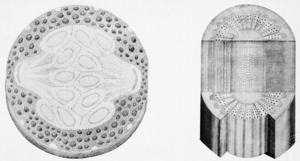
Plant anatomy or phytotomy is the general term for the study of the internal structure of plants. Originally it included plant morphology, the description of the physical form and external structure of plants, but since the mid-20th century plant anatomy has been considered a separate field referring only to internal plant structure. Plant anatomy is now frequently investigated at the cellular level, and often involves the sectioning of tissues and microscopy.
Structural divisions
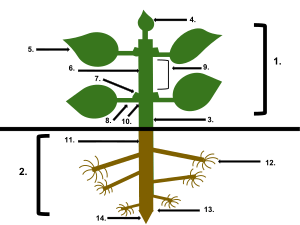
Some studies of plant anatomy use a systems approach, organized on the basis of the plant's activities, such as nutrient transport, flowering, pollination, embryogenesis or seed development. Others are more classically divided into the following structural categories:
- Flower anatomy, including study of the Calyx, Corolla, Androecium, and Gynoecium
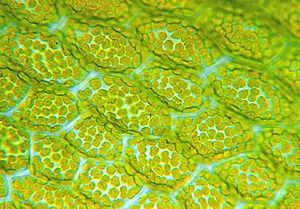
- Leaf anatomy, including study of the Epidermis, stomata and Palisade cells
- Stem anatomy, including Stem structure and vascular tissues, buds and shoot apex
- Fruit/Seed anatomy, including structure of the Ovule, Seed, Pericarp and Accessory fruit
- Wood anatomy, including structure of the Bark, Cork, Xylem, Phloem, Vascular cambium, Heartwood and sapwood and branch collar
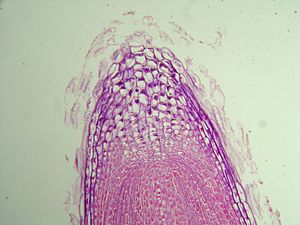
- Root anatomy, including structure of the Root, root tip, endodermis
Images for kids
-
Nehemiah Grew, Father of Plant Anatomy
See also
 In Spanish: Anatomía vegetal para niños
In Spanish: Anatomía vegetal para niños