Taekkyon facts for kids
[[Image: |200px]] |200px]] |
|
| Also known as | Taekgyeon, Taekkyeon, Taekkyon |
|---|---|
| Focus | Self-defense with a focus on kicks, trips, throws in competitions |
| Hardness | Light-contact (pushing hands) Full-contact (strikes, kicks, throws, takedowns etc...) |
| Country of origin | Korea |
| Parenthood | Subak |
| Official website | Four associations:
|
| Taekkyon | |
|---|---|
|
UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage
|
| Popular spelling | |
| Hangul | |
|---|---|
| Hanja | |
| Revised Romanization | Taekgyeon |
| McCune–Reischauer | T'aekkyŏn |
| IPA | tʰɛk̚k̕jʌn |
| Dictionary spelling | |
| Hangul | |
| Hanja | |
| Revised Romanization | Taekkyeon |
| McCune–Reischauer | T'aekkyŏn |
Taekkyon, Taekgyeon, Taekkyeon, or Taekyun (Korean: 태껸/ 택견/ 托肩, pronunciation: Korean pronunciation: [tʰɛk̚k͈jʌn]) is a traditional Korean martial art.
It is characterized by fluid, dynamic foot movement called pum balki, or "stepping-on-triangles". Taekkyon includes hands and feet techniques to unbalance, trip, or throw the opponent. Taekkyon has many leg and whole-body techniques with fully integrated armwork. A Taekkyon practitioner is called a "Taekkyon-kkun".
Since the twentieth century, Taekkyon has come to be seen as a living link to Korea's past. As such, it has provided historical references for modern Korean martial arts and is often considered as the oldest martial discipline of Korea. It was almost wiped out during the Japanese Occupation, before being rediscovered after the Korean War. It has influenced the name and conceptualization of Taekwondo.
Taekkyon was the first martial art enlisted in the UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage. It is also the 76th Intangible Cultural Property of South Korea.
Contents
History of Taekkyon
Historical records regarding Taekkyon are scant and ambiguous. The term is described as a Martial art, and probably is descended from earlier dynasties' Subak or as a folk game. The earliest written source of the term appears during the reign of King Jeongjo (1776–1800) of the Joseon Dynasty, in the book Jaemulbo (also Manmulbo), which included an entry about a 2nd century Book of Han reference of contests of unarmed combat. In this entry, author Lee Sung-Ji extended a 3rd century annotation of this reference to say that such competitions are like the Taekkyon of his time:
- "Byeon: Byeon is hand to hand combat (Subak), competing in a martial game, (Lee Sung-Ji extension starts here) like today's Taekkyon."
The word Taekkyon is written in Hangul, which denotes its connection with the common people while the other terms are written in hanja.
Song Deok-gi who was the main preserver of Taekkyon during the 20th century, writes in the preface of his only book: "It cannot be said for sure when and how Taekkyon came into existence, but until the end of the Korean kingdom, certain people did Taekkyon together."

Taekkyon was documented for the first time in the West as a living martial art by anthropologist Stewart Culin in his book Korean Games, written in 1895. In the 1921 book Haedong Jukji (East Sea Annals) by Choe Yeong-nyeon, Taekkyon is called "flying leg technique". Taekkyon was widely practiced during the Joseon period. Two versions existed at the time: one for combat application used by militaries, the other as a game, very popular among lower classes alongside Ssireum. Both combat sports were often done together at festivals, attended by all social classes. For example, during the Dan-O-Festival, a tournament called Gyeoll-yeon-taekkyon was carried out. Players who beat five opponents consecutively could take a rest and re-enter the tournament again later.
Taekkye\on's popularity suffered as Neo-Confucianism became widespread among the elite and underwent a long period of decline. At the dawn of the 20th century, it was only practiced around the capital city of Hanyang (Seoul), in the district of Jongro. The subsequent Japanese occupation prohibited indigenous fighting techniques, which nearly made the art extinct.
The onslaught of the subsequent Korean War left only one surviving Master: Song Deok-gi. Being part of the last generation who received a traditional education under the tutelage of Master Im Ho, he had maintained his practice in secret throughout the Japanese occupation and subsequently laid the seeds for the art's regeneration. The style he practiced was called "Widae" ("high-village") after his village of Sajik. Song was critical in the preservation of Taekkyon, since most of the current knowledge came from him. Revealed to the public on 26 March 1958 after a Martial arts demonstration given for then-president Syngman Rhee's birthday, Song became known as "the Last Taekkyon Master of the Joseon Dynasty".
Deok-gi taught a handful of students who in turn taught others. On June 1, 1983, owing to the efforts of his pupil Shin Han-seung, Taekkyon was given the classification as Important Intangible Cultural Asset No. 76" by the Korean government. It is only one of two Korean martial arts which possesses such a classification. Song Deok-gi and Shin Han-seung were subsequently given living national treasure status by the South Korean government. Since then, Taekkyon has been enjoying a renaissance with the establishment of university clubs, the opening of new schools and active promotional efforts from the government and associations alike. The first contemporary Taekkyon competition took place in Busan on June 30, 1985. Afterwards, other schools have been established, splitting-up the Taekkyon scene between the followers of Song's teaching (current leaders of the Widae Taekkyon Preservation Association), and the tenants of Shin's, more focused on a sportive approach and bringing the art on the global stage.
Deok-Gi died on 23 July 1987, at the age of 94. In November 2011, Taekkyon was recognized by UNESCO and placed on its Intangible Cultural Heritage List, being honored as the first martial art on UNESCO's list, the other being Ssireum.
Techniques
Taekkyon utilizes a wide variety of techniques including kicks, hands, knee, elbow strikes, pressure point attacks, throws, joint locks, headbutt and grapples. The whole body is used in each movement. Although Taekkyon primarily utilizes kicking, punching, and arm strikes thrown from a mobile stance and does not provide a framework for groundfighting, it does incorporate a variety of different throws, takedowns, and grappling techniques to complement its striking focus. The main purpose of Taekkyon is to catch the opponent off-timing by using the whole weight of the body and catching the opponent's attack off-balance before returning it against him.
The basic steps are geometric and at the core of all advanced movement. All movements are natural to the human body. The movements of Taekkyon are fluid with the practitioners constantly moving. One of its most striking characteristics is the motion called gumsil or neung-cheong: It is a constant bending and stretching of one's knees, giving the art a dance-like appearance. This motion is also used in the Korea mask dance Talchum, so both arts look similar in a way: the art is like a dance in which the fighter constantly changes stance from left to right by stepping forward and backwards with arms up and ready to guard, blending arm movements with leg. Taekkyon does not make use of abrupt knee motions. The principles and methods used to extend the kick put more emphasis on grace and alignment for whole-body strength, as with the arm motions.
There are evolving forms in Taekkyon. One form can be performed many different ways with its variations over the basic ten-year training period. The curriculum is adjustable within the traditional system. Masters may create their own personalized approach for teaching the basic Taekkyon system.
Pumbalki (Footwork)
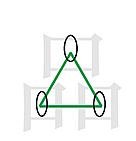
The most unique feature of Taekkyon is its triangular foot work called pumbalki or pum balbki (품밟기) which looks like a dance. The meaning of pumbalkki is "to step the Pum". Pum refers to the triangular look of the hanja 品, as pumbalki has a triangular form as well. The hanja "Pum" means "level" or "goods", but it is used only because of its shape, not because of its meaning. Footwork is smooth and rhythmic and enables rapid shifting of the center of gravity. It has the effect of strengthening the waist and lower part of the body as well as harmonizing attack and defense.
Taekkyon's pumbalki is in the shape of an equilateral triangle (△). It is practiced in one place, but when fighting with real opponents it involves continual advancing and retreating moves.
Hwalgaejit (arms swinging)
Hwalgaejit looks like the movement of a bird's wings. The shoulders are expanded naturally and must flow harmoniously with the footwork. While improving the body's reflexes, responsiveness and balance, it also help distract the opponent's attention before the counterattack. It is mainly used defensively to block or catch an opponent blow. Hwalgejit movements transfer power from the body to the arms in order to enhance power for quick action.
Kick Techniques (Baljil)
Taekkyon has been so renowned for its leg techniques that ancient chronicles referred to it with poetic names such as "one-hundred godlike flying leg skills" (baek gisintong bigaksul), "leg art" (gak sul), or "flying leg skills" (bi gak sul). Modern Taekkyon schools teach a great variety of kicks, low, medium, and high, as well as jumps. Sweeps with straight forward low kicks using the ball of the foot and the heel and flowing crescent-like high kicks. There are many kicks that move the leg outward from the middle, which is called gyeot chigi, and inward from the outside using the side of the heels and the side of the feet. The art also uses tricks like inward trips, wall-jumping, fake-outs, tempo, and slide-stepping.
Hand Techniques (Sonjil)
Though renowned for the variety of its kicks since the ancient ages, Taekkyon uses a lot of hand techniques. They target all area of the body and use every part of the arm: forearm, elbow, hand edge, back of the hand, fingertips. Techniques must be used in coordination with the pumbalki so that the springing power can be transferred to the upper members. The palm or fist is often used to strike.
Though hand techniques have been used for self-defense until the Widae style, the three modern schools only teach it at an advanced level as part of the "Yetbeop Taekkyon".
Throwing and tripping (Taejil)
Taekkyon uses techniques for throwing the opponent to the front or backward. Once the opponent is unbalanced, the user can follow with either a throw or a trip. The important thing is to use the opponent's own power to counterattack.
Joint Locks (Ttanjuk)
These techniques are for locking and twisting an opponent's articulations. Counter an opponent's attack by locking a joint and follow with a hand or leg attack.
As a competitive martial art

Taekkyon jousts have evolved into a modern sport and tournaments are held by the three modern schools all over Korea. And also authorized discipline in Korea National Championships. When Taekkyon is practiced in competition, it uses a limited subset of techniques, focusing on grappling and kicking only. Points are scored by throwing (or tripping) the opponent to the ground, pushing them out of the ring, or kicking them in the head. There are no hand strikes or headbutts, and purposefully injuring your opponent is prohibited. The head kicks are often quite sharp, but usually not full force, and fighters may not attempt to wear the opponent down with body blows as in western Boxing or Muay Thai. Matches are sometimes decided by the best of three falls—the first fighter to score two points wins. However, different modern associations employ slightly different rules. The contestants circle each other, changing their footwork constantly using pumbalkki and feinting with low kicks, before attacking suddenly.
Modern development
Various Taekkyon organisations currently exist in Korea and overseas. These include:
- The Widae Taekkyeon Preservation Society, also called World Wide Taekkyon Organization (WWTO) or simply Widae Taekkyeon. Based in Seoul and Los Angeles. Led by Lee Jun-seo (1962-) and Ko Yong-woo (1952-), the two most senior students of Song Deok-gi. This association was established by Song Deok-gi and Lee Jun-seo in 1983 and does not dispense the sportive innovations brought to the art in the mid 1980s.
- The Korea Traditional Taekgyeon Association (KTTA). Headquartered in Chungju, therefore sometimes referred to as Chungju Taekkyon. The KTTA is led by Jeong Kyung-hwa (1954-) who was given the title of "living national treasure of the second generation" by the Korean Government in 1995. He was the main pupil of Shin Han-seung. The KTTA was responsible for the recognition of Taekkyon as an Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity.
- The Korea Taekkyon Federation (KTF). Sometimes called Daehan Taekkyon. Based in Seoul Olympic park, established in 1991 and led by Lee Yong-bok (1948-) until 2015. Originally an 8th Dan in Taekwondo, he mainly learnt Taekkyon as an autodidact with a brief stint under Song Deok-gi and Shin Han-seung. KTF has participated in Korea Olympic Committee since 2007. As a national federation of Taekkyon, Korea Taekkyon Federation has a right to organize and manage Korea National Championships and Sports for All festival annually. This federation is by far the biggest and the most developed of all the Taekkyon associations in Korea and abroad. This school helped shape the modern perception of Taekkyon as a non-violent folk-game with techniques focusing on kicks.
- The Kyulyun Taekyun Association (KTK). Based in Seoul, established in 2000. The KTK is led by Do Ki-hyun (1962-) who mainly learned from Song Deok-gi after starting his training under Shin Han-Seung. The school is famous for organizing each year since 2004 the Taekyun Battle (or TK Battle), one of the most prestigious tournaments of Korea.
Taekkyon is also practiced around the world with schools in Australia, China, Denmark, France, Germany, Japan, Kazakhstan, Norway, Russia, United Kingdom and the USA.
Historical records on Taekkyon and street fighting
Medieval records mention that several street fighting games and techniques existed in Korea at the time, up until the twentieth century. Due to the elite's scorn and contempt for martial activities, Taekkyon came to be perceived as a fighting method for thugs and sometimes confused with such disciplines: Sibak (시박), Pyeonssaum (편싸움), Nalparam (날파람), Nanjanbaksi (난잔박시), Taegyeok (태격). Some barehand techniques for street fighting are currently taught as part of the curriculum of the three modern schools as part of the "Yetbeop Taekkyon" or "Old style Taekkyon".
Taekkyon myths and facts
There is a common modern myth about Taekkyon being depicted as a kicking game as well as an "ancient version of Taekwondo" in the public eye. This is mainly due to the spread of Taekwondo as the national martial sport of Korea after the Korean War. Since then, Taekkyon has been known to the general public mainly through Taekwondo's association and rendition based on incomplete information via bits and pieces of records emphasizing its kicking techniques. Even though the Taekwondo establishment claims an ancient lineage through Taekkyon, and even partially modeled its name on it, the two disciplines don't have much in common. In fact, Taekkyon associations do not acknowledge having any relationship to taekwondo, and explicitly deny any link.
See also
 In Spanish: Taekkyon para niños
In Spanish: Taekkyon para niños
- Korean martial arts
- Song Deok-gi
- Korean culture