Allosaurus facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Allosaurus |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
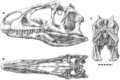
| Replica of Allosaurus skull (San Diego Natural History Museum). | |
| Conservation status | |
|
???
|
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Superorder: | |
| Order: | |
| Suborder: | |
| Family: |
Allosauridae
|
| Genus: |
Allosaurus
Marsh, 1877
|

Allosaurus was a large, meat-eating dinosaur that lived during the Late Jurassic period, about 155 to 150 million years ago. Imagine a giant, fierce bird with sharp teeth and powerful claws – that's kind of what Allosaurus was like! Its name means "different lizard" because its vertebrae (backbones) were different from other dinosaurs known at the time it was discovered.
Allosaurus was a truly remarkable dinosaur. Its powerful build, sharp teeth, and hunting skills made it a formidable predator. By studying Allosaurus, we can learn more about the fascinating world of dinosaurs and the prehistoric ecosystems they inhabited.
Contents
Description

Allosaurus was a fearsome predator with several distinctive features:
- Size: Allosaurus was a large dinosaur, typically measuring around 8.5 meters (28 feet) long, but some specimens suggest they could grow up to 12 meters (39 feet) long! That's longer than a school bus!
- Weight: They weighed around 2.3 metric tons (2.5 short tons). That's about the same weight as a small elephant!
- Skull: Allosaurus had a large skull with bony crests above and in front of its eyes. These crests were probably used for display, maybe to attract mates or intimidate rivals.
- Teeth: It had dozens of sharp, serrated teeth that were perfect for tearing meat. These teeth were constantly replaced throughout its life, so if one broke or fell out, a new one would grow in its place.
- Arms and Hands: Allosaurus had relatively short arms with three-fingered hands. The claws on its fingers were sharp and curved, ideal for grabbing and holding onto prey.
- Legs and Feet: It had strong, muscular legs that allowed it to run quickly. Its feet had three weight-bearing toes with large claws.
- Tail: Allosaurus had a long, heavy tail that helped it balance while running and maneuvering.
Where did Allosaurus live?
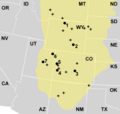
Allosaurus lived in North America, specifically in what is now the western United States. Fossils of Allosaurus have been found in states like Colorado, Utah, Wyoming, Montana, and South Dakota. It shared its environment with other famous dinosaurs like Stegosaurus, Apatosaurus, and Brachiosaurus.
What did Allosaurus eat?

Allosaurus was a carnivore, which means it ate meat. It was a top predator in its ecosystem, meaning it was at the top of the food chain. It likely preyed on large herbivores like Stegosaurus and sauropods (long-necked dinosaurs).
Scientists have different ideas about how Allosaurus hunted:
- Ambush Predator: Some scientists think Allosaurus may have been an ambush predator, hiding and waiting for prey to come close before attacking.
- Active Hunter: Others believe it was an active hunter, chasing down its prey over long distances.
- Cooperative Hunter: Some evidence suggests that Allosaurus may have hunted in groups, working together to take down larger prey.
Allosaurus had several adaptations that made it a successful hunter:
- Powerful Bite: Although its bite force wasn't as strong as some other large theropods like Tyrannosaurus Rex, Allosaurus had a unique way of using its jaws. It may have used its strong neck muscles to slash at its prey with its upper jaw, causing significant damage.
- Sharp Claws: Its sharp claws were used to grab and hold onto prey, preventing it from escaping.
- Speed and Agility:Allosaurus was a relatively fast and agile dinosaur, allowing it to chase down its prey.
Discovery
The first Allosaurus fossil was discovered in 1869 by Ferdinand Vandiveer Hayden in Colorado. However, it wasn't until 1877 that paleontologist ppOthniel Charles Marsh]] officially named it Allosaurus fragilis.
Over the years, many more Allosaurus fossils have been found, making it one of the best-known theropod dinosaurs. One of the most famous Allosaurus specimens is "Big Al," which was discovered in Wyoming in 1991. Big Al was a nearly complete skeleton that showed evidence of several injuries and diseases, giving scientists valuable insights into the life of Allosaurus.
Allosaurus and other dinosaurs
Allosaurus lived alongside many other dinosaurs, both herbivores and carnivores. Some of its contemporaries included:
- Stegosaurus: A large herbivore with plates along its back and spikes on its tail.
- Apatosaurus: A massive, long-necked sauropod.
- Brachiosaurus: Another giant sauropod with very long front legs.
- Ceratosaurus: Another theropod dinosaur that was smaller than Allosaurus.
Allosaurus likely competed with Ceratosaurus for food, and it may have preyed on the young of the larger herbivores.
In popular culture

Allosaurus has appeared in many books, movies, and television shows. It is often portrayed as a fierce and powerful predator, sometimes even as a rival to Tyrannosaurus Rex, even though they lived millions of years apart!
Some notable appearances of Allosaurus include:
- The Lost World (1925): One of the earliest dinosaur movies featured Allosaurus.
- Walking with Dinosaurs (1999): A BBC documentary series that featured Allosaurus hunting Stegosaurus.
- Dinosaur (2000): A Disney animated movie that included Allosaurus as a predator.
Fun facts about Allosaurus
- The Allosaurus did not look like the other dinosaurs that existed at that time. Because of this, the word Allosaurus means "different lizard".
- The Allosaurus is in the theropod (meaning "beast foot") family.
- Allosaurus had a relatively large brain compared to other dinosaurs of its size.
- The bony crests above its eyes may have been brightly colored.
- The top speed of Allosaurus has been estimated at 30 to 55 kilometers per hour (19 to 34 miles per hour).
- Some scientists believe that Allosaurus may have been able to regenerate lost limbs, like some lizards do today.
- Allosaurus is the official state fossil of Utah.
Species
There are five recognised species of Allosaurus:
- A. fragilis
- A. tendagurensis (?)
- A. atrox (?)
- A. europaeus
- A. jimmadseni
Images for kids
-
"Big Al" at the Museum of the Rockies
-
Restored skeleton of Saurophaganax or A. maximus
-
Skeletons at different growth stages on display, the Natural History Museum of Utah
-
A. fragilis showing its maximum possible gape, based on Bakker (1998) and Rayfield et al. (2001)
-
Allosaurus and Stegosaurus skeletons, the Denver Museum of Nature and Science
-
Restoration of Barosaurus rearing to defend itself against a pair of A. fragilis
-
Locations in the Morrison Formation (yellow) where Allosaurus remains have been found
See also
 In Spanish: Allosaurus para niños
In Spanish: Allosaurus para niños