Vancouver Coastal Sea wolf facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Vancouver Coastal Sea wolf |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Captive wolf at Grouse Mountain | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Canidae |
| Genus: | Canis |
| Species: | |
| Subspecies: |
C. l. crassodon
|
| Trinomial name | |
| Canis lupus crassodon Hall, 1932
|
|
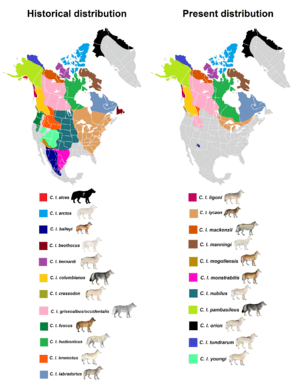 |
|
| Historical and present range of grey wolf subspecies in North America | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Canis crassodon crassodon |
|
The Vancouver Coastal sea wolf or Vancouver coastal island wolf (Canis lupus crassodon) is a subspecies of grey wolf, endemic to Great Bear Rainforest and northern Vancouver Island within the Pacific Northwest Coast of North America. It lives in packs of five to twenty individuals. These coastal wolves are popularly known as sea wolves. In some coastal regions, the main food source is fish, making up 90 percent of their diet, with salmon accounting for nearly a quarter of that. They also forage on barnacles, clams, herring eggs, seals, river otters, and whale carcasses. These wolves will also commonly feed on deer and small mammals.
Description and behaviour
The Vancouver sea wolf is of medium size, measuring roughly 26 to 32 inches high, 4 to 5 feet from nose to end of tail, and weighing roughly 60 pounds. It is usually a mix of grey, brown, and black. Pure white individuals are occasionally seen.
Sea wolves of the Great Bear Rainforest are fast, powerful distance swimmers and move stealthily in the water, their backs and bodies submerged and with only their eyes, ears and snouts peeking above the surface. Many swim from island to island throughout the year. At times the wolves follow the salmon, but other times they appear even when there are no salmon. This is because sea wolves have a diverse diet, which a recent study found to be up to 90 percent marine-based: lone wolves take down seals and otters, while packs have been spotted feasting on the occasional whale carcass. The carnivores also eat shellfish. Using their paws, they dig in the sand for clams and use their powerful jaws to crack open the shells of mussels.
Mythical creatures Gonakadet and Wasgo, found among the Tsimshian, Tlingit and Haida peoples of British Columbia and Alaska, were inspired by these pescatarian sea wolves.
Taxonomy and genetics
The sea wolf is recognized as a subspecies of Canis lupus in the taxonomic authority Mammal Species of the World (2005). Studies using mitochondrial DNA have indicated that the wolves of coastal southeast Alaska are genetically distinct from inland grey wolves, reflecting a pattern also observed in other taxa. They show a phylogenetic relationship with extirpated wolves from the south (Oklahoma), indicating that these wolves are the last remains of a once widespread group that has been largely extirpated during the last century and that the wolves of northern North America had originally expanded from southern refuges below the Wisconsin glaciation after the ice had melted at the end of the Last Glacial Maximum. These findings call into question the taxonomic classification of C.l. nulibus proposed by Nowak. Another study found that the wolves of coastal British Columbia were genetically and ecologically distinct from the inland wolves, including other wolves from inland British Columbia. A study of the three coastal wolves indicated a close phylogenetic relationship across regions that are geographically and ecologically contiguous, and the study proposed that Canis lupus ligoni (Alexander Archipelago wolf), Canis lupus columbianus (British Columbia wolf), and Canis lupus crassodon (Vancouver sea wolf) should be recognized as a single subspecies of Canis lupus.
In 2016, two studies compared the DNA sequences of 42,000 single nucleotide polymorphisms in North American grey wolves and found the coastal wolves to be genetically and phenotypically distinct from other wolves. They share the same habitat and prey species, and form one of the study's six identified ecotypes - a genetically and ecologically distinct population separated from other populations by their different type of habitat. The local adaptation of a wolf ecotype most likely reflects the wolf's preference to remain in the type of habitat that it was born into. Wolves that prey on fish and small deer in wet, coastal environments tend to be smaller than other wolves.
See also
 In Spanish: Lobo de Vancouver para niños
In Spanish: Lobo de Vancouver para niños


