Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia
Socijalistička Federativna Republika Jugoslavija
Социјалистичка Федеративна Република Југославија |
|||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1945–1992 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
Motto: Bratstvo i jedinstvo
"Brotherhood and Unity" |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Anthem: "Hej, Sloveni'"'
"Hej, Sloveni" |
|||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Belgrade | ||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Serbo-Croatian, Slovene, and Macedonian |
||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Various | ||||||||||||||||||
| President | |||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1945 - 1953 (first)
|
Ivan Ribar | ||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1953 - 1980
|
Josip Broz Tito | ||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1991 - 1992 (last)
|
Stjepan Mesić | ||||||||||||||||||
| Prime Minister | |||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1945 - 1953 (first)
|
Josip Broz Tito | ||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1989 - 1991 (last)
|
Ante Marković | ||||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Cold War | ||||||||||||||||||
|
• Proclamation
|
November 29 1945 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 24 October 1945 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
• Constitutional reform
|
21 February 1974 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 25 June 1991 - 27 April 1992 1992 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||
| July 1989 | 255,804 km2 (98,766 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||||||||
|
• July 1989
|
23724919 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Yugoslav dinar | ||||||||||||||||||
| Time zone | UTC+1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Calling code | 38 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
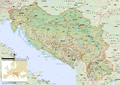
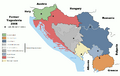
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was the Yugoslav state that existed from the second half of World War II (1945) until it was formally dissolved in 1992 (de facto dissolved in 1991 with no leaders representing it) amid the Yugoslav wars. It was a socialist state and a federation made up of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, and Slovenia. In 1992, the two remaining states still committed to a union, Serbia and Montenegro, formed the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, which had not been recognized as the successor of the SFRY by international leaders.
A provisional parliament met in August 1945, comprising delegates from all parts of the country plus 68 representatives of prewar political parties and 13 independents. Elections for a bicameral parliament, which was to comprise a federal council and a council of nationalities and was to have the powers of a constituent assembly, were held on 11 November 1945: no political opposition to the People's Front was allowed. This situation caused the three royalist representatives, Grol-Subasic-Juraj Sutej, to secede from the provisional government indeed voting was on a single list of People's Front candidates with provision for opposition votes to be cast in separate voting boxes but this procedure made electors identifiable by OZNA agents. A powerful election campaign was mounted to ensure a large majority for Josip Broz Tito's People's Front, the general organization behind which the communist party operated.
Legacy
The modern countries whose territory formerly made up Yugoslavia are still today sometimes called the "former Yugoslavia". These countries are:
 Slovenia (since 1991)
Slovenia (since 1991) Croatia (since 1991)
Croatia (since 1991) Macedonia (since 1991)
Macedonia (since 1991) Bosnia and Herzegovina (since 1992)
Bosnia and Herzegovina (since 1992) Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (Serbia and Montenegro) (1992 to 2006)
Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (Serbia and Montenegro) (1992 to 2006)
 Montenegro (since 2006)
Montenegro (since 2006) Serbia (since 2006)
Serbia (since 2006)
 Kosovo (since 2008; recognized by 98 United Nations member countries)
Kosovo (since 2008; recognized by 98 United Nations member countries)
Images for kids
-
Marshal Josip Broz Tito led Yugoslavia from 1944 to 1980.
-
Yugoslav ration stamps for milk, 1950
-
The parliament building of Bosnia and Herzegovina burning amid the Yugoslav wars
-
JAT McDonnell Douglas DC-10-30 at Sydney Airport, 1985, with classic livery
-
The main building of the University of Zagreb and adjacent Faculty of Law
-
The main building of the University of Ljubljana
-
Ivo Andrić, awarded the 1961 Nobel Prize for Literature
See also
 In Spanish: República Federativa Socialista de Yugoslavia para niños
In Spanish: República Federativa Socialista de Yugoslavia para niños