Sinoceratops facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Sinoceratops |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Superorder: | |
| Order: | |
| Infraorder: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: |
Centrosaurinae
|
| Genus: |
Sinoceratops
Xu et al., 2010
|
Sinoceratops is an extinct genus of ceratopsian dinosaur that lived approximately 73 million years ago during the latter part of the Cretaceous Period in what is now Shandong province in China. It was named in 2010 by Xu Xing et al. for three skulls from Zhucheng, China. The name of its type species Sinoceratops zhuchengensis means "Chinese horned face from Zhucheng", after the location of its discovery.
Sinoceratops was a medium-sized, averagely-built, ground-dwelling, quadrupedal herbivore. It could grow up to an estimated 6 m (19.7 ft) length and 2 metres (6.6 ft) height, and weigh up to 2 tonnes (2.0 long tons; 2.2 short tons). It was the first ceratopsid dinosaur discovered in China, and the only ceratopsid known from Asia. All other centrosaurines, and all chasmosaurines, are known from fossils discovered in North America, except for possibly Turanoceratops. Sinoceratops is also significant because it is one of the largest known centrosaurines, and is much larger than any other known basal members of this group.
Sinoceratops was discovered in the Xingezhuang Formation, which was deposited during the late Cretaceous. It lived alongside leptoceratopsids, saurolophines, and tyrannosaurines. The most common creature in the formation was Shantungosaurus, to which most of the material has been assigned. The animals living alongside Sinoceratops and Shantungosaurus were Zhuchengceratops, Zhuchengtitan, and Zhuchengtyrannus.
Description
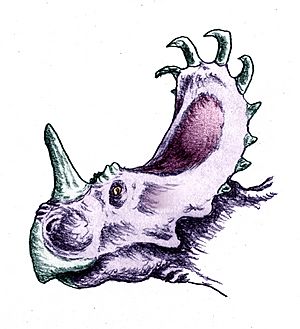
Sinoceratops was a larger ceratopsian ornithischian, with an estimated length of about 6 metres (19.7 ft), weight of 2 tonnes (2.0 long tons; 2.2 short tons), and height of about 2 metres (6.6 ft). Thomas R. Holtz Jr. estimated its length at 7 metres (23 ft) and weight at 2.3 tonnes (2.3 long tons; 2.5 short tons), the weight of a rhinoceros. It has a short, hooked horn on its nose (called a nasal horn), no horns above its eyes (brow horns), and a short neck frill with a series of forward-curving hornlets that gave the frill a crown-like appearance. Inside this row of hornlets there is a series of low knobs on the top of the frill, which are not seen in any other horned dinosaur. Sinoceratops is a member of the short-frilled ceratopsids, the Centrosaurinae. Holotype specimen ZCDM V0010 consists of a partial skull with most elements of the skull roof and partial braincase. The skull of Sinoceratops is estimated to be 180 cm (5.9 ft) long making it one of the largest known centrosaurine skulls.
Features that differentiate an animal from most or all others are called a diagnosis. Some, but not all, of the features in a diagnosis are also autapomorphies. An autapomorphy is a distinctive anatomical feature that is unique to a given organism. According to Xu (2010), Sinoceratops can be distinguished based on the following diagnostic characteristics: there are at least ten robust, strongly curved hornlike processes along the rear margin of the combined parietals, while at the same time at least four hornlike processes on the combined squamosals are present; there is a large accessory fenestra in front of the antorbital fenestra (differing from all other known centrosaurines); the external margin of the parietals is only weakly undulating (differing from all other known centrosaurines); and the presence of broad-based epoccipitals (differing from all other known centrosaurines).
Images for kids