Stereophonic sound facts for kids
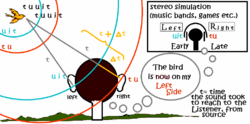
Stereophonic sound or, more commonly, stereo, is a method of sound reproduction that creates an illusion of multi-directional audible perspective. This is usually achieved by using two or more independent audio channels through a configuration of two or more loudspeakers (or stereo headphones) in such a way as to create the impression of sound heard from various directions, as in natural hearing. Thus the term "stereophonic" applies to so-called "quadraphonic" and "surround-sound" systems as well as the more common two-channel, two-speaker systems. It is often contrasted with monophonic, or "mono" sound, where audio is heard as coming from one position, often ahead in the sound field (analogous to a visual field). Stereo sound has been in common use since the 1970s in entertainment systems such as broadcast radio, TV, recorded music, internet, computer audio, and cinema.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Sonido estereofónico para niños
In Spanish: Sonido estereofónico para niños