Samuel Pepys facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Samuel Pepys
|
|
|---|---|

Portrait of Samuel Pepys by J. Hayls.
Oil on canvas, 1666. |
|
| Born | 23 February 1633 |
| Died | 26 May 1703 (aged 70) |
| Resting place | St Olave's, London |
| Known for | Diary |
| Spouse(s) | Elisabeth Marchant de St Michel |
Samuel Pepys, (23 February 1633 – 26 May 1703) was an English administrator at the Admiralty and Member of Parliament. He is famous for his diary.
Pepys rose to be the Chief Secretary to the Admiralty under Charles II, and later under James II. Although Pepys had no maritime experience, he rose by patronage, hard work and his talent for administration.
The detailed private diary that he kept from 1660–1669 was first published in the nineteenth century. It is one of the most important primary sources for the English Restoration period. It provides a combination of personal notes and eyewitness accounts of great events, such as the Great Plague of London, the Second Dutch War and the Great Fire of London.
Contents
Early life

Pepys was born in Salisbury Court, Fleet Street, London, on 23 February 1633, the son of John Pepys (1601–1680), a tailor, and Margaret Pepys (née Kite; died 1667), daughter of a Whitechapel butcher. His great uncle Talbot Pepys was Recorder and briefly Member of Parliament (MP) for Cambridge in 1625. His father's first cousin Sir Richard Pepys was elected MP for Sudbury in 1640, appointed Baron of the Exchequer on 30 May 1654, and appointed Lord Chief Justice of Ireland on 25 September 1655.
Pepys was the fifth of 11 children, but child mortality was high and he was soon the oldest survivor. He was baptised at St Bride's Church on 3 March 1633. Pepys did not spend all of his infancy in London; for a while, he was sent to live with nurse Goody Lawrence at Kingsland, just north of the city. In about 1644, Pepys attended Huntingdon Grammar School before being educated at St Paul's School, London, c. 1646–1650. He attended the execution of Charles I in 1649.
In 1650, he went to the University of Cambridge, having received two exhibitions from St Paul's School (perhaps owing to the influence of George Downing, who was chairman of the judges and for whom he later worked at the Exchequer) and a grant from the Mercers' Company. In October, he was admitted as a sizar to Magdalene College; he moved there in March 1651 and took his Bachelor of Arts degree in 1654.
Later in 1654 or early in 1655, he entered the household of one of his father's cousins, Sir Edward Montagu, who was later created the 1st Earl of Sandwich.
When he was 22, Pepys married 14-year-old Elisabeth de St Michel, a descendant of French Huguenot immigrants, first in a religious ceremony on 10 October 1655 and later in a civil ceremony on 1 December 1655 at St Margaret's, Westminster.
Diary
On 1 January 1660 ("1 January 1659/1660" in contemporary terms), Pepys began to keep a diary. He recorded his daily life for almost 10 years. This record of a decade of Pepys' life is more than a million words long and is often regarded as Britain's most celebrated diary. Pepys has been called the greatest diarist of all time due to his frankness in writing concerning his own weaknesses and the accuracy with which he records events of daily British life and major events in the 17th century. Pepys wrote about the contemporary court and theatre (including his amorous affairs with the actresses), his household, and major political and social occurrences. Historians have been using his diary to gain greater insight and understanding of life in London in the 17th century. Pepys wrote consistently on subjects such as personal finances, the time he got up in the morning, the weather, and what he ate. He wrote at length about his new watch which he was very proud of (and which had an alarm, a new accessory at the time), a country visitor who did not enjoy his time in London because he felt that it was too crowded, and his cat waking him up at one in the morning. Pepys' diary is one of a very few sources which provides such length in details of everyday life of an upper-middle-class man during the 17th century. The descriptions of the lives of his servants like Jane Birch provide a valuable detailed insight into their lives.
Aside from day-to-day activities, Pepys also commented on the significant and turbulent events of his nation. Pepys' diary provides a first-hand account of the Restoration, and includes detailed accounts of several major events of the 1660s, along with the lesser known diary of John Evelyn. In particular, it is an invaluable source for the study of the Second Anglo-Dutch War of 1665–7, the Great Plague of 1665, and the Great Fire of London in 1666. In relation to the Plague and Fire, C. S. Knighton has written: "From its reporting of these two disasters to the metropolis in which he thrived, Pepys's diary has become a national monument." Robert Latham, editor of the definitive edition of the diary, remarks concerning the Plague and Fire: "His descriptions of both—agonisingly vivid—achieve their effect by being something more than superlative reporting; they are written with compassion. As always with Pepys it is people, not literary effects, that matter."
Pepys stopped writing his diary in 1669. His eyesight began to trouble him and he feared that writing in dim light was damaging his eyes. He did imply in his last entries that he might have others write his diary for him, but doing so would result in a loss of privacy and it seems that he never went through with those plans. In the end, Pepys lived another 34 years without going blind, but he never took to writing his diary again.
Great Plague
Outbreaks of plague were not unusual events in London; major epidemics had occurred in 1592, 1603, 1625 and 1636. Furthermore, Pepys was not among the group of people who were most at risk. He did not live in cramped housing, he did not routinely mix with the poor, and he was not required to keep his family in London in the event of a crisis. It was not until June 1665 that the unusual seriousness of the plague became apparent, so Pepys' activities in the first five months of 1665 were not significantly affected by it. Claire Tomalin wrote that 1665 was, to Pepys, one of the happiest years of his life. He worked very hard that year, and the outcome was that he quadrupled his fortune.
Nonetheless, Pepys was certainly concerned about the plague. He chewed tobacco as a protection against infection. Furthermore, it was Pepys who suggested that the Navy Office should evacuate to Greenwich, although he did offer to remain in town himself. He later took great pride in his stoicism. Meanwhile, Elisabeth Pepys was sent to Woolwich. She did not return to Seething Lane until January 1666 and was shocked by the sight of St Olave's churchyard, where 300 people had been buried.
Great Fire of London
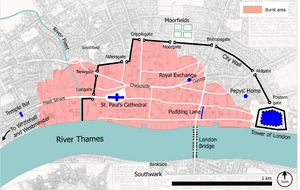
In the early hours of 2 September 1666, Pepys was awakened by Jane the maid, his servant, who had spotted a fire in the Billingsgate area. He decided that the fire was not particularly serious and returned to bed. Shortly after waking, his servant returned and reported that 300 houses had been destroyed and that London Bridge was threatened. Pepys went to the Tower of London to get a better view. Without returning home, he took a boat and observed the fire for over an hour. In his diary, Pepys recorded his observations as follows:
I down to the water-side, and there got a boat and through bridge, and there saw a lamentable fire. Poor Michell's house, as far as the Old Swan, already burned that way, and the fire running further, that in a very little time it got as far as the Steeleyard, while I was there. Everybody endeavouring to remove their goods, and flinging into the river or bringing them into lighters that layoff; poor people staying in their houses as long as till the very fire touched them, and then running into boats, or clambering from one pair of stairs by the water-side to another. And among other things, the poor pigeons, I perceive, were loth to leave their houses, but hovered about the windows and balconys till they were, some of them burned, their wings, and fell down. Having staid, and in an hour's time seen the fire: rage every way, and nobody, to my sight, endeavouring to quench it, but to remove their goods, and leave all to the fire, and having seen it get as far as the Steele-yard, and the wind mighty high and driving it into the City; and every thing, after so long a drought, proving combustible, even the very stones of churches, and among other things the poor steeple by which pretty Mrs.———— lives, and whereof my old school-fellow Elborough is parson, taken fire in the very top, and there burned till it fell down...
—Diary of Samuel Pepys, Sunday, 2 September 1666
The wind was driving the fire westward, so he ordered the boat to go to Whitehall and became the first person to inform the king of the fire. According to his entry of 2 September 1666, Pepys recommended to the king that homes be pulled down in the path of the fire in order to stem its progress. Accepting this advice, the king told him to go to Lord Mayor Thomas Bloodworth and tell him to start pulling down houses. Pepys took a coach back as far as St Paul's Cathedral before setting off on foot through the burning city. He found the Lord Mayor, who said, "Lord! what can I do? I am spent: people will not obey me. I have been pulling down houses; but the fire overtakes us faster than we can do it." At noon, he returned home and "had an extraordinary good dinner, and as merry, as at this time we could be", before returning to watch the fire in the city once more. Later, he returned to Whitehall, then met his wife in St James's Park. In the evening, they watched the fire from the safety of Bankside. Pepys writes that "it made me weep to see it". Returning home, Pepys met his clerk Tom Hayter who had lost everything. Hearing news that the fire was advancing, he started to pack up his possessions by moonlight.

A cart arrived at 4 a.m. on 3 September and Pepys spent much of the day arranging the removal of his possessions. Many of his valuables, including his diary, were sent to a friend from the Navy Office at Bethnal Green. At night, he "fed upon the remains of yesterday's dinner, having no fire nor dishes, nor any opportunity of dressing any thing." The next day, Pepys continued to arrange the removal of his possessions. By then, he believed that Seething Lane was in grave danger, so he suggested calling men from Deptford to help pull down houses and defend the king's property. He described the chaos in the city and his curious attempt at saving his own goods:
Sir W. Pen and I to Tower-streete, and there met the fire burning three or four doors beyond Mr. Howell's, whose goods, poor man, his trayes, and dishes, shovells, &c., were flung all along Tower-street in the kennels, and people working therewith from one end to the other; the fire coming on in that narrow streete, on both sides, with infinite fury. Sir W. Batten not knowing how to remove his wine, did dig a pit in the garden, and laid it in there; and I took the opportunity of laying all the papers of my office that I could not otherwise dispose of. And in the evening Sir W. Pen and I did dig another, and put our wine in it; and I my Parmazan cheese, as well as my wine and some other things.
—Diary of Samuel Pepys, Tuesday, 4 September 1666
Pepys had taken to sleeping on his office floor; on Wednesday, 5 September, he was awakened by his wife at 2 a.m. She told him that the fire had almost reached All Hallows-by-the-Tower and that it was at the foot of Seething Lane. He decided to send her and his gold — about £2,350 — to Woolwich. In the following days, Pepys witnessed looting, disorder, and disruption. On 7 September, he went to Paul's Wharf and saw the ruins of St Paul's Cathedral, of his old school, of his father's house, and of the house in which he had had his bladder stone removed. Despite all this destruction, Pepys' house, office, and diary were saved.
Personal life

The diary gives a detailed account of Pepys' personal life. He was fond of wine, plays, and the company of other people. He also spent time evaluating his fortune and his place in the world. He was always curious and often acted on that curiosity, as he acted upon almost all his impulses. Periodically, he would resolve to devote more time to hard work instead of leisure. For example, in his entry for New Year's Eve, 1661, he writes: "I have newly taken a solemn oath about abstaining from plays and wine…" The following months reveal his lapses to the reader; by 17 February, it is recorded, "Here I drank wine upon necessity, being ill for the want of it."
Pepys was one of the most important civil servants of his age, and was also a widely cultivated man, taking an interest in books, music, the theatre, and science. Aside from English, he was fluent in French and read many texts in Latin. His favourite author was Virgil. He was passionately interested in music; he composed, sang, and played for pleasure, and even arranged music lessons for his servants. He played the lute, viol, violin, flageolet, recorder, and spinet to varying degrees of proficiency. He was also a keen singer, performing at home, in coffee houses, and even in Westminster Abbey. He and his wife took flageolet lessons from master Thomas Greeting. He also taught his wife to sing and paid for dancing lessons for her (although these stopped when he became jealous of the dancing master).
Pepys was an investor in the Company of Royal Adventurers Trading to Africa, which held the Royal monopoly on trading along the west coast of Africa in gold, silver, ivory, and slaves.
Royal Society

He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1665 and served as its President from 1 December 1684 to 30 November 1686. Isaac Newton's Principia Mathematica was published during this period, and its title page bears Pepys' name. There is a probability problem called the "Newton–Pepys problem" that arose out of correspondence between Newton and Pepys about whether one is more likely to roll at least one six with six dice or at least two sixes with twelve dice. It has only recently been noted that the gambling advice that Newton gave Pepys was correct, while the logical argument with which Newton accompanied it was unsound.
Retirement and death
He was imprisoned on suspicion of Jacobitism from May to July 1689 and again in June 1690, but no charges were ever successfully brought against him. After his release, he retired from public life at age 57. He moved out of London 10 years later (1701) to a house in Clapham owned by his friend William Hewer, who had begun his career working for Pepys in the admiralty. Clapham was in the country at the time; it is now part of inner London.
Pepys lived there until his death on 26 May 1703. He had no children and bequeathed his estate to his unmarried nephew John Jackson.
Pepys was buried along with his wife in St Olave's Church, Hart Street in London.
Pepys Library

Pepys was a lifelong bibliophile and carefully nurtured his large collection of books, manuscripts, and prints. At his death, there were more than 3,000 volumes, including the diary, all carefully catalogued and indexed; they form one of the most important surviving 17th-century private libraries. The most important items in the Library are the six original bound manuscripts of Pepys' diary, but there are other remarkable holdings, including:
- Incunabula by William Caxton, Wynkyn de Worde, and Richard Pynson
- Sixty medieval manuscripts
- The Pepys Manuscript, a late-15th-century English choirbook
- Naval records such as two of the 'Anthony Rolls', illustrating the Royal Navy's ships c. 1546, including the Mary Rose
- Sir Francis Drake's personal almanac
- Over 1,800 printed ballads, one of the finest collections in existence.
Pepys made detailed provisions in his will for the preservation of his book collection. His nephew and heir John Jackson died in 1723, when it was transferred intact to Magdalene College, Cambridge, where it can be seen in the Pepys Library. The bequest included all the original bookcases and his elaborate instructions that placement of the books "be strictly reviewed and, where found requiring it, more nicely adjusted".
The Ephemera Society emblem uses Pepys' portrait and characterizes him as “the first general ephemerist.” Two large albums of ephemera saved by Pepys are in his library.
Images for kids
-
A short letter from Samuel Pepys to John Evelyn at the latter's home in Deptford, written by Pepys on 16 October 1665 and referring to "prisoners" and "sick men" during the Second Dutch War
-
Dutch Attack on the Medway, June 1667 by Pieter Cornelisz van Soest, painted c. 1667. The captured ship Royal Charles is right of centre.
-
Samuel Pepys painted by Sir Godfrey Kneller in 1689
See also
 In Spanish: Samuel Pepys para niños
In Spanish: Samuel Pepys para niños