Amoeba facts for kids
An amoeba, often called amoeboid, is a type of cell or unicellular organism which has the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting pseudopods. The shells of amoebas are often composed of calcium. The proteins or materials are synthesized in the cell and exported just outside the cell membrane.
Amoebae are often found within freshwater, typically on vegetation in decay in still or slow moving water, or in the benthic zone of some lakes.
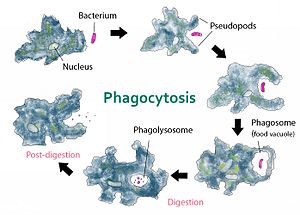
Amoebae move and eat by using pseudopods, which are bulges of cytoplasm formed by the coordinated action of ]microfilaments pushing out the plasma membrane that surrounds the cell.
The food sources of amoebae vary. Some amoebae are predatory and live by consuming bacteria. Some eat dead organic material.
Amoebae ingest their food by encircling and engulfing live prey or particles of scavenged material. They don't have a mouth so there's no fixed place where they ingest their food.
Some amoebae also feed by dissolved nutrients through vesicles formed within the cell membrane .
Amoebas do not form a single taxonomic group; instead, they are found in every major lineage of eukaryotic organisms. Amoeboid cells occur not only among the protozoa, but also in fungi, algae, and animals.
Other well known species include the so-called "brain-eating amoeba" Naegleria fowleri, the intestinal parasite Entamoeba histolytica, which causes amoebic dysentery, and the multicellular "social amoeba" or slime mould Dictyostelium discoideum.
They are common organisms of study because it is easy to keep them in a laboratory. They are used to study protozoa and to demonstrate cell structure and function.
The best known amoeboid protists are the "giant amoebae" Chaos carolinense and Amoeba proteus, both of which have been widely cultivated and studied in classrooms and laboratories.
Images for kids
-
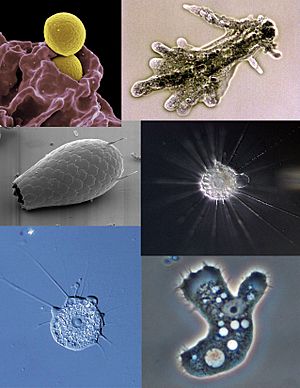
The forms of pseudopodia, from left: polypodial and lobose; monopodial and lobose; filose; conical; reticulose; tapering actinopods; non-tapering actinopods
-
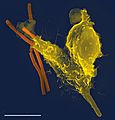
Neutrophil (white blood cell) engulfing anthrax bacteria
-
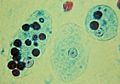
Trophozoites of the pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica with ingested red blood cells
See also
 In Spanish: Ameboide para niños
In Spanish: Ameboide para niños