Rhodri the Great facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Rhodri ap Merfyn |
|
|---|---|
| King of Gwynedd | |
 |
|
| King of Gwynedd | |
| Reign | 844 – 873 or 877 (disputed) |
| Predecessor | Merfyn Frych |
| Successor | Anarawd ap Rhodri |
| King of Powys | |
| Reign | c.856 – 873 or 877 |
| Predecessor | Gorm the Old |
| Successor | Merfyn ap Rhodri |
| King of Seisyllwg | |
| Reign | c.871 – 873 or 877 |
| Successor | Cadell ap Rhodri |
| Spouse | Angharad ferch Meurig |
| Issue | Anarawd ap Rhodri Cadell ap Rhodri Merfyn ap Rhodri Tudwal ap Rhodri |
| House | Gwynedd |
| Father | Merfyn Frych |
| Mother | Nest ferch Cadell |
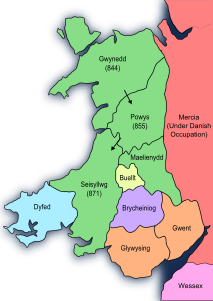
Rhodri ap Merfyn (c. 820 – 873/877/878), popularly known as Rhodri the Great (Welsh: Rhodri Mawr), succeeded his father, Merfyn Frych, as King of Gwynedd in 844. Rhodri annexed Powys c. 856 and Seisyllwg c. 871. He is called "King of the Britons" by the Annals of Ulster. In some later histories, he is referred to as "King of Wales", although the title is anachronistic and his realm did not include southern Wales.
Lineage and inheritance
Rhodri was the son of King Merfyn Frych, who had claimed Gwynedd upon the extinction of Cunedda's male line. Rhodri then inherited the realm after his father's death around 844. Merfyn hailed from "Manaw" which may either refer to the Isle of Man or Manau, the ancestral homeland of all Gwynedd's kings since Cunedda.
According to later genealogies, his mother or grandmother was Nest ferch Cadell of the ruling dynasty in Powys, and Rhodri inherited the kingdom through his uncle Cyngen and then the rule of the southern realms on the death of Gwgon, Rhodri's brother-in-law. Although surviving texts of Welsh law expressly forbid inheritance along the maternal line, Nest and Rhodri's supposed inheritance was later used to justify Gwynedd's annexation of Powys after the c. 855 death of Cyngen ap Cadell in preference to Cyngen's other heirs.
Similarly, Rhodri's marriage to Angharad ferch Meurig was used to explain his supposed inheritance of her brother Gwgon's kingdom of Ceredigion after that king's death in 872 via a principle of jure uxoris that does not survive in our sources for Welsh law.
Reign
Now the master of much of modern Wales, Rhodri faced pressure both from the English and, increasingly, from Vikings, called the "black gentiles" in the Welsh sources. The Danish are recorded ravaging Anglesey in 854. In 856, Rhodri won a notable victory and killed their leader Gorm.
The Chronicle of the Princes records two victories by Rhodri in 872: the first at a place given variously as Bangolau, Bann Guolou, or Bannoleu, where he defeated the Vikings on Anglesey "in a hard battle" and the second at Manegid or Enegyd where the Vikings "were destroyed".
The Chronicle of the Princes records his death occurring at the Battle of Sunday on Anglesey in 873; the Annals of Wales record the two events in different years and Phillimore's reconstruction of its dates places Rhodri's death in 877. According to the Chronicle, Rhodri and his brother Gwriad were killed during a Saxon invasion (which probably would have been under Ceolwulf of Mercia, given that the Wessex forces under Alfred the Great were fighting Vikings in East Anglia at the time). The Annals record no great details of the death, but where the B text calls Gwriad Rhodri's brother, the A text has him as Rhodri's son instead. It is likely he was killed in battle given that all the sources call his son Anarawd's victory over the Mercians at the Battle of the Conwy a few years later "God's vengeance for Rhodri".
Succession
Rhodri died leaving at six sons to share his land among themselves. The traditional account is that his eldest, Anarawd, became king of Gwynedd and the head of the subsequent House of Aberffraw. Another, Cadell, was given Ceredigion . Cadell's family was later known as the House of Dinefwr, after its base of operations was moved by Cadell's son, Rhodri's grandson, Hywel Dda to Dyfed following another (supposed) inheritance via Hywel's marriage to Elen ferch Llywarch. Hywel's wide domain, later known as Deheubarth, briefly eclipsed Gwynedd under his immediate heirs before fracturing.
A fourth son, possibly too young to have been considered for the first division of Rhodri's lands, took part in Anarawd's 881 revenge victory over the Mercians and, wounded there, became known to history as Tudwal the Lame, a condition disqualifying him from rule under Cyfraith Hywel, Welsh customary law.
Children
- Anarawd ap Rhodri (died 913)
- Cadell ap Rhodri (854–907)
- Gwriad ap Rhodri: He had a son named Gwgawn who was killed in 955.
- Tudwal ap Rhodri (born 860)
See also
 In Spanish: Rhodri el Grande para niños
In Spanish: Rhodri el Grande para niños
- Family tree of Welsh monarchs