Seljuk Empire facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Seljuk Empire
آلِ سلجوق
Āl-e Saljuq |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1037–1194 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
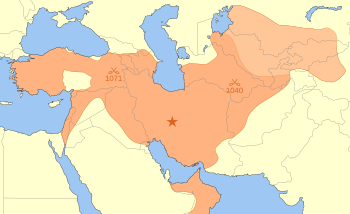
Seljuq Empire at its greatest extent in 1092,
upon the death of Malik Shah I |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Sunni Islam (Hanafi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Government | De facto: Independent Sultanate De jure: Under Caliphate |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Caliph | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1031–1075
|
Al-Qa'im | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1180-1225
|
Al-Nasir | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sultan | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1037–1063
|
Toghrul I (first) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1174–1194
|
Toghrul III (last) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Tughril formed the state system
|
1037 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Battle of Dandanaqan
|
1040 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1071 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1095–1099 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Battle of Qatwan
|
1141 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Replaced by the Khwarezmian Empire
|
1194 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1080 est. | 3,900,000 km2 (1,500,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Seljuk Empire was a high medieval Turko-Persian Sunni Muslim empire, originating from the Qiniq branch of Oghuz Turks. At its greatest extent, the Seljuk Empire controlled a vast area stretching from western Anatolia and the Levant to the Hindu Kush in the east, and from Central Asia to the Persian Gulf in the south.
The Seljuk empire was founded by Tughril Beg (990–1063) and his brother Chaghri Beg (989–1060) in 1037. From their homelands near the Aral Sea, the Seljuks advanced first into Khorasan and then into mainland Persia, before eventually conquering eastern Anatolia. Here the Seljuks won the battle of Manzikert in 1071 and conquered most of Anatolia from the Byzantine Empire, which became one of the reasons for the first crusade (1095-1099). From c. 1150-1250, the Seljuk empire declined, and was invaded by the Mongols around 1260. The Mongols divided Anatolia into emirates. Eventually one of these, the Ottoman, would conquer the rest.
Seljuk gave his name to both the empire and the Seljuk dynasty. The Seljuks united the fractured political landscape of the eastern Islamic world and played a key role in the first and second crusades. Highly Persianized in culture and language, the Seljuks also played an important role in the development of the Turko-Persian tradition, even exporting Persian culture to Anatolia. The settlement of Turkic tribes in the northwestern peripheral parts of the empire, for the strategic military purpose of fending off invasions from neighboring states, led to the progressive Turkicization of those areas.
Images for kids
-
Head of male royal figure, 12–13th century, found in Iran.
-
Mausoleum of Sultan Sanjar in Merv, Turkmenistan.
-
Bowl with an Enthronement Scene,12th-13th century, Brooklyn Museum
-
Seljuk-era art: Ewer from Herat, Afghanistan, dated 1180–1210CE. Brass worked in repousse and inlaid with silver and bitumen. British Museum.
-
Section of a Water Jug, Habb, 12th-13th century, Brooklyn Museum
-
Toghrol Tower, a 12th-century monument south of Tehran in Iran commemorating Tughril Beg.
-
The Kharāghān twin towers, built in 1053 in Iran, is the burial of Seljuk princes.
See also
 In Spanish: Imperio selyúcida para niños
In Spanish: Imperio selyúcida para niños