Red shift facts for kids
Red shift is a way astronomers use to tell the distance of any object that is very far away in the Universe. The red shift is one example of the Doppler effect.
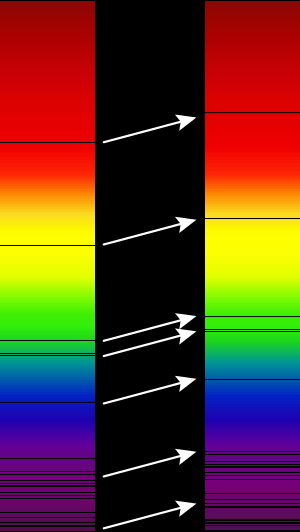
The easiest way to experience the Doppler effect is to listen to a moving train. As the train moves towards a person, the sound it makes as it comes towards them sounds like it has a higher tone, since the frequency of the sound is squeezed together a little bit. As the train speeds away, the sound gets stretched out, and sounds lower in tone. The same happens with light when an object that emits light moves very fast. An object, like a star or a galaxy that is far away and moving toward us, will look more blue than it normally does. This is called blue shift. A star or galaxy moving away from us will look more red than it would if the source were not moving in our frame of reference. This is where red shift got its name, since the colors are shifted towards the red end of the spectrum.
The reason astronomers can tell how far the light gets shifted is because chemical elements, like hydrogen and oxygen, have unique fingerprints of light that no other element has. Astronomers use spectroscopy to analyse the light from an object (galaxy or star}. Once they know that, they check to see the difference between where the spectral lines are compared to where they normally are. From that, they can tell whether it is moving toward us or away from us, and also how fast it is going. The faster it goes, the farther the spectral lines are from their normal position in the spectrum.
Images for kids
-
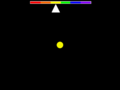
Doppler effect, yellow (~575 nm wavelength) ball appears greenish (blueshift to ~565 nm wavelength) approaching observer, turns orange (redshift to ~585 nm wavelength) as it passes, and returns to yellow when motion stops. To observe such a change in color, the object would have to be traveling at approximately 5,200 km/s, or about 75 times faster than the speed record for the fastest man-made space probe.
-
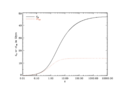
Plot of distance (in giga light-years) vs. redshift according to the Lambda-CDM model. dH (in solid black) is the proper distance from Earth to the location with the Hubble redshift z while ctLB (in dotted red) is the speed of light multiplied by the lookback time to Hubble redshift z. The proper distance is the physical space-like distance between here and the distant location, asymptoting to the size of the observable universe at some 47 billion light-years. The lookback time is the distance a photon traveled from the time it was emitted to now divided by the speed of light, with a maximum distance of 13.8 billion light-years corresponding to the age of the universe.
-
Matter waves (protons, electrons, photons, etc.) falling into a gravity well become more energetic and undergo observer-independent blueshifting.
See also
 In Spanish: Corrimiento al rojo para niños
In Spanish: Corrimiento al rojo para niños