White-faced storm petrel facts for kids
Quick facts for kids White-faced storm petrel |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Pelagodroma
|
| Species: |
marina
|
 |
|
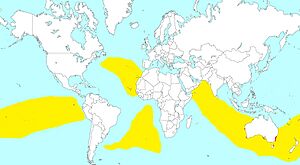
| Distribution map of the species | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
The white-faced storm petrel (Pelagodroma marina), also known as white-faced petrel is a small seabird of the austral storm petrel family Oceanitidae. It is the only member of the monotypic genus Pelagodroma.
Description
The white-faced storm petrel is 19 to 21 centimetres (7.5 to 8.3 in) in length with a 41 to 44 centimetres (16 to 17 in) wingspan. It has a pale brown to grey back, rump and wings with black flight feathers. It is white below, unlike other north Atlantic petrels, and has a white face with a black eye mask like a phalarope. Its plumage makes it one of the easier petrels to identify at sea.
Behaviour
The white-faced storm petrel is strictly pelagic outside the breeding season, and this, together with its often-remote breeding sites, makes this petrel a difficult bird to see from land. Only in severe storms might this species be pushed into headlands. There have been a handful of western Europe records from France, the United Kingdom and the Netherlands. It has a direct gliding flight and will patter on the water surface as it picks planktonic food items from the ocean surface. It is highly gregarious, but does not follow ships. Like most petrels, its walking ability is limited to a short shuffle to the burrow.
Breeding
The white-faced storm petrel breeds on remote islands in the south Atlantic, such as Tristan da Cunha and also Australia and New Zealand. There are north Atlantic colonies on the Cape Verde Islands, Canary Islands and Savage Islands. It nests in colonies close to the sea in rock crevices and lays a single white egg. It spends the rest of the year at sea. It is strictly nocturnal at the breeding sites to avoid predation by gulls and skuas, and will even avoid coming to land on clear moonlit nights.
Subspecies
Here are six recognised subspecies, breeding in island colonies through subtropical to subantarctic regions of the Atlantic, Indian and south-western Pacific Oceans:
- P. m. albiclunis Murphy & Irving, 1951 – Kermadec Islands
- P. m. dulciae Mathews, 1912 – islands off southern Australia
- P. m. eadesi Bourne, 1953 – Cape Verde Islands
- P. m. hypoleuca (Webb, Berthelot & Moquin-Tandon, 1842) – Savage Islands
- P. m. maoriana Mathews, 1912 – islands around New Zealand, including the Chatham and Auckland Islands
- P. m. marina (Latham, 1790) – Tristan da Cunha and Gough Island (Nominate subspecies)
Diseases
White-faced storm petrels are affected by a trematode Syncoelium filiferum, which uses the krill species Nematoscelis megalops as an intermediate host. The petrels appear to be an accidental or dead-end host for the larvae of the trematode, which need to attach themselves to the gill filaments of near-surface fish to continue their life cycle. Metacercariae of S. filiferum attach using sticky filaments reaching 60 millimetres (2.4 in) long, which adhere to the legs of the petrel and subsequently dry out as the petrels leave the water, resulting in trematode death. The petrels can become caught in vegetation and die. This phenomenon has been described among white-faced storm petrel populations in the Chatham Islands, where it reportedly causes mortality epidemics. The trematode larvae also attach to the legs of fairy prions but do not often cause bridging leg connections in that species.
Status and conservation
Widespread throughout its large range, the white-faced storm petrel is evaluated as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.



