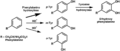Tyrosine facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Tyrosine |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
 |
|
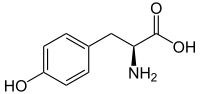
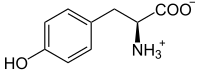
| IUPAC name | (S)-Tyrosine |
| Other names | L-2-Amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | DB03839 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:58315 |
| SMILES | N[C@@H](Cc1ccc(O)cc1)C(O)=O |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | |
| Molar mass | 0 g mol-1 |
| .0453 g/100 mL | |
| -105.3·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 |
|
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) | |
Tyrosine (Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is an amino acid.
Tyrosine is one of the 20 standard amino acids used by cells to make proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid, meaning the body can make it. Its codons are UAC and UAU.
Tyrosine can be synthesized in the body from phenylalanine. It is also found in many high-protein food products such as chicken, turkey, fish, milk, yogurt, cottage cheese, cheese, peanuts, almonds, pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds, soy products, lima beans, avocados, bananas and eggs.
It is called tyrosyl when referred to as a functional group or side chain.
Images for kids
-
The decomposition of tyrosine to acetoacetate and fumarate. Two dioxygenases are necessary for the decomposition path. The end products can then enter into the citric acid cycle.
-
Enzymatic oxidation of tyrosine by phenylalanine hydroxylase (top) and non-enyzmatic oxidation by hydroxyl free radicals (middle and bottom).
See also
 In Spanish: Tirosina para niños
In Spanish: Tirosina para niños