Socorro County, New Mexico facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Socorro County
|
|
|---|---|

Socorro County Courthouse in Socorro
|
|
Location within the U.S. state of New Mexico
|
|
 New Mexico's location within the U.S. |
|
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | January 9, 1852 |
| Seat | Socorro |
| Largest city | Socorro |
| Area | |
| • Total | 6,649 sq mi (17,220 km2) |
| • Land | 6,647 sq mi (17,220 km2) |
| • Water | 2.1 sq mi (5 km2) 0.03%% |
| Population
(2020)
|
|
| • Total | 16,595 |
| • Density | 2.49586/sq mi (0.96366/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−7 (Mountain) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−6 (MDT) |
| Congressional district | 2nd |
Socorro County (Spanish: Condado de Socorro) is a county in the U.S. state of New Mexico. As of the 2020 census, the population was 16,595. The county seat is Socorro. The county was formed in 1852 as one of the original nine counties of New Mexico Territory. Socorro was originally the name given to a Native American village (see: Puebloan peoples) by Don Juan de Oñate in 1598. Having received vitally needed food and assistance from the native population, Oñate named the pueblo Socorro ("succor" in English).
Socorro County is home to multiple scientific research institutions including New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology, the National Radio Astronomy Observatory and its associated Very Large Array, the Magdalena Ridge Observatory, and the Langmuir Laboratory for Atmospheric Research. Federal public lands in Socorro County include parts of the Cibola National Forest, the Bosque del Apache National Wildlife Refuge, the Sevilleta National Wildlife Refuge, the Bureau of Land Management (BLM) Socorro Field Office, parts of the Salinas Pueblo Missions National Monument, and parts of the El Camino Real de Tierra Adentro National Historic Trail.
Contents
History
Socorro County's history is intimately linked with the rich history of the surrounding area. Basham noted in his report documenting the archeological history of the Cibola National Forest's Magdalena Ranger District, which is almost entirely within Socorro County, that “[t]he heritage resources on the district are diverse and representative of nearly every prominent human evolutionary event known to anthropology. Evidence for human use of district lands date back 14,000 years to the Paleoindian period providing glimpses into the peopling of the New World and megafaunal extinction.“ Much of the now Magdalena Ranger District were a province of the Apache. Bands of Apache effectively controlled the Magdalena-Datil region from the seventeenth century until they were defeated in the Apache Wars in the late nineteenth century.
Outlaw renegades Butch Cassidy and the Wild Bunch and notorious Apaches like Cochise and Geronimo have ties to Socorro County's San Mateo Mountains. Vicks Peak was named after Victorio, “a Mimbreño Apache leader whose territory included much of the south and southwest New Mexico.” Famous for defying relocation orders in 1879 and leading his warriors “on a two-year reign of terror before he was killed,” Victorio is at least as highly regarded as Geronimo or Cochise among Apaches. Perhaps most famous outlaw was the Apache Kid whose supposed grave lies within the Apache Kid Wilderness. Stories of depredations by the Apache Kid, and of his demise, became so common and dramatic that in southwestern folklore they may be exceeded only by tales of lost Spanish gold. Native Americans lingered in the San Mateos well into the 1900s. We know this by an essay written by Aldo Leopold in 1919 where he documents stumbling upon the remains of a recently abandoned Indian hunting camp.
- Cultural or Historic Figures with Ties to Socorro County
A mining rush followed the Apache wars – gold, silver, and copper were found in the mountains. It wasn't until this time that extensive use of the area by non-Native Americans occurred. While some mining activity, involving gold, silver, and copper, occurred in the southern part of the range near the end of the nineteenth century, the prospecting/mining remnants are barely visible today due to collapse, topographic screening, and vegetation regrowth. While miners combed the mountains for mineral riches during the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, stockmen drove tens of thousands of sheep and cattle to stockyards at the village of Magdalena, then linked by rail with Socorro. In fact, the last regularly used cattle trail in the United States stretched 125 miles westward from Magdalena. The route was formally known as the Magdalena Livestock Driveway, but more popularly known to cowboys and cattlemen as the Beefsteak Trail. The trail began use in 1865 and its peak was in 1919. The trail was used continually until trailing gave way to trucking and the trail officially closed in 1971.
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 6,649 square miles (17,220 km2), of which 6,647 square miles (17,220 km2) is land and 2.1 square miles (5.4 km2) (0.03%) is water. It is the second-largest county in New Mexico by area, after Catron County.
Socorro County ranges in elevation from approximately 4,528 ft (1,380 m) on the banks of the Rio Grande to 10,784 ft (3,287 m) at the top of South Baldy peak in the Magdalena Mountains. The southern portion of the Rocky Mountains extend into New Mexico and Socorro County. There are several mountain ranges that spread throughout the county. The Forest Service manages portions of four mountain ranges: the Bear, Datil, Magdalena, and San Mateo Mountains. Most of the land that comprises these mountains are within the Cibola National Forest. These ranges, as well as Ladron Peak located in Socorro County, are classified as sky islands.
Adjacent counties
- Cibola County – northwest
- Valencia County – north
- Torrance County – northeast
- Lincoln County – east
- Sierra County – south
- Catron County – west
National protected areas
- Bosque del Apache National Wildlife Refuge
- Sevilleta National Wildlife Refuge
- Cibola National Forest (part)
- National System of Public Lands managed by the BLM’s Socorro Field Office (part)
- El Camino Real de Tierra Adentro National Historic Trail (part)
- Salinas Pueblo Missions National Monument (part)
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1860 | 5,787 | — | |
| 1870 | 6,603 | 14.1% | |
| 1880 | 7,875 | 19.3% | |
| 1890 | 9,595 | 21.8% | |
| 1900 | 12,195 | 27.1% | |
| 1910 | 14,761 | 21.0% | |
| 1920 | 14,061 | −4.7% | |
| 1930 | 9,611 | −31.6% | |
| 1940 | 11,422 | 18.8% | |
| 1950 | 9,670 | −15.3% | |
| 1960 | 10,168 | 5.1% | |
| 1970 | 9,763 | −4.0% | |
| 1980 | 12,566 | 28.7% | |
| 1990 | 14,764 | 17.5% | |
| 2000 | 18,078 | 22.4% | |
| 2010 | 17,866 | −1.2% | |
| 2020 | 16,595 | −7.1% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 1790-1960 1900–1990 1990-2000 2010 |
|||
2010 census
As of the 2010 census, there were 17,866 people, 7,014 households, and 4,349 families residing in the county. The population density was 2.7 inhabitants per square mile (1.0/km2). There were 8,059 housing units at an average density of 1.2 per square mile (0.46/km2). The racial makeup of the county was 75.1% white, 11.7% American Indian, 1.2% Asian, 1.1% black or African American, 8.1% from other races, and 2.8% from two or more races. Those of Hispanic or Latino origin made up 48.5% of the population. In terms of ancestry, 7.1% were English, 6.8% were German, and 4.2% were American.
Of the 7,014 households, 30.4% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 43.1% were married couples living together, 12.9% had a female householder with no husband present, 38.% were non-families, and 30.8% of all households were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.46 and the average family size was 3.09. The median age was 36.9 years.
The median income for a household in the county was $33,284 and the median income for a family was $41,964. Males had a median income of $40,295 versus $27,819 for females. The per capita income for the county was $17,801. About 22.7% of families and 26.8% of the population were below the poverty line, including 33.1% of those under age 18 and 19.0% of those age 65 or over.
Ecology, recreation and tourism
With multiple mountain ranges, extents of grasslands and marshes providing a wide array of available habitats, Socorro County is home to an extensive variety of ecosystems and wildlife. Socorro County contains 826 species of wildlife, including 14 amphibians, 60 reptiles, 336 birds, and 96 mammals. Wildlife in the County includes coyote, deer, elk, pronghorn antelope, bighorn sheep, Barbary sheep, black bear, mountain lion, wild turkey, various furbearers, Mexican spotted owl, and quail.
There are three congressionally designated Wilderness areas located within Socorro County. The Apache Kid and the Withington Wilderness Areas are both located in the San Mateo Mountains within the Cibola National Forest's Magdalena Ranger District. The Bosque del Apache Wilderness comprises two separate sections, totaling 30,427 acres of the National Wildlife Refuge. There are an additional 172,143 acres of Forest Service Inventoried Roadless Areas and 159,891 acres of BLM Wilderness Study Areas in the county. These undeveloped lands without roads offer outstanding opportunities to experience the area's amazing natural heritage, to getaway and enjoy the outdoors and, for the hearty, to explore deep into the backcountry and challenge yourself in the area's big wild.
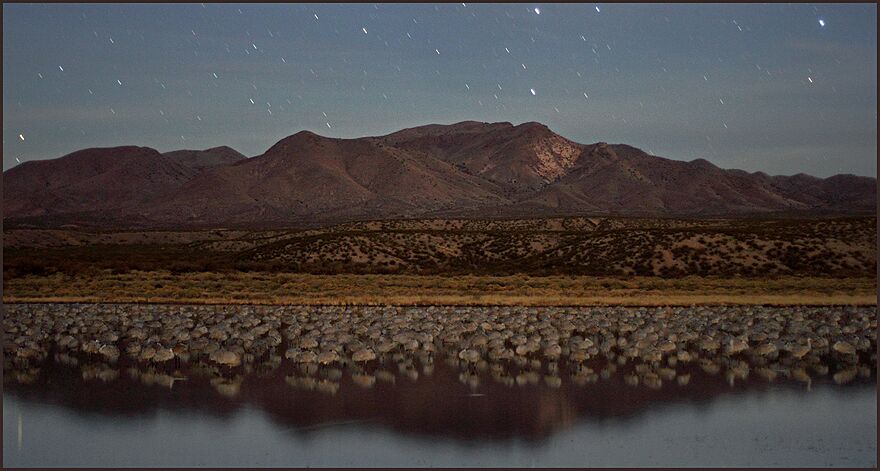
The high mountains, remote canyons, pristine forests and diverse wildlife found on the area's national forests, national wildlife refuges, national monuments, and BLM's national system of public lands provide for phenomenal recreation opportunities, including picnicking, hiking, backpacking, wildlife viewing, horseback-riding, and hunting. In fact, the four biggest elk in New Mexico were bagged in Socorro county and the Datil Mountains. The two most popular recreational activities on the Cibola National Forest are hiking/walking and viewing natural features with 35% and 15% of visitors citing these as their main activities, respectively. The Bosque del Apache National Wildlife Refuge hosts the Festival of the Cranes every November, celebrating the arrival of sandhill cranes and other migratory birds. Rare whooping cranes are also found occasionally on the Bosque del Apache.
- Wildlife in Socorro County, New Mexico
-
Sandhill cranes at Bosque del Apache National Wildlife Refuge during the Festival of the Cranes.
The natural amenities in Socorro contribute to a strong tourism industry for the county. Visitors spent $47.4 million in Socorro County in 2011. Recreation alone accounted for more than $4 million in visitor spending in both 2010 and 2011. Tourism accounts for 8.8% of employment and 4.5% of labor income for the county. Additionally, tourism resulted in $7.7 million of total tax revenue, including $1.1 million in local tax revenue.
Communities

City
- Socorro (county seat)
Village
Census-designated places
Unincorporated communities
Populated Places
- Bingham
- Sabinal
Ghost towns
- Adobe
- Alamillo Pueblo
- Bosquecito
- Canta Recio
- Carthage
- Contadero
- Council Rock
- Field
- Kelly
- Pueblito de la Parida
- Paraje
- Park City
- Pilabó
- Qualacu
- Riley
- Rosedale
- San Felipe
- San Marcial
- San Pascual Pueblo
- San Pedro
- Senecú
- Tajo
- Tokay
- Val Verde
Education
School districts include:
- Belen Consolidated Schools
- Carrizozo Municipal Schools
- Corona Municipal Schools
- Magdalena Municipal Schools
- Mountainair Public Schools
- Socorro Consolidated Schools
See also
 In Spanish: Condado de Socorro para niños
In Spanish: Condado de Socorro para niños














