Al Ain facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
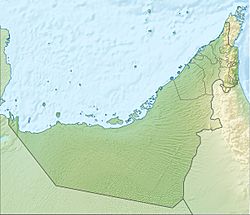
Al Ain
Al-ʿAyn (ٱلْعَيْن)
|
|
|---|---|
|
Clockwise, from top: Green Mubazzarah, Sheikha Salama Mosque, the neighbouring desert, the campus of Abu Dhabi University, and Qasr Al Muwaiji
|
|
| Nickname(s): | |
| Country | |
| Emirate | |
| Municipal region | Al-Ain |
| Subdivisions |
Al Jimi
Al Qattara Al Muawiji Al Mutaredh Al Towayya Al Foah Al Masoudi Al Khrair Al Sarooj Hili Falaj Hazza Zakher Al Maqam Sh'ab Al Ashkher Al Khalidiya Al Shoaibah Al Bateen Al Agabiyya Al Khabisi Al Markhaniya Ne'mah Al Niyadat Al Kuwaitat Al Jahli Al Salamat Al Yahar Mezyad Al Dhahir Um Ghafah Oud Al Tobah Al Hiyar Nahil Sweihan Al Sadd Rimah Al Khazna Al Arad Al Dhahrah Al Manaseer Al Basrah Al Wagan Al Qoua Al Mutraid Al Kharis Al Amarah Al Salamt |
| Government | |
| • Type | Absolute monarchy |
| • Body | Al Ain City Municipality |
| Area | |
| • Total | 15,123 km2 (5,839 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 292 m (958 ft) |
| Population
(2021)
|
|
| • Total | 846,747 |
| • Density | 55.9907/km2 (145.015/sq mi) |
| GDP | |
| • Total | US$ 38.0 billion (2023) |
| • Per capita | US$ 58,900 (2023) |
| Time zone | UTC+4 (UAE Standard Time) |
| UNESCO World Heritage Site | |
| Official name | Cultural Sites of Al Ain (Hafit, Hili, Bidaa Bint Saud and Oases Areas) |
| Criteria | Cultural: iii, iv, v |
| Inscription | 2011 (35th Session) |
Al Ain (Arabic: ٱلْعَيْن, al-ʿayn, literally, the spring) is a city in the Emirate of Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates and the seat of the administrative division of the Al Ain Region. The city is bordered to the east by the Omani town of Al-Buraimi. Al Ain is the largest inland city in the Emirates, the fourth-largest city (after Dubai, Abu Dhabi, and Sharjah), and the second-largest in the Emirate of Abu Dhabi. The freeways connecting Al Ain, Abu Dhabi, and Dubai form a geographic triangle in the country, each city being roughly 130 kilometres (81 mi) from the others.
Contents
Climate and geography
Al Ain is known as the "Garden City" (Arabic: مَدِيْنَة ٱلْحَدِيْقَة, romanized: Madīnat Al-Ḥadīqah, lit. 'City of The Garden') of Abu Dhabi, the UAE or the Gulf, due to its greenery, particularly with regard to the city's oases, parks, tree-lined avenues and decorative roundabouts, with strict height controls on new buildings, to no more than seven floors. According to one author, an oasis around Al Ain and Al-Hasa in Saudi Arabia are the most important in the region of the Gulf.
The city is located approximately 160 kilometres (99 mi) east of the capital Abu Dhabi, and about 120 kilometres (75 mi) south of Dubai. The eastern region covers an area of approximately 13,100 km2 (5,100 sq mi). Oman lies to the east, Dubai and Sharjah to the north, Abu Dhabi to the west and the Empty Quarter desert and Saudi Arabia to the south. The topography of Al Ain is unique and varies as one travels to the east. The ecologically important Jebel Hafeet ("Mount Hafeet"), an outlier of the main Hajar range, is considered one of the monuments of Al Ain, lying just to the south of the city. Rising to 1,100–1,400 metres (3,600–4,600 feet) in elevation, Jebel Hafeet is one of the highest mountains in the country, and has a number of ridges which stretch to the inner part of the city, two of which are Jabal Al Naqfah (which touches Al Ain Oasis), and the Western ridge. Sand dunes of varying texture that are tinged red with iron oxide lie to the north and east of Al Ain.
The city has a hot desert climate (Köppen climate classification BWh), featuring long, extremely hot summers and warm winters. In Al-Ain, the mean annual rainfall is 96 mm (3.8 in) and the average relative humidity is 60% (United Arab Emirates University, 1993). Low humidity in Al-Ain, particularly during the summers, makes it a popular destination for many people during this time of the year. Boer (1997) classified the UAE climate as hyper-arid and divided it into four climatic regions: the coastal zone along the Persian Gulf, the mountain areas northeast of UAE, the gravel plains around Al Ain, and the central and southern sand desert. More rainfall and lower temperature occur in the northeast than in the southern and western regions. The monthly average rainfall around Al-Ain was 100–120 mm (3.9–4.7 in) from the period 1970 to 1992.
To the south of the city, near Oman, there is the man-made Lake Zakher, which resulted from the release of waste water from desalination plants. Also in this region, to the east of Jebel Hafeet, lies the area of Mezyad, which has a border crossing with Oman, and is where the historic Mezyad Fort is located.
| Climate data for Al Ain International Airport (1991–2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 31.8 (89.2) |
36.6 (97.9) |
42.9 (109.2) |
44.4 (111.9) |
49.3 (120.7) |
49.4 (120.9) |
49.2 (120.6) |
48.8 (119.8) |
47.8 (118.0) |
43.7 (110.7) |
37.5 (99.5) |
35.0 (95.0) |
49.4 (120.9) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 24.7 (76.5) |
27.5 (81.5) |
31.3 (88.3) |
36.9 (98.4) |
42.1 (107.8) |
44.6 (112.3) |
44.9 (112.8) |
44.6 (112.3) |
42.0 (107.6) |
37.7 (99.9) |
31.4 (88.5) |
26.9 (80.4) |
36.2 (97.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 18.5 (65.3) |
20.7 (69.3) |
24.0 (75.2) |
29.1 (84.4) |
33.7 (92.7) |
36.0 (96.8) |
37.2 (99.0) |
37.1 (98.8) |
34.4 (93.9) |
30.3 (86.5) |
24.8 (76.6) |
20.4 (68.7) |
28.9 (84.0) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 12.8 (55.0) |
14.5 (58.1) |
17.3 (63.1) |
21.7 (71.1) |
25.7 (78.3) |
28.1 (82.6) |
30.2 (86.4) |
30.6 (87.1) |
27.6 (81.7) |
23.7 (74.7) |
19.0 (66.2) |
14.8 (58.6) |
22.2 (72.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 5.6 (42.1) |
5.9 (42.6) |
9.9 (49.8) |
13.2 (55.8) |
18.0 (64.4) |
19.9 (67.8) |
22.8 (73.0) |
21.9 (71.4) |
21.8 (71.2) |
16.2 (61.2) |
13.0 (55.4) |
7.4 (45.3) |
5.6 (42.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 14.7 (0.58) |
4.6 (0.18) |
17.9 (0.70) |
6.1 (0.24) |
0.7 (0.03) |
0.6 (0.02) |
4.9 (0.19) |
1.5 (0.06) |
0.8 (0.03) |
0.5 (0.02) |
2.2 (0.09) |
7.3 (0.29) |
62.0 (2.44) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1 mm) | 3.2 | 2.0 | 2.6 | 1.7 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 1.3 | 1.8 | 20.0 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 63 | 55 | 48 | 36 | 30 | 33 | 37 | 35 | 39 | 43 | 53 | 61 | 44 |
| Average dew point °C (°F) | 10 (50) |
10 (50) |
10 (50) |
10 (50) |
12 (54) |
16 (61) |
18 (64) |
18 (64) |
16 (61) |
15 (59) |
14 (57) |
11 (52) |
13 (56) |
| Source 1: NOAA | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Time and Date (dewpoints, between 2005 and 2015) | |||||||||||||
Demographics
With a population of 766,936 (as of 2017), it has the highest percentage of Emirati nationals (30.8%) in the country, though the majority of its residents are expatriates, particularly from the Indian subcontinent. Many people are from Bangladesh and Pakistan. There is also a significant number of Afghans in the city.
Economy
Al Ain is an important services centre for a wide area extending into Oman. There are three major shopping centres, Al Ain Mall, Al Jimi Mall, Al Hili Mall and Al Bawadi Mall (opened in 2009 in Al Khrair area) as well as traditional souqs for fruit and vegetables and livestock. One such souq exists for camels near an IKEA store and Bawadi Mall on Zayed Bin Sultan Street, the road which leads to Mezyad. Industry is growing on a small scale, and includes the Coca-Cola bottling plant and the Al Ain Portland Cement Works. The water in Al-Ain is of good quality. Service industries such as car sales, mechanics and other artisans are located in the area known as Sanaiya and Pattan Market. Social and governmental infrastructure include the Higher Colleges of Technology, well-equipped medical facilities including the teaching hospital at Tawam, Al Ain International Airport, and military training areas. Al Ain also has world's largest dates processing and marketing company, Al Foah Company LLC. The place is also famous for Al Ain Dairy Farm located just outside Al Ain.
History and prehistory
The region of Al Ain and Buraimi, together known as the Buraimi Oasis, is of cultural and historical importance. For example, the area witnessed events relevant to the history of Islam during the Rashidun, Umayyad and Abbasid eras, similar to Dibba and Ras Al-Khaimah. It was at this place Sheikh Zayed bin Sultan Al Nahyan, the founder of the United Arab Emirates,had spent considerable time of his life (approximately from 1927 till he became the Ruler of the Emirate of Abu Dhabi in 1966). Though it is often said that he was born in Abu Dhabi, some others were of the opinion that he was born in Al-Ain. Al-Ain could also be the place for the oldest mosque in the country, which is in the premises of the Sheikh Khalifa Mosque.
Part of the historically important Western Hajar region, the area of Al Ain has been inhabited for nearly 8,000 years, with archaeological sites showing human settlement at places like Rumailah, Hili and Jabel Ḥafeet. The early Hafit culture built "beehive" tombs for their dead and engaged in hunting and gathering in the area. The oases provided water for early farms until the modern age. In the 1950s, Sheikh Zayed discovered the tombs, and brought this to the attention of a Danish team, leading to an excavation at the tombs in 1959. In 1971, Al Ain Museum was built to house items from this area. In the 2000s, the Abu Dhabi Authority for Culture & Heritage lobbied for its recognition as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO, and in 2011, Al Ain became the first World Heritage Site in the UAE to be recognized by UNESCO.
Bronze Age burial sites often re-used materials from earlier burials. For instance, the Wadi Suq communal tomb at Qattara Oasis is thought to have been constructed from stones recovered from previous Umm Al Nar burials.
Finds at Qattara include Wadi Suq era chlorite jugs and bowls and late Bronze Age short swords and daggers. Artefacts recovered also include carnelian jewellery, often associated by UAE historians with trading links to the Indus Valley. A find of particular interest from Qattara is a Bronze Age pendant discovered in the 1970s depicting a double-bodied or entwined pair of horned animals. Made from electrum, an alloy of silver and gold, the motif is found repeated in a number of Bronze Age sites in the UAE. Iron Age finds in and around Al Ain include aflaj (underground water channels) in Bidaa bint Saud, Al Ain and Buraimi which have been placed several centuries prior to the qanats of the Achaemenid Empire, which had previously been credited with the innovation.
Al Ain was originally within the area of influence of the Dhawahir, a Bedouin tribe who settled Dhahirah before Buraimi. A later wave of settlers, the Na'im, have long had an uneasy relationship with the Dhawahir and the two tribes were frequently in dispute. Numbering 4,500, the Dhawahir consists of three subsections: the Daramikah, who populated Hili, Mutared and Qattara; the Jawabir in Al Ain and the Bani Saad who lived in Jimi. Staying in the villages for the summer date season, in winter the community would move throughout the Trucial States.
A number of interests jostled for influence over the tribes of Buraimi, including the Sultan of Muscat, the Wahhabis (who had made a number of incursions) and the Sheikhs of the Trucial States, particularly the Bani Yas of Abu Dhabi, who acquired large tracts of land, principally from the Dhawahir. This suzerainty over Al Ain was cemented by Sheikh Zayed bin Khalifa Al Nahyan, known as 'Zayed the Great', a strong and charismatic leader who took the Dhawahir's main settlement 'Ain Dhawahir (the original name of Al Ain) when the tribe rebelled against him in 1877. He built a fort, one of a number of fortifications established by the various interests vying for control over the oasis, to underline his dominion over the oasis and established a wali, appointing a member of the Dhawahir as his headman.
Wilfred Thesiger visited Al Ain in the late 1940s, during his travels across the Empty Quarter. He met Sheikh Zayed and stayed with him at Al Muwaiji Fort. An ongoing dispute between Saudi Arabia, Abu Dhabi and Oman led to the Buraimi Dispute, a series of incidents which saw a Saudi armed force enter the oasis. Forces from the Trucial Oman Scouts, as well as the army of Muscat-Oman, arrived to recapture the oasis. With British intervention, the Saudi forces surrendered, leaving the oasis back in the hands of Abu Dhabi and Oman.
In 1971, Queen Elizabeth II visited the Hilton Hotel in the area, during her tour of the Persian Gulf. Following independence in 1971, Al Ain experienced rapid growth and investment as part of the emirate of Abu Dhabi, quickly becoming larger and more successful than Oman's Al-Buraimi. In 1972, Oman and Abu Dhabi agreed on the final borders to divide Buraimi and Al Ain. Until Sheikh Zayed's death in 2004, Al Ain's municipal code forbade construction of buildings over four stories, with the exceptions of the Hilton (now Radisson Blu), Danat Al Ain Resort, and Rotana hotels. Until 2006, Buraimi and Al Ain shared an open border. This border was closed in November 2006, and passport controls were imposed.
-
Jebel Hafeet, as viewed from Mezyad Fort near the southern border with Al Buraimi Governorate in Oman
-
Qasr Al Muwaiji, the birthplace of Sheikh Khalifa bin Zayed Al Nahyan, the former Ruler of Abu Dhabi and President of the UAE, and former home of his father, Sheikh Zayed
Oases and Aflaj
The city's wāḥāt (Arabic: وَاحَات, lit. 'oases') are known for their underground irrigation system (falaj or qanāt) that brings water from boreholes to water farms and palm trees. Falaj irrigation is an ancient system dating back thousands of years, and is used widely in Oman, the UAE, China, Iran and other countries. There are seven oases here. The largest is Al Ain Oasis, near Old Sarooj, and the smallest is Al-Jahili Oasis. The rest are Al Qattara, Al-Muʿtaredh, Al-Jimi, Al-Muwaiji, and Hili.
Examples of aflaj include Falaj Hazza, which is named after Sheikh Zayed's elder brother, Hazza bin Sultan Al Nahyan, and has a district named after it.
Infrastructure
The city is known for its combination of modern and pre-modern buildings. The latter offer an insight into the city's and country's cultural heritage. The city used to have roundabouts in every intersection but recently it has been replaced by traffic signals.
Education
Al-Ain is home to the main federal university in the UAE, the United Arab Emirates University, and to two campuses of the Higher Colleges of Technology – Al Ain Men's College and Al Ain Women's College. Al-Ain is also the home of Horizon International flight academy, Etihad Airways's cadet pilot training centre. Private higher education institutions include the Al Ain University and campus of Abu Dhabi University. Al-Ain also houses the eastern zone headquarters of the Abu Dhabi Department of Education and Knowledge, Abu Dhabi's education authority.
Many of Al-Ain's private schools, catering mainly to the expatriate population, are located in the Al-Manaseer area. They include Al-Ain International school (British curriculum, private school, part of the Aldar group), Al Ain English Speaking School, Al Dhafra Private School, Manor Hall School, Al-Sanawbar School, Liwa International School, Al-Madar International School, Global English School, Emirates Private School, a branch of the International School of Choueifat, and an Institute of Applied Technology campus. Other private schools include the CBSE affiliated school Indian School, Al-Ain, Our Own English High School, Al Adhwa Private School, Brighton College Al Ain and Al Ain Juniors School. A new British International School, Belvedere International School is located in the Al Hili district. In 1977, the Zayed Central Library was established. Al-Khwarizmi International College has started a Campus at Al-Ain and is offering BBA programme and various other licensed, accredited and approved courses.
Places of worship
Formerly, the city's largest mosque was that of Shaikha Salamah. In 2021, the Sheikh Khalifa Grand Mosque became the biggest in the city, as well as one of the largest mosques in the country.
Transportation
Al-Ain is connected via the Dubai–Al-Ain Road to Al Faqa' and Dubai in the north, which also connects to Al Madam in the Emirate of Sharjah via Al-Shwaib. It is also connected to Abu Dhabi in the west, Al-Qu'a in the southeast, and Mezyad in the southwest. Bus and taxi services are available between these areas. The southern border area of Mezyad lies on the road to Dhank, Ibri and Nizwa in Oman. The city's airport (Al Ain International Airport) has scheduled passenger flights to Egypt, Pakistan and India. A new railway line linking Al-Ain to Abu Dhabi and to the Port of Sohar in Oman is being planned.
Tourism and recreation
Al-Ain is developing as a tourist destination. The dry desert air makes it a welcome retreat from the coastal humidity of the larger cities. Many Emirati nationals in Abu Dhabi have holiday houses in the city making it a popular weekend destination for families from the capital city. Its attractions include the Al Ain National Museum, the Al Ain Palace Museum, several restored forts and the Hili Archaeological Park site, dating back to the Bronze Age. Jebel Hafeet dominates the surrounding area. It is popular to visit to the mineral springs at Green Mubazzarah at the base of the mountain, and to drive to the mountaintop at sunset. Other attractions include Al Ain Zoo, an amusement park named "Hili Fun City", many well-maintained parks popular with families in the summer evenings, and a heritage village. Opened in 2012, Wadi Adventure is located near Jebel Hafeet and provides a range of water-based activities including surfing, kayaking and rafting. On top of Jabel Hafeet is the Mercure Hotel. Mount Hafeet and the nearby 'beehive' tombs are part of what is known as "Jebel Hafeet Desert Park" or "Mezyad Desert Park", which is meant to preserve the nature and geology of the area, besides attracting tourists.
Al-Ain has five major malls – Al Ain Mall in the town centre, Al-Jimi Mall in Al-Jimi District, Bawadi Mall in Al-Khrair District, Remal Mall located in the Sanaiya district, and Hili Mall located in the Hili District. Most commercial activity is centred in and around town centre.
Another popular pastime for Emiratis and expatriates alike is spending time in coffee shops and shisha cafes. Like the rest of the UAE, Al-Ain has strict laws governing the consumption and distribution of alcohol. Five facilities in the city currently serve alcohol, four of which are hotels. There are many café's in Al-Ain, ranging in size and quality. The city also has an International standard go-kart circuit.
The city has two English-language radio stations – 100.1 Star FM, which plays English-speaking hits alternating with Arabic-speaking hits, and 105.2 Abu Dhabi Classic FM, which plays classical music.
Sport, culture and arts
Al-Ain is a cultural retreat for residents of the cities of Dubai and Abu Dhabi. It is home to a major festival of classical music, and is the home of Al Ain Football Club, which is one of the most successful football clubs in the UAE and Asia. It has many titles and championships to its name. Al-Ain Club contains also eight other games which are: handball, volleyball, basketball, swimming, Table Tennis, Athletics, Jiu jitsu, and Taekwondo. The Al Ain Amblers are a well known rugby club with a long history fielding men's, women's and junior rugby teams in the UAE and Gulf competitions, based at the Al Ain Club.
Hili Fun City hosts two ice hockey teams, the Al Ain Vipers and Ghantoot. Each team has adult and youth teams starting from age 4. The Al-Ain Vipers Men's Team won the Emirates Hockey League in the 2009–10 season.
The Palm Resort to the west of the town hosts a popular rugby club with adult and youth teams, and the Al-Ain International Soccer Club which has three youth teams, including one for 7-9-year-old's. There is a water sports centre called "Wadi Adventure", with a wave pool and surf instructors. Additionally, the park has facilities for kayaking and rafting on an artificial river.
Gallery
-
Dromedaries at the city's Camel Market. The camel is important to the cultures of Arabia, the Middle East, and elsewhere.
See also
 In Spanish: Al Ain para niños
In Spanish: Al Ain para niños