Sauk County, Wisconsin facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Sauk County
|
|
|---|---|

Sauk County Courthouse in June 2012
|
|
Location within the U.S. state of Wisconsin
|
|
 Wisconsin's location within the U.S. |
|
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | 1844 |
| Named for | Sauk people |
| Seat | Baraboo |
| Largest city | Baraboo |
| Area | |
| • Total | 849 sq mi (2,200 km2) |
| • Land | 831 sq mi (2,150 km2) |
| • Water | 18 sq mi (50 km2) 2.1%% |
| Population
(2020)
|
|
| • Total | 65,763 |
| • Estimate
(2023)
|
65,920 |
| • Density | 77.46/sq mi (29.907/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−6 (Central) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| Congressional district | 2nd |
Sauk County is a county in Wisconsin. It is named after a large village of the Sauk people. As of the 2020 census, the population was 65,763. Its county seat and largest city is Baraboo. The county was created in 1840 from Wisconsin Territory and organized in 1844. Sauk County comprises the Baraboo, WI Micropolitan Statistical Area and is included in the Madison metropolitan area.
Contents
History
Sauk County was a New England settlement. The original founders of Sauk County consisted entirely of settlers from New England as well as some from upstate New York who had parents who moved to that region from New England shortly after the American Revolution. These people were "Yankee" settlers, that is to say they were descended from the English Puritans who settled New England in the 1600s. While most of them came to Wisconsin directly from New England, there were many who came from upstate New York. These were people whose parents had moved from New England to upstate New York in the immediate aftermath of the American Revolution. They were part of a wave of New England farmers who headed west into what was then the wilds of the Northwest Territory during the early 1800s. In the case of Wisconsin this migration primarily occurred in the 1830s. Due to the prevalence of New Englanders and New England transplants from upstate New York, Wisconsin was very culturally continuous with early New England culture for much of its early history.
The Yankee migration to Wisconsin in the 1830s was a result of several factors, one of which was the overpopulation of New England. The old stock Yankee population had large families, often bearing up to ten children in one household. Most people were expected to have their own piece of land to farm, and due to the massive and nonstop population boom, land in New England became scarce as every son claimed his own farmstead. As a result, there was not enough land for every family to have a self-sustaining farm, and Yankee settlers began leaving New England for the Midwestern United States.
They were aided in this effort by the construction and completion of the Erie Canal which made traveling to the region much easier, causing an additional surge in migrants coming from New England. Added to this was the end of the Black Hawk War, which made the region much safer to travel through and settle in for white settlers.
They got to what is now Sauk County in the 1830s by sailing up the Wisconsin River from the Mississippi River on small barges which they constructed themselves out of materials obtained from the surrounding woodlands. When they arrived in what is now Sauk County there was nothing but dense virgin forest, the "Yankee" New Englanders laid out farms, constructed roads, erected government buildings and established post routes. They brought with them many of their Yankee New England values, such as a passion for education, establishing many schools as well as staunch support for abolitionism. They were mostly members of the Congregationalist Church though some were Episcopalian. Due to the second Great Awakening some of them had converted to Methodism and some became Baptist before moving to what is now Sauk County. Sauk County, like much of Wisconsin, would be culturally very continuous with early New England culture for most of its early history.
In the late 1890s, German immigrants began to settle in Sauk County, making up less than one out of thirty settlers in the county before this date. Generally there was little conflict between them and the "Yankee" settlers, however when conflict did arise it focused around the issue of prohibition of alcohol. On this issue the Yankees were divided and the Germans almost unanimously were opposed to it, tipping the balance in favor of opposition to prohibition. Later the two communities would be divided on the issue of World War I in which, once again, the Yankee community would be divided and the Germans were unanimously opposed to American entry into the war. The Yankee community was generally pro-British, however many of the Yankees also did not want America to enter the war themselves. The Germans were sympathetic to Germany and did not want the United States to enter into a war against Germany, but the Germans were not anti-British. Prior to World War I, many German community leaders in Wisconsin spoke openly and enthusiastically about how much better America was than Germany, due primarily (in their eyes) to the presence of English law and the English political culture the Americans had inherited from the colonial era, which they contrasted with the turmoil and oppression in Germany which they had so recently fled. In the early 1900s immigrants from Ireland, Sweden, Norway and Poland also arrived in Sauk County. The area around Baraboo was first settled by Abe Wood in 1838, and was originally known as the village of Adams. In 1846 it became the county seat of Sauk County after a fierce fight with the nearby village of Reedsburg. In 1852, the village was renamed "Baraboo", after the nearby river. It was incorporated as a city in 1882.
New England settlers set up several sawmills early in the history of what is now Baraboo because of its location near the Baraboo and Wisconsin Rivers.
The city was the home of the Ringling brothers. From 1884 to 1917 it was the headquarters of their circus and several others, leading to the nickname "Circus City". Today Circus World Museum is located in Baraboo. A living history museum, it has a collection of circus wagons and other circus artifacts. It also has the largest library of circus information in the United States. The museum previously hosted the Great Circus Parade, which carried circus wagons and performers through the streets of Baraboo, across the state by train, and then through downtown Milwaukee.
The Al. Ringling Theatre is a grand scale movie palace in downtown Baraboo, made possible through the financial assistance of the Ringling family. The Al Ringling home still exists.
Located near Baraboo is the Badger Army Ammunition Plant, which was the largest munitions factory in the world during World War II, when it was known as "Badger Ordnance Works". The plant is no longer in use.
The Culver's restaurant franchise has its headquarters in Prairie du Sac, and was first opened in Sauk City in 1984. That same year, Cirrus Aircraft, now of Duluth, Minnesota, was founded in a rural Baraboo barn by brothers Alan and Dale Klapmeier to produce the VK-30 kit aircraft.
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 849 square miles (2,200 km2), of which 831 square miles (2,150 km2) is land and 18 square miles (47 km2) (2.1%) is water. Pewits Nest is located in Sauk County. Sauk Point is the county's highest point. The summit is nestled in the Baraboo bluffs and stands to 1,593 feet (486 m) above sea level.
Major highways
 Interstate 90
Interstate 90 Interstate 94
Interstate 94 U.S. Highway 12
U.S. Highway 12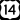 U.S. Highway 14
U.S. Highway 14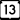 Highway 13
Highway 13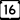 Highway 16
Highway 16 Highway 23
Highway 23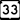 Highway 33
Highway 33 Highway 58
Highway 58 Highway 60
Highway 60 Highway 78
Highway 78 Highway 113
Highway 113 Highway 130
Highway 130 Highway 136
Highway 136 Highway 154
Highway 154
Railroads
- Canadian Pacific
- Wisconsin and Southern Railroad
Buses
- Baraboo Transit
Airports
- Baraboo-Wisconsin Dells Airport (KDLL) serves the county and surrounding communities.
- Tri-County Regional Airport (KLNR)
- Sauk–Prairie Airport (91C)
- Reedsburg Municipal Airport (C35)
Adjacent counties
- Juneau County - north
- Adams County - northeast
- Columbia County - east
- Dane County - southeast
- Iowa County - south
- Richland County - west
- Vernon County - northwest
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1840 | 102 | — | |
| 1850 | 4,371 | 4,185.3% | |
| 1860 | 18,963 | 333.8% | |
| 1870 | 23,860 | 25.8% | |
| 1880 | 28,729 | 20.4% | |
| 1890 | 30,575 | 6.4% | |
| 1900 | 33,006 | 8.0% | |
| 1910 | 32,869 | −0.4% | |
| 1920 | 32,548 | −1.0% | |
| 1930 | 32,030 | −1.6% | |
| 1940 | 33,700 | 5.2% | |
| 1950 | 38,120 | 13.1% | |
| 1960 | 36,179 | −5.1% | |
| 1970 | 39,057 | 8.0% | |
| 1980 | 43,469 | 11.3% | |
| 1990 | 46,975 | 8.1% | |
| 2000 | 55,225 | 17.6% | |
| 2010 | 61,976 | 12.2% | |
| 2020 | 65,763 | 6.1% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 1790–1960 1900–1990 1990–2000 2010–2020 |
|||
2020 census
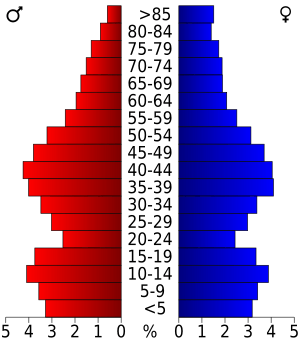
As of the census of 2020, the population was 65,763. The population density was 79.1 people per square mile (30.5 people/km2). There were 30,784 housing units at an average density of 37.0 units per square mile (14.3 units/km2). The racial makeup of the county was 89.1% White, 1.3% Native American, 0.9% Black or African American, 0.6% Asian, 3.1% from other races, and 4.9% from two or more races. Ethnically, the population was 6.2% Hispanic or Latino of any race.
Communities
Cities
- Baraboo (county seat)
- Reedsburg
- Wisconsin Dells (mostly in Columbia County, Adams County and Juneau County)
Villages
- Cazenovia (partly in Richland County)
- Ironton
- La Valle
- Lake Delton
- Lime Ridge
- Loganville
- Merrimac
- North Freedom
- Plain
- Prairie du Sac
- Rock Springs
- Sauk City
- Spring Green
- West Baraboo
Towns
Census-designated places
- Bluffview
- Lake Wisconsin (partial)
Other unincorporated communities
- Black Hawk
- Cassell
- Crawford Crossing
- Dellwood
- Denzer
- Greens Corners
- Hill Point
- La Rue
- Leland
- Loddes Mill
- Loreta
- Moon Valley
- Sandusky
- Valton
- Witwen
Economy
The county's largest employer is the Ho-Chunk Nation, which employs roughly 3100 people combined in Jackson and Sauk counties.
See also
 In Spanish: Condado de Sauk para niños
In Spanish: Condado de Sauk para niños