Second Polish Republic facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Republic of Poland
Rzeczpospolita Polska
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1918–1939 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
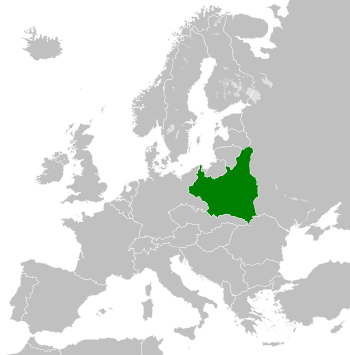
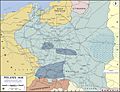
Second Polish Republic in 1930
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Warsaw 52°14′N 21°1′E / 52.233°N 21.017°E |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Official: Polish Unofficial:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | 1931 census Majority: 64.8% Roman Catholicism 'Minorities:'
11.8% Eastern Orthodox
10.5% Greek Catholic 9.8% Jewish 2.6% Protestant 0.5% Other Christian 0.02% Other |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional republic (1918-1935)
Unitary presidential constitutional republic (1935-1939) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| President | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1918–1922
|
Józef Piłsudskia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1922
|
Gabriel Narutowicz | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1922–1926
|
Stanisław Wojciechowski | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prime Minister | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1918–1919 (first)
|
Jędrzej Moraczewski | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1936–1939 (last)
|
Felicjan S. Składkowski | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Legislature | Sejm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Upper chamber
|
Senate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Lower chamber
|
Sejm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Interwar period | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• End of World War I
|
11 November 1918 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 28 June 1919 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18 March 1921 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 September 1939 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 17 September 1939 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Fall of Warsaw
|
28 September 1939 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Complete occupation
|
6 October 1939 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1921 | 387,000 km2 (149,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1931 | 388,634 km2 (150,052 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1938 | 389,720 km2 (150,470 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1921
|
27,177,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1931
|
32,107,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 1938
|
34,849,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Marka (until 1924) Złoty (after 1924) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | PL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Second Polish Republic, commonly known as interwar Poland, refers to the country of Poland in the period between the First and Second World Wars (1918–1939). Officially known as the Republic of Poland (Polish: Rzeczpospolita Polska), the state was re-established in 1918, in the aftermath of World War I. The Second Republic ceased to exist in 1939, when Poland was invaded by Nazi Germany, the Soviet Union and the Slovak Republic, marking the beginning of the European theatre of World War II.
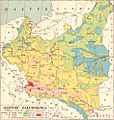
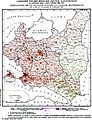
In 1938, the Second Republic was the sixth largest country in Europe. According to the 1921 census, the number of inhabitants was 27.2 million. By 1939, just before the outbreak of World War II, this had grown to an estimated 35.1 million. Almost a third of population came from minority groups: 13.9% Ruthenians; 10% Ashkenazi Jews; 3.1% Belarusians; 2.3% Germans and 3.4% Czechs and Lithuanians. At the same time, a significant number of ethnic Poles lived outside the country's borders.
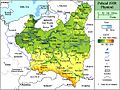
When, after several regional conflicts, the borders of the state were finalised in 1922, Poland's neighbours were Czechoslovakia, Germany, the Free City of Danzig, Lithuania, Latvia, Romania and the Soviet Union. It had access to the Baltic Sea via a short strip of coastline either side of the city of Gdynia, known as the Polish Corridor. Between March and August 1939, Poland also shared a border with the then-Hungarian governorate of Subcarpathia. The political conditions of the Second Republic were heavily influenced by the aftermath of World War I and conflicts with neighbouring states as well as the emergence of Nazism in Germany.
The Second Republic maintained moderate economic development. The cultural hubs of interwar Poland – Warsaw, Kraków, Poznań, Wilno and Lwów – became major European cities and the sites of internationally acclaimed universities and other institutions of higher education.
Images for kids
-
Polish pavilion at Expo 1937 in Paris
-
Polish pavilion at the 1939 World's Fair in New York City
-
Poland's MS Batory, and MS Piłsudski, at the sea port of Gdynia, 18 December 1937
-
The Eastern Trade Fair in Lwów, 1936
-
Gdynia, a modern Polish seaport established in 1926
-
Industry and communications in Poland before the start of the Second World War
-
Prime Minister Kazimierz Bartel, also a scholar and mathematician
-
The National Museum in Warsaw (Polish: Muzeum Narodowe w Warszawie), popularly known as the MNW, opened in 1938.
-
ORP Orzeł was the lead ship of her class of submarines serving in the Polish Navy during the Second World War.
See also
 In Spanish: Segunda República polaca para niños
In Spanish: Segunda República polaca para niños