YaCy facts for kids
 |
|
 |
|
| Original author(s) | Michael Christen |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | YaCy community |
| Initial release | 2003 |
| Stable release |
1.924 / 14 December 2020
|
| Written in | Java |
| Operating system | Cross-platform |
| Type | Overlay network, Search engine |
| License | GPL-2.0-or-later |
YaCy (pronounced “ya see”) is a free distributed search engine built on the principles of peer-to-peer (P2P) networks, created by Michael Christen in 2003. The engine is written in Java and distributed on several hundred computers, as of September 2006[update], so-called YaCy-peers. Each YaCy-peer independently crawls through the Internet, analyzes and indexes found web pages, and stores indexing results in a common database (so-called index) which is shared with other YaCy-peers using principles of peer-to-peer.
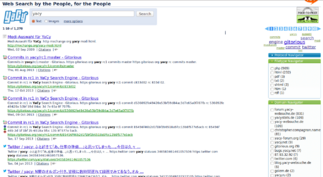
Compared to semi-distributed search engines, the YaCy network has a distributed architecture. All YaCy-peers are equal and no central server exists. It can be run either in a crawling mode or as a local proxy server, indexing web pages visited by the person running YaCy on their computer. Several mechanisms are provided to protect the user's privacy. Access to the search functions is made by a locally run web server which provides a search box to enter search terms, and returns search results in a similar format to other popular search engines.
Contents
System components
YaCy search engine is based on four elements:
- Crawler
- A search robot that traverses between web pages, analyzing their content.
- Indexer
- It creates a reverse word index (RWI), i.e., each word from the RWI has its list of relevant URLs and ranking information. Words are saved in the form of word hashes.
- Search and administration interface
- Made as a web interface provided by a local HTTP servlet with a servlet engine.
- Data storage
- Used to store the reverse word index database utilizing a distributed hash table.
Search-engine technology
- YaCy is a complete search appliance with user interface, index, administration, and monitoring.
- YaCy harvests web pages with a web crawler. Documents are then parsed, and indexed and the search index is stored locally. If your peer is part of a peer network, then your local search index is also merged into the shared index for that network.
- A search is started, then the local index contributes with a global search index from peers in the YaCy search network.
- The YaCy Grid is a second-generation implementation of the YaCy peer-to-peer search. A YaCy Grid installation comprises microservices that communicate using the Master Connect Program (MCP).
- The YaCy Parser is a microservice that can be deployed using Docker. When the Parser Component is started, it searches for and connects to an MCP. By default, the local host is searched for an MCP, but you can configure one yourself.
YaCy platform architecture
YaCy uses a combination of techniques for the networking, administration, and maintenance of indexing the search engine, including blacklisting, moderation, and communication with the community. Here is how YaCy performs these operations:
- Community components
- Web forum
- Statistics
- XML API
- Maintenance
- Web Server
- Indexing
- Crawler with Balancer
- Peer-to-Peer Server Communication
- Content organization
- Blacklisting and Filtering
- Search interface
- Bookmarks
- Monitoring search results
Distribution
YaCy is available in packages for Linux, Windows, and Macintosh, and also as a Docker image. YaCy can also be installed on other operating systems either by manually building it, or using a tarball. YaCy requires Java 8, OpenJDK 8 is recommended.
The Debian package can be installed from a repository available at the subdomain of the project's website. The package is not maintained in the official Debian package repository yet.
See also
 In Spanish: YaCy para niños
In Spanish: YaCy para niños
- Dooble – an open-source web browser with an integrated YaCy Search Engine Tool Widget