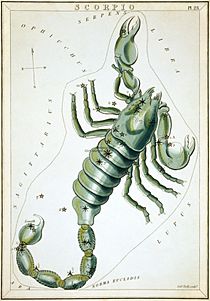
Scorpius facts for kids
| Constellation | |
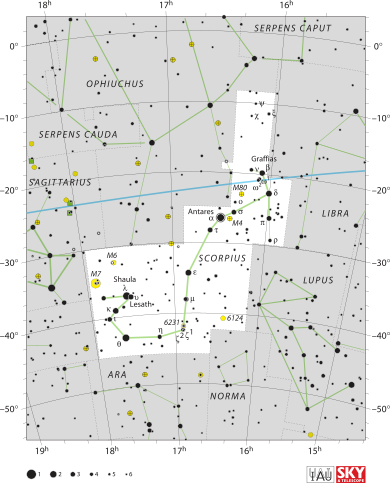
List of stars in Scorpius
|
|
| Abbreviation | Sco |
|---|---|
| Genitive | Scorpii |
| Pronunciation | genitive |
| Symbolism | the Scorpion |
| Right ascension | 16.8875h |
| Declination | −30.7367° |
| Quadrant | SQ3 |
| Area | 497 sq. deg. (33rd) |
| Main stars | 18 |
| Bayer/Flamsteed stars |
47 |
| Stars with planets | 14 |
| Stars brighter than 3.00m | 13 |
| Stars within 10.00 pc (32.62 ly) | 3 |
| Brightest star | Antares (α Sco) (0.96m) |
| Messier objects | 4 |
| Meteor showers | Alpha Scorpiids Omega Scorpiids |
| Bordering constellations |
Sagittarius Ophiuchus Libra Lupus Norma Ara Corona Australis |
| Visible at latitudes between +40° and −90°. Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of July. |
|
Scorpius is one of the constellations of the zodiac and is located in the Southern celestial hemisphere. Its name is Latin for scorpion, and its symbol is ![]() (Unicode ♏).
(Unicode ♏).
Scorpius is one of the 48 constellations identified by the Greek astronomer Ptolemy in the second century. It is an ancient constellation that pre-dates the Greeks.
It lies between Libra to the west and Sagittarius to the east. It is a large constellation located in the southern hemisphere near the center of the Milky Way.
It has 47 stars.
Notable features
Stars
Scorpius contains many bright stars, including Antares (α Sco), "rival of Mars," so named because of its distinct reddish hue; β1 Sco (Graffias or Acrab), a triple star; δ Sco (Dschubba, "the forehead"); θ Sco (Sargas, of unknown origin); ν Sco (Jabbah); ξ Sco; π Sco (Fang); σ Sco (Alniyat); and τ Sco (Paikauhale).
Marking the tip of the scorpion's curved tail are λ Sco (Shaula) and υ Sco (Lesath), whose names both mean "sting." Given their proximity to one another, λ Sco and υ Sco are sometimes referred to as the Cat's Eyes.
The constellation's bright stars form a pattern like a longshoreman's hook. Most of them are massive members of the nearest OB association: Scorpius-Centaurus.
The star δ Sco, after having been a stable 2.3 magnitude star, flared in July 2000 to 1.9 in a matter of weeks. It has since become a variable star fluctuating between 2.0 and 1.6. This means that at its brightest it is the second brightest star in Scorpius.
U Scorpii is the fastest known nova with a period of about 10 years.
The close pair of stars ω¹ Scorpii and ω² Scorpii are an optical double, which can be resolved by the unaided eye. They have contrasting blue and yellow colours.
The star once designated γ Sco, is today known as σ Lib. The entire constellation of Libra was considered to be claws of Scorpius in Ancient Greek times, with a set of scales held aloft by Astraea (represented by adjacent Virgo) being formed from these western-most stars during later Greek times. The division into Libra was formalised during Roman times.
Deep-sky objects
Due to its location straddling the Milky Way, this constellation contains many deep-sky objects such as the open clusters Messier 6 (the Butterfly Cluster) and Messier 7 (the Ptolemy Cluster), NGC 6231 (by ζ² Sco), and the globular clusters Messier 4 and Messier 80.
Messier 80 (NGC 6093) is a globular cluster of magnitude 7.3, 33,000 light-years from Earth. It is a compact Shapley class II cluster; the classification indicates that it is highly concentrated and dense at its nucleus. M80 was discovered in 1781 by Charles Messier. It was the site of a rare discovery in 1860 when Arthur von Auwers discovered the nova T Scorpii.
NGC 6302, also called the Bug Nebula, is a bipolar planetary nebula. NGC 6334, also known as the Cat's Paw Nebula, is an emission nebula and star-forming region.
Mythology
In Greek mythology, several myths associated with Scorpio attribute it to Orion.
According to one version, Orion boasted to the goddess Artemis and her mother, Leto, that he would kill every animal on Earth. Artemis and Leto sent a scorpion to kill Orion. Their battle caught the attention of Zeus, who raised both combatants to the sky to serve as a reminder for mortals to curb their excessive pride. In another version of the myth, Artemis' twin brother, Apollo, was the one who sent the scorpion to kill Orion after the hunter earned the goddess' favor by admitting she was better than him. After Zeus raised Orion and the scorpion to the sky, the former hunts every winter but flees every summer when the scorpion comes. In both versions, Artemis asked Zeus to raise Orion.
In a Greek myth without Orion, the celestial scorpion encountered Phaethon while he was driving his father Helios' Sun Chariot.
Origins
The Babylonians called this constellation MUL.GIR.TAB - the 'Scorpion', the signs can be literally read as 'the (creature with) a burning sting'.
In some old descriptions the constellation of Libra is treated as the Scorpion's claws. Libra was known as the Claws of the Scorpion in Babylonian (zibānītu (compare Arabic zubānā)) and in Greek (χηλαι).
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Escorpio (constelación) para niños
In Spanish: Escorpio (constelación) para niños