Boroughs of New York City facts for kids
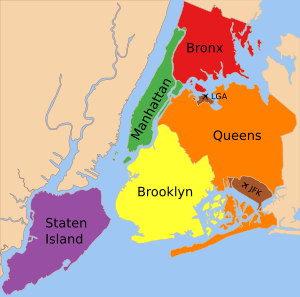
The boroughs of New York City are the five major governmental districts that compose New York City. The boroughs are the Bronx, Brooklyn, Manhattan, Queens, and Staten Island. Each borough is coextensive with a respective county of the State of New York: The Bronx is Bronx County, Brooklyn is Kings County, Manhattan is New York County, Queens is Queens County, and Staten Island is Richmond County.
All five boroughs came into existence with the creation of modern New York City in 1898, when New York County (then including the Bronx), Kings County, Richmond County, and part of Queens County were consolidated within one municipal government under a new city charter. All former municipalities within the newly consolidated city were dissolved.
New York City was originally confined to Manhattan Island and the smaller surrounding islands that formed New York County. As the city grew northward, it began annexing areas on the mainland, absorbing territory from Westchester County into New York County in 1874 (West Bronx) and 1895 (East Bronx). During the 1898 consolidation, this territory was organized as the Borough of the Bronx, though still part of New York County. In 1914, Bronx County was split off from New York County so that each borough was then coterminous with a county.
When the western part of Queens County was consolidated with New York City in 1898, that area became the Borough of Queens. In 1899, the remaining eastern section of Queens County was split off to form Nassau County on Long Island, thereafter making the borough and county of Queens coextensive with each other.
Contents
Terminology
The term borough was adopted in 1898 to describe a form of governmental administration for each of the five fundamental constituent parts of the newly consolidated city. Under the 1898 City Charter adopted by the New York State Legislature, a borough is a municipal corporation that is created when a county is merged with populated areas within it. The limited powers of the boroughs are inferior to the authority of the government of New York City, contrasting significantly with the powers of boroughs as that term is used in Connecticut, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania, where a borough is an independent level of government, as well as with borough forms used in other states and in Greater London.
Background
|
New York City's five boroughs
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jurisdiction | Population | Land area | Density | |||
| Borough | County | Estimate (2015) |
square miles |
square km |
persons / sq. mi |
persons / sq. km |
|
|
|
1,644,518 | 22.83 | 59.1 | 72,033 | 27,826 |
|
|
|
1,455,444 | 42 | 110 | 34,653 | 13,231 |
|
|
|
2,636,735 | 71 | 180 | 37,137 | 14,649 |
|
|
|
2,339,150 | 109 | 280 | 21,460 | 8,354 |
|
|
|
474,558 | 58.5 | 152 | 8,112 | 3,132 |
|
|
8,550,405 | 303.33 | 781.1 | 28,188 | 10,947 | |
|
|
19,795,791 | 47,214 | 122,284 | 416.4 | 159 | |
|
|
||||||
New York City is often referred to collectively as the five boroughs, which can unambiguously refer to the city proper as a whole, avoiding confusion with any particular borough or with the Greater New York metropolitan area. The term is also used by politicians to counter a frequent focus on Manhattan and thereby to place all five boroughs on equal footing. In the same vein, the term outer boroughs refers to all of the boroughs excluding Manhattan, even though the geographic center of the city is along the Brooklyn–Queens border.
Changes
All five boroughs were created in 1898 during consolidation, when the city's modern boundaries were established.
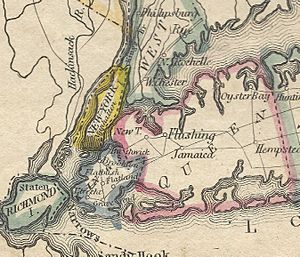
The Bronx originally included parts of New York County outside of Manhattan that had previously been ceded by neighboring Westchester County in two stages; in 1874 (southern Yonkers, and the towns of Kingsbridge, West Farms, and Morrisania) and then following a referendum in 1894 (towns of Westchester, Williamsbridge, and the southern portion of Eastchester). Ultimately in 1914, the present-day separate Bronx County became the most recent county to be created in the State of New York.
The borough of Queens consists of what formerly was only the western part of a then-larger Queens County. In 1899, the three eastern towns of Queens County that had not joined the city the year before—the towns of Hempstead, North Hempstead, and Oyster Bay—formally seceded from Queens County to form the new Nassau County.
The borough of Staten Island, coextensive with Richmond County, was officially the borough of Richmond until the name was changed in 1975 to reflect its common appellation, while leaving the name of the county unchanged.
Description of the boroughs
There are hundreds of distinct neighborhoods throughout the five boroughs of New York City, many with a definable history and character to call their own.
Manhattan

- Manhattan (co-extensive with New York County) is the geographically smallest and most densely populated borough; is the symbol of New York City, as home to most of the city's skyscrapers and prominent landmarks, including Times Square and Central Park; and may be locally known simply as The City. Manhattan's (New York County's) population density of 72,033 people per square mile (27,812/km2) in 2015 makes it the highest of any county in the United States and higher than the density of any individual U.S. city. Manhattan is the cultural, administrative, and financial center of New York City and contains the headquarters of many major multinational corporations, the United Nations Headquarters, Wall Street, and a number of important universities. Manhattan is often described by Americans as the cultural, financial, media, and entertainment capital of the world. Most of the borough is situated on Manhattan Island, at the mouth of the Hudson River. Several small islands are also part of the borough of Manhattan, including Randall's Island, Wards Island, and Roosevelt Island in the East River, and Governors Island to the south in New York Harbor; Liberty Island, on which the Statue of Liberty stands, is a Manhattan exclave, as is the original portion of Ellis Island. Manhattan Island is loosely divided into Lower, Midtown, and Uptown regions. Uptown Manhattan is divided by Central Park into the Upper East Side and the Upper West Side, and above the park is Harlem. Marble Hill was part of the northern tip of Manhattan Island, but the Harlem River Ship Canal, dug in 1895, separated it from the remainder of Manhattan. Before World War I, the old channel was filled in and Marble Hill became part of the mainland. After a May 1984 court ruled that Marble Hill was part of Bronx County (not New York County), the matter was definitively settled later that year when the New York Legislature overwhelmingly passed legislation declaring the neighborhood part of both New York County and the Borough of Manhattan. New York City's remaining four boroughs are collectively referred to as the outer boroughs.
Brooklyn

- Brooklyn (co-extensive with Kings County), on the western tip of Long Island, is the city's most populous borough. Brooklyn is known for its cultural, social, and ethnic diversity, an independent art scene, distinct neighborhoods, and a distinctive architectural heritage. Downtown Brooklyn is the largest central core neighborhood in the outer boroughs. The borough has a long beachfront shoreline including Coney Island, established in the 1870s as one of the earliest amusement grounds in the country. Marine Park and Prospect Park are the two largest parks in Brooklyn. Since the early 2010s, Brooklyn has evolved into a thriving hub of entrepreneurship and high technology startup firms, and of postmodern art and design.
Queens
- Queens (co-extensive with Queens County), on Long Island north and east of Brooklyn, is geographically the largest borough, the most ethnically diverse county in the United States, as well as the most ethnically diverse urban area in the world. Historically a collection of small towns and villages founded by the Dutch, the borough has since developed both commercial and residential prominence. Downtown Flushing has become one of the busiest central core neighborhoods in the outer boroughs. Parts of Queens such as Bellerose and Forest Hills are relatively suburban in character. Queens is the site of Citi Field, the baseball stadium of the New York Mets, and hosts the annual U.S. Open tennis tournament at Flushing Meadows-Corona Park. Additionally, two of the three busiest airports serving the New York metropolitan area, John F. Kennedy International Airport and LaGuardia Airport, are located in Queens. (The third is Newark Liberty International Airport in Newark, New Jersey.)
The Bronx

- The Bronx (co-extensive with Bronx County) is New York City's northernmost borough and is the only New York City borough that is part of the United States mainland (excluding some islands that are part of the borough). It is the location of Yankee Stadium, the baseball stadium of the New York Yankees, and home to Co-op City, the largest cooperatively owned housing complex in the United States. It is also home to the Bronx Zoo, the world's largest metropolitan zoo, which covers 265 acres (107 ha) and houses over 6,000 animals. Directly to the zoo's north is the New York Botanical Garden, a botanical garden and National Historic Landmark. Pelham Bay Park is the largest park in New York City, at 2,772 acres (1,122 ha).
Staten Island

- Staten Island (co-extensive with Richmond County) is generally the most suburban in character of the five boroughs. Staten Island is connected to Brooklyn by the Verrazzano-Narrows Bridge and to Manhattan by way of the Staten Island Ferry, a free commuter ferry and popular tourist attraction which provides unobstructed views of the Statue of Liberty, Ellis Island, and Lower Manhattan. In central Staten Island, the Staten Island Greenbelt spans approximately 2,500 acres (10 km2), including 28 miles (45 km) of walking trails and one of the last undisturbed forests in the city. Designated in 1984 to protect the island's natural lands, the Greenbelt comprises seven city parks.
Governance
Since 1914, each of New York City's five boroughs has been coextensive with a county of New York State – unlike most U.S. cities, which lie within a single county or extend partially into another county, constitute a county in themselves, or are completely separate and independent of any county.
Each borough is represented by a borough president. Brooklyn, Queens, and Staten Island each have a Borough Hall with limited administrative functions. The Manhattan Borough President's office is situated in the Manhattan Municipal Building. The Bronx Borough President's office used to be in its own Bronx Borough Hall but has been in the Bronx County Courthouse for decades. Since the abolition of the Board of Estimate in 1990 (due to a 1989 ruling of the U.S. Supreme Court), the borough presidents have minimal executive powers, and there is no legislative function within a borough. Executive functions in New York City are the responsibility of the Mayor of New York City, while legislative functions reside with the New York City Council. The borough presidents primarily act as spokesmen, advocates, and ceremonial leaders for their boroughs, have budgets from which they can allocate relatively modest sums of money to community organizations and projects, and appoint the members of the 59 largely advisory community boards in the city's various neighborhoods. The Brooklyn and Queens borough presidents also appoint trustees to the local public library systems in those boroughs.
Being coextensive with an individual county, each borough also elects a district attorney, as does every other county of New York State. While the district attorneys of Manhattan and Brooklyn are popularly referred to as "Manhattan D.A. Cyrus Vance, Jr.", or "Brooklyn D.A. Kenneth P. Thompson" by the media, they are technically and legally the district attorneys of New York County and Kings County, respectively. The same goes for Staten Island. There is no such distinction made for the district attorneys of the other two counties, Queens and the Bronx, since these boroughs share the respective counties' names. Because the five district attorneys are, technically speaking, state officials (since the counties are considered to be arms of the state government), rather than officials of the city government, they are not subject to the term limitations that govern other New York City officials such as the mayor, the New York City Public Advocate, members of the city council, or the borough presidents. Some civil court judges also are elected on a borough-wide basis, although they generally are eligible to serve throughout the city.
In some document collections the boroughs used to be designated with a one-letter abbreviation: K for Brooklyn, M for Manhattan, Q for Queens, R for Staten Island (Richmond County), and X for the Bronx.
Sixth borough
The term "sixth borough" is used to describe any of a number of places that have been metaphorically called a part of New York City because of their geographic location, demographics (they include large numbers of former New Yorkers), special affiliation, or cosmopolitan character. They have included adjacent cities and counties in the New York metropolitan area as well as in other states, U.S. territories, and foreign countries. In 2011, New York Mayor Michael Bloomberg referred to the city's waterfront and waterways as a composite sixth borough during presentations of planned rehabilitation projects along the city's shoreline, including Governor's Island in the Upper New York Bay. The Hudson Waterfront, in the U.S. state of New Jersey, lies opposite Manhattan on the Hudson River, and during the Dutch colonial era, it was under the jurisdiction of New Amsterdam and known as Bergen. Jersey City and Hoboken, in New Jersey's Hudson County, are sometimes referred to as the sixth borough, given their proximity and connections by rapid transit PATH trains to the city. Fort Lee, in Bergen County, opposite Upper Manhattan and connected by the George Washington Bridge, has also been called the sixth borough. Yonkers, New York is often referred to as the sixth borough as well.
See also
 In Spanish: Borough (Nueva York) para niños
In Spanish: Borough (Nueva York) para niños