Virginia Colony facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Colony of Virginia
|
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1606–1776 | |||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
|
Motto:
|
|||||||||
 |
|||||||||
 |
|||||||||
| Status | Colony of the British Empire in Eastern North America | ||||||||
| Capital |
|
||||||||
| Common languages | English, Siouan languages, Iroquoian languages, Algonquian languages | ||||||||
| Religion | Church of England (Anglicanism) | ||||||||
| Government | Constitutional monarchy | ||||||||
| Governor | |||||||||
|
• 1606
|
Edward Wingfield (first) | ||||||||
|
• 1776
|
Lord Dunmore (last) | ||||||||
| Legislature | House of Burgesses (1619–1776) | ||||||||
| Historical era | European colonisation of the Americas | ||||||||
|
• Founding
|
April 10, 1606 | ||||||||
|
• Became Royal Colony
|
1624 | ||||||||
| July 4, 1776 | |||||||||
| Currency | Virginia pound (1624-1793) | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||
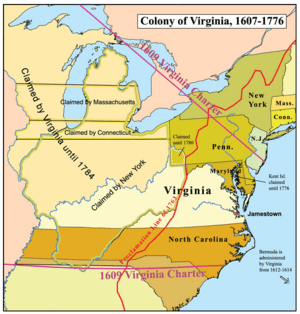
The Colony of Virginia was the first enduring English colony in North America. It was chartered in 1606 and settled in 1607, after failed attempts at settlement on Newfoundland by Sir Humphrey Gilbert in 1583 and the colony of Roanoke (further south, in modern eastern North Carolina) by Sir Walter Raleigh in the late 1580s.
The founder of the new colony was the Virginia Company, which built the first two settlements in Jamestown on the north bank of the James River and Popham Colony on the Kennebec River in modern-day Maine, both in 1607. The Popham colony quickly failed due to a famine, disease, and conflicts with local Native American tribes in the first two years. Jamestown occupied land belonging to the Powhatan Confederacy, and was also at the brink of failure before the arrival of a new group of settlers and supplies by ship in 1610. Tobacco became Virginia's first profitable export.
In 1624, the Virginia Company's charter was revoked by King James I, and the Virginia colony became a crown colony. After the English Civil War in the 1640s and 50s, the Virginia colony was nicknamed "The Old Dominion" by King Charles II for its perceived loyalty to the English monarchy during the era of the Protectorate and Commonwealth of England.
From 1619 to 1775/1776, Virginia was goverened by the General Assembly, which governed in conjunction with a colonial governor. Jamestown on the James River remained the capital of the Virginia colony until 1699; from 1699 until its dissolution the capital was in Williamsburg.
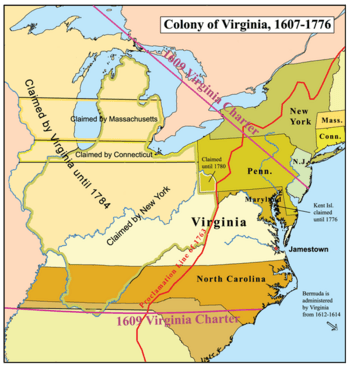
After declaring independence from the Kingdom of Great Britain in 1775, before the Declaration of Independence was officially adopted, the Virginia colony became the Commonwealth of Virginia, one of the original thirteen states of the United States, adopting as its official slogan "The Old Dominion". The entire modern states of West Virginia, Kentucky, Indiana and Illinois, and portions of Ohio and Western Pennsylvania were later created from the territory claimed by the colony of Virginia at the time of further American independence in July 1776.
Names and etymology
In 1584, Sir Walter Raleigh sent Philip Amadas and Arthur Barlowe to explore what is now the North Carolina coast, and they returned with word of a regional king (weroance) named Wingina, who ruled a land supposedly called Wingandacoa.
The name Virginia for a region in North America may have been originally suggested by Sir Walter Raleigh, who named it for Queen Elizabeth I (also nicknamed 'the Virgin Queen'), in approximately 1584. In addition, the term Wingandacoa may have influenced the name Virginia. On his next voyage, Raleigh learned that while the chief of the Secotans was indeed called Wingina, the expression wingandacoa heard by the English upon arrival actually meant "What good clothes you wear!" in Carolina Algonquian, and was not the name of the country as previously misunderstood.
"Virginia" was originally a term used to refer to North America's entire eastern coast from the 34th parallel (close to Cape Fear) north to 45th parallel. This area included a large section of Canada and the shores of Acadia.
The colony was also known as the Virginia Colony, the Province of Virginia, and occasionally as the Dominion and Colony of Virginia or His Majesty's Most Ancient Colloney[sic] and Dominion of Virginia
Images for kids
-
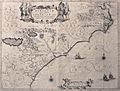
Map depicting the Colony of Virginia (according to the Second Charter). Made by Willem Blaeu between 1609 and 1638.
-
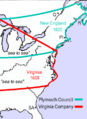
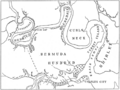
Lines show legal treaty frontiers between Virginia Colony and Indian Nations in various years, as well as today's state boundaries. Red: Treaty of 1646. Green: Treaty of Albany (1684). Blue: Treaty of Albany (1722). Orange: Proclamation of 1763. Black: Treaty of Camp Charlotte (1774). Area west of this line in present-day Southwest Virginia was ceded by the Cherokee in 1775.
-
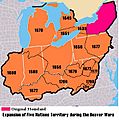
Map of Iroquois expansion during Beaver Wars 1638-1711.
-
Hanover County Courthouse (c. 1735–1742), with its arcaded front, is typical of a numerous colonial courthouse built in Virginia.
-
Rear view of the Wren Building at the College of William and Mary, begun in 1695
See also
 In Spanish: Colonia de Virginia para niños
In Spanish: Colonia de Virginia para niños