Region of Murcia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Region of Murcia
Región de Murcia
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Región de Murcia (Spanish) |
|||
|
|||
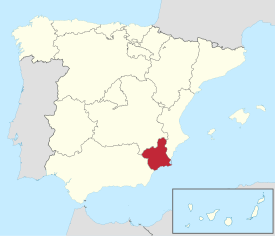
Location of the Region of Murcia within Spain
|
|||
| Country | Spain | ||
| Capital | Murcia | ||
| Area
(2.2% of Spain; Ranked 9th)
|
|||
| • Total | 11,313 km2 (4,368 sq mi) | ||
| Population
(2018)
|
|||
| • Total | Lua error in Module:Wd at line 1,575: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). | ||
| • Pop. rank | 10th | ||
| • Percent | 3.0% of Spain | ||
| Demonym(s) | English: Murcian Spanish: murciano (m), murciana (f) |
||
| Ethnic groups | |||
| ISO 3166 code |
ES-MC (region) ES-MU (province)
|
||
| Official languages | Spanish | ||
| Parliament | Regional Assembly of Murcia | ||
| Congress seats | 10 (of 350) | ||
| Senate seats | 6 (of 265) | ||
| HDI (2017) | 0.869 very high · 12th |
||
| Website | Comunidad Autónoma de la Región de Murcia | ||
The Region of Murcia is an autonomous community of Spain located in the southeast of the state, between Andalusia and the Valencian Community, on the Mediterranean coast.
The autonomous community consists of a single province, unlike most autonomous communities, which have several provinces within the same territory. Because of this, the autonomous community and the province are operated as one unit of government. The city of Murcia is the capital of the region and seat of government organs, except for the parliament, the Regional Assembly of Murcia, which is located in Cartagena. The autonomous community and province is subdivided into municipalities.
The Region of Murcia is bordered by Andalusia (the provinces of Almería and Granada), Castile–La Mancha (the province of Albacete, which was historically connected to Murcia until 1980), the Valencian Community (province of Alicante), and the Mediterranean Sea. The community covers 11,313 km² in area and has a population of 1.4 million. About one-third of its population lives in the capital. Its highest mountain is Los Obispos, which measures 2,015 m high.
The region is a major producer of fruits, vegetables, and flowers for the rest of Spain and Europe. Wineries have developed near the towns of Bullas, Yecla, and Jumilla, as well as olive oil near Moratalla. Murcia is mainly a warm region which has made it very suitable for agriculture. However the precipitation level is low and water supply is a hot subject today since, in addition to the traditional water demand for crops, there is now also a demand of water for the booming tourist developments. Water is supplied by the Segura River and, since the 1970s, by the Tajo transvasement, a major civil engineering project which, under some environmental and sustainability restraints, brings water from the Tajo into the Segura.
Geography
Relief
The region is located in the eastern part of the Cordilleras Béticas mountains and it is influenced by their orography. These mountain ranges are divided as well in the Prebética, Subbética and Penibética mountain ranges (from north to the south).
Traditionally it has been considered that the peak of Revolcadores, in the range of the same name, was the highest point in the Region of Murcia, with a height of 2,027 meters; but in measurements of the most recent maps of the SNIG (National Service of Geographic Information of Spain), Revolcadores appears with a height of 1,999 m, and the mountain, Los Obispos ("The Bishops"), located slightly further north, is higher (2,015 m).
Approximately 27% of the Murcian territory can be described as mountainous, 38% as intramountainous depressions and running valleys, and the remaining 35% as flat lands and plateaux.
Climatology
The Region of Murcia enjoys a Mediterranean climate of semi-arid type, with mild winters (an average of 11 °C in December and January) and warm summers (where the daily maximum regularly exceeds 40 °C). The average annual temperature is 18 °C.
With little precipitation of about 300 to 350 mm per year, the region has between 120 and 150 days in the year where the sky is totally clear. April and October are the months with the most precipitation, there being frequent heavy downpours in a single day.
The distance to the sea and the relief causes a thermal difference between the coast and the interior, specially in winter, when the temperature rarely descends below 10 °C on the coast, while in the interior regions the minimum does not usually rise above 6 °C and the precipitation level is higher (up to 600 mm).
The city of Murcia holds the record temperature of the 20th century in Spain. It reached 46.1 °C (115 °F) on July 4, 1994. The winter of 2005 was the coldest in a long time, with snow even falling on the Murcian coast. [1]

Hydrography
Rivers
The hydrographic network of the region is made up of the Segura river and its affluents:
- Mundo (which is born in Albacete), it is the one that contributes to the Segura with the greatest volume.
- Alhárabe and its affluent, the Benamor.
- Mula river.
- Guadalentín, Sangonera or Reguerón (which is born upper before Lorca).
Due to the water supplying incapacity of the Segura river basin, contributions to this river basin are made, originated from the basin of the Tajo river, by means of the Tajo-Segura transvasement.
Seas
The greatest natural lake of Spain can be found in the region: the Mar Menor (Small Sea) lagoon. It is a salt water lagoon, adjacent to the Mediterranean Sea. Its special ecological and natural characteristics make the Mar Menor a unique natural place and the largest saltwater lake in Europe. With a semicircular shape, it is separated from the Mediterranean Sea by a sand strip 22 km in length and between 100 and 1200 m wide, known as La Manga del Mar Menor (the Minor Sea's Sandbar). The lagoon has been designated by the United Nations as a Specially Protected Zone of Importance for the Mediterranean. Its coastal perimeter accounts for 73 km of coast in which beaches follow one another with crystal clear shallow water (the maximum depth does not exceed 7m). The lake has an area of 170 square kilometers.
Images for kids
-
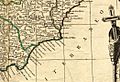
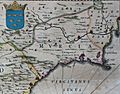
Map of the Kingdom of Murcia in La Geographia Blaviana by Joan Blaeu (1659). In the upper left quadrant appears the coat of arms of the kingdom, which was included in the flag and coat of arms of the Region of Murcia.
-
Ibn Hud as depicted in the Cantigas de Santa Maria
See also
 In Spanish: Región de Murcia para niños
In Spanish: Región de Murcia para niños