Winona Site facts for kids
|
Winona Site
|
|
| Nearest city | Winona, Arizona |
|---|---|
| NRHP reference No. | 66000177 |
Quick facts for kids Significant dates |
|
| Added to NRHP | October 15, 1966 |
| Designated NHLD | July 19, 1964 |
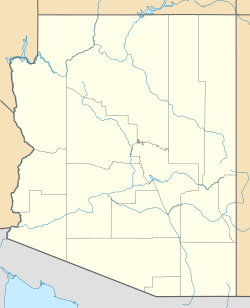
The Winona Site is a complex of archaeological sites in Coconino County in the state of Arizona, within the Coconino National Forest. It is located near Sunset Crater, which erupted in 1066. Cultural changes following this eruption are evidenced by findings at this site. It was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1964.
The Winona Site was first investigated formally in the 1940s by John McGregor, an archaeologist affiliated with the Museum of Northern Arizona. McGregor excavated six pit houses with architectural features distinctive of the Hohokam people of the 10th century. He theorized that the Hohokam, more typically found further to the south, migrated to this area by the fertility of the landscape created by the eruptions of the crater. In addition to the pit houses, McGregor uncovered trash mounds and a ball court. Pottery finds at the site were also characteristically Hohokam in their color, decoration, and design.
Subsequent researchers have cast some doubt on the initial theories put forward by McGregor, suggesting instead that the site was primarily a trading site, rather than a permanent relocation. Additional finds at the site are more typical of the Sinagua people who dominated the surrounding area, including Sinagua-style pottery and a number of human remains buried in manners associated with known Sinagua practices. There were also shell fragments, consistent with being debitage left over from the manufacture of jewelry. The source of the shells appears to have been the Gulf of California, an area the Hohokam had access to.