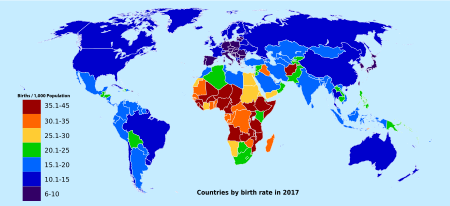
Birth rate facts for kids
Birth rate, also known as natality, is the total number of live human births per 1,000 population for a given period divided by the length of the period in years. The number of live births is normally taken from a universal registration system for births; population counts from a census, and estimation through specialized demographic techniques. The birth rate (along with mortality and migration rates) is used to calculate population growth. The estimated average population may be taken as the mid-year population.
When the crude death rate is subtracted from the crude birth rate (CBR), the result is the rate of natural increase (RNI). This is equal to the rate of population change (excluding migration).
The total (crude) birth rate (which includes all births)—typically indicated as births per 1,000 population—is distinguished from a set of age-specific rates (the number of births per 1,000 persons, or more usually 1,000 females, in each age group). The first known use of the term "birth rate" in English was in 1856.
| Years | CBR | Years | CBR |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1950–1955 | 36.9 | 2000–2005 | 21.0 |
| 1955–1960 | 35.4 | 2005–2010 | 20.3 |
| 1960–1965 | 35.2 | 2010–2015 | 19.5 |
| 1965–1970 | 34.0 | 2015–2020 | 18.5 |
| 1970–1975 | 31.4 | 2020–2025 | 17.5 |
| 1975–1980 | 28.5 | 2025–2030 | 16.6 |
| 1980–1985 | 27.7 | 2030–2035 | 16.0 |
| 1985–1990 | 27.4 | 2035–2040 | 15.5 |
| 1990–1995 | 24.2 | 2040–2045 | 15.0 |
| 1995–2000 | 22.2 | 2045–2050 | 14.6 |
The average global birth rate was 18.1 births per 1,000 total population in 2021. The death rate was 7.7 per 1,000. The RNI was thus 1.6 percent. In 2012 the average global birth rate was 19.611 according to the World Bank and 19.15 births per 1,000 total population according to the CIA, compared to 20.09 per 1,000 total population in 2007.
The 2021 average of 18.1 births per 1,000 total population equates to approximately 4.3 births per second or about 259 births per minute for the world.
Factors affecting birth rate
There are many factors that interact in complex ways, influencing the birth rates of a population. Developed countries have a lower birth rate than underdeveloped countries. A parent's number of children strongly correlates with the number of children that each person in the next generation will eventually have. Factors generally associated with increased fertility include religiosity, intention to have children, and maternal support. Factors generally associated with decreased fertility include wealth, education, female labor participation, urban residence, intelligence, increased female age, women's rights, and (to a lesser degree) increased male age. Many of these factors however are not universal, and differ by region and social class.
See also
 In Spanish: Tasa bruta de natalidad para niños
In Spanish: Tasa bruta de natalidad para niños
- Population ageing
- Population decline