Air pollution facts for kids
Air pollution is a type of environmental pollution that affects the air and is usually caused by smoke or other harmful gases, mainly oxides of carbon, sulphur, and nitrogen.
Many of the world's large cities today have polluted air or low air quality.
Even 2,000 years ago, the Romans were complaining about the polluted air in their cities. At that time, the air was thick with smoke from fires and the smell of sewers. Air pollution has been classified as a danger to human health and Earth's many ecosystems for a long time.
Contents
Air quality
Pollution can be in the form of a gas, liquid, or solid. It can also be classified chemically, such as oxides, hydrocarbons, acids, or other kinds of chemicals.
Many pollutants go into the air from natural sources. These pollutants include dust, sea salt, volcanic ash and gases, smoke from forest fires, pollen, and many other materials.
Primary and secondary pollutants
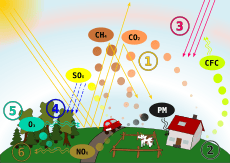
Air pollution is usually described as either a primary pollutant or a secondary pollutant. Primary pollutants are pollutants that are put directly into the air by humans or natural sources. Examples of primary pollutants are exhaust fumes (gas) from cars, soot from smoke, dust storms, and ash from volcanic eruptions (as seen in the picture on the left).
Secondary pollutants are pollutants that are made from chemical reactions when pollutants mix with other primary pollutants or natural materials like water vapor. Many secondary pollutants are made when a primary pollutant reacts with sunlight. Ozone and smog are secondary pollutants. Ozone is a gas that stops harmful ultraviolet rays from the sun. When it is near the ground, though, it can poison people and other organisms.
Human-made air pollution comes from many things. Most air pollution made by humans today is because of transportation. Automobiles, for instance, make up about 60% of human-made air pollution. The gases inside car exhaust, like nitrogen oxide, make smog and acid rain.
Farmlands and forests sometimes burn in wildfires, producing soot (a black powder made mainly of carbon and produced when coal, grasses, wood, etc. is burned) from the smoke. Soot can affect people and other life forms.
Industrial air pollution
Many industrial power plants burn fossil fuels to get their energy. However, burning fossil fuels can make a lot of oxides (chemical compounds that have oxygen and other elements inside). The burning of fossil fuels makes 96% of the sulfur oxides in the atmosphere. Some industries also make chemicals that make poisonous fumes (smoke).
Indoor air pollution
Air pollution does not only happen outside. The insides of homes, schools, and buildings can also have air pollution. Sometimes the air inside a building, especially if its windows are closed, is even worse than the air outside. Many things that humans use every day can pollute the air. Compounds inside carpets, paints, building materials, and furniture also pollute the air, especially when they are new.
Acid precipitation
Acid precipitation is precipitation, like rain, sleet, or snow, that contains acids from air pollution. When fossil fuels are burned, they let out oxides into the air. When these oxides mix with water in the atmosphere, they make acid, which falls as precipitation. Acid precipitation can kill living things like fish and trees by making the place where they live too acidic. Acid rain can also damage buildings made of limestone and concrete.
Ozone hole

A worldwide concern is the hole in the ozone layer in the stratosphere. The Earth's ozone layer protects life from the sun's harmful ultraviolet rays, but in the 1970s, scientists found out that some chemicals let out into the atmosphere makes the ozone turn into oxygen. This lets more ultraviolet rays reach the Earth. During the 1980s, scientists found that the ozone layer above the South Pole had thinned by 50 to 98%.
Human health
On March 17, 1992, in Mexico City, all children under the age of 14 were not allowed to go to school because of air pollution. This does not happen often, but being exposed to air pollution every day can cause people to have many health problems. Children, elderly (old) people, and people with allergies can develop health problems because of air pollution. Studies from the University of Birmingham showed that air pollution from motor vehicles could be the cause of some pneumonia-related deaths.
The World Health Organization said that 2.4 million people died because of problems that air pollution causes. Some of the problems include:
|
|
|
Agricultural effects
India published a report in 2014 that showed that air pollution in 2010 had cut the amount of crops harvested by almost half in the most affected areas when compared to 1980 levels. Sometimes, crops can produce better when air quality improves.
Interesting facts about air pollution
- Air pollution is caused by human and natural contributors. Industries, mining, factories, vehicles, forest fires, volcanic eruptions, and wind erosion can all cause air pollution.
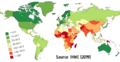
- 92% of the world's population live in areas in which air pollution is higher than safe limits.
- Inhaling air pollution is thought to take away 1-2 years of an average human life.
- Babies whose mothers live in high-traffic areas have a 22% higher risk of being born with poor lung function than those whose mothers live in less polluted areas.
- Air pollution is more dangerous for children because of their smaller size and lung capacity.
- The IQ of children can be negatively affected by air pollution.
- ADHD can worsen or be caused by Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH).
- Waiting in traffic and breathing in the air pollution is thought to increase a person's chance of death due to a heart attack.
- The 1952 Great Smog of London is said to have killed 8,000 people.
- Scientists have guessed that by 2050, six million people per year will die as a result of air pollution.
- Larger cities control the amount of emissions allowed from vehicles to help reduce air pollution and protect the public.
- Deforestation is a major cause of air pollution.
Images for kids
-
Air pollution from a coking oven
-
Controlled burning of a field outside of Statesboro, Georgia, in preparation for spring planting
-
Dust storm approaching Stratford, Texas, in 1935
-
Air quality monitoring, New Delhi, India
-
Support, use and infrastructure-expansion of forms of public transport that do not cause air pollution may be a critical key alternative to pollution.
-
Tarps and netting are often used to reduce the amount of dust released from construction sites.
-
Before flue-gas desulfurization was installed, the emissions from this power plant in New Mexico contained excessive amounts of sulfur dioxide.
See also
 In Spanish: Contaminación atmosférica para niños
In Spanish: Contaminación atmosférica para niños