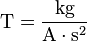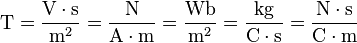Tesla (unit) facts for kids
The tesla (symbol T) is the SI derived unit used to measure the strength of magnetic fields. Tesla can be measured in different ways; for example, one tesla is equal to one weber per square meter.
The tesla was first defined in 1960 by the General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM). It was named in honor of the physicist, electrical engineer, and inventor, Nikola Tesla.
Definitions
Using only the seven base SI units, the definition of a tesla is:
Using other SI derived units, a tesla is also equal to:
The units used are:
A = ampere
C = coulomb
kg = kilogram
m = meter
N = newton
s = second
T = tesla
V = volt
Wb = weber
A tesla is also equal to 10,000 (104) gauss in the CGS system of units.
Example values
- 3.1×10−5–5.8-5 T – the Earth's magnetic field at its surface
- 5×10-3 T – the strength of a typical refrigerator magnet
- 0.3 T – the strength of solar sunspots
- 1.25T – the strength of the surface of a neodymium magnet
- 1.5−3 T – strength of medical magnetic resonance imaging systems
- 4 T – strength of the superconducting magnet built around the CMS detector at CERN
- 13 T – strength of ITER fusion reactor
- 16 T – magnetic field strength required to levitate a frog as part of an Ig Nobel Prize winning project.
See also
 In Spanish: Tesla (unidad) para niños
In Spanish: Tesla (unidad) para niños

All content from Kiddle encyclopedia articles (including the article images and facts) can be freely used under Attribution-ShareAlike license, unless stated otherwise. Cite this article:
Tesla (unit) Facts for Kids. Kiddle Encyclopedia.